When examining the indigenous communities in Mexico during the Spanish conquest, one group stands out as the dominant force in the region. The influence and control of this community greatly impacted the Mexican terrain at the time.
As we explore the dynamics of this indigenous group and their interactions with the Spaniards, a clearer understanding of the historical context begins to emerge. But who were they, and what made them so influential? These questions drive us to unravel the complex tapestry of Mexico's indigenous history, shedding light on a pivotal moment in time.
Key Takeaways
- The indigenous group that was concentrated in Mexico by the time the Spaniards arrived was the Aztecs.
- The Aztecs had established a vast empire known as the Aztec Empire and held significant political and religious authority.
- Aztec society was stratified into nobles, commoners, serfs, and slaves, with the nobles holding political and economic power.
- The Aztecs had complex religious practices and beliefs, with a pantheon of deities and elaborate ceremonies held to honor the gods.
Arrival of the Spaniards in Mexico
When the Spaniards arrived in Mexico in the early 16th century, their impact on the indigenous groups was profound and far-reaching. Spanish colonization brought about significant changes in the social, economic, and political structures of the indigenous societies.
The imposition of Spanish rule led to the exploitation of indigenous labor, the introduction of new diseases, and the forced conversion to Christianity. The indigenous populations were subjected to harsh treatment, land dispossession, and cultural assimilation under the encomienda system, which further exacerbated their suffering.
In response to the Spanish colonization, indigenous groups developed various resistance strategies to protect their autonomy and cultural heritage. Some communities engaged in armed resistance, such as the famous Aztec rebellion against the Spanish conquistadors. Others employed more subtle tactics, including maintaining traditional practices in secret and preserving their languages and belief systems.
Additionally, some indigenous leaders collaborated with the Spaniards strategically to safeguard their people's interests.
Power and Influence of the Aztecs
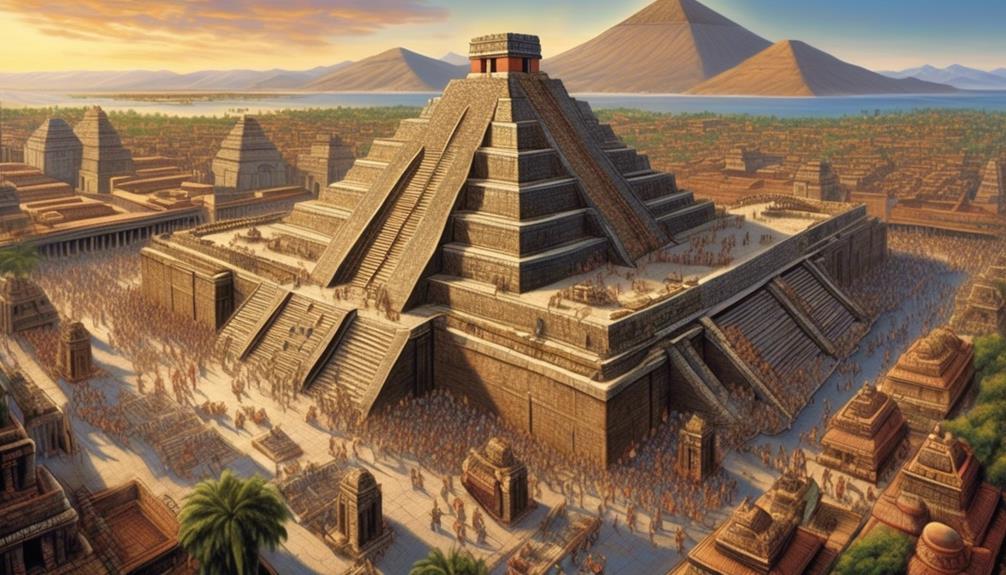

The Aztecs, a powerful and influential indigenous group in Mexico, wielded significant political and religious authority before the arrival of the Spaniards. At the zenith of their power, the Aztecs established a vast empire known as the Aztec Empire, encompassing a large part of Mesoamerica. This empire was characterized by a complex system of governance, with a hierarchical structure that allowed the Aztec rulers, known as tlatoani, to exert control over a diverse range of territories and peoples. The Aztec society was deeply ingrained with religious practices, and the rulers held immense religious authority, often serving as intermediaries between the people and the gods.
The Aztecs also boasted remarkable cultural achievements, particularly in the fields of architecture, art, and agriculture. Their capital city, Tenochtitlan, was a marvel of urban planning and engineering, built on an island in Lake Texcoco. The Aztecs constructed intricate networks of canals, causeways, and floating gardens, showcasing their advanced understanding of hydraulic engineering. Additionally, Aztec art, characterized by intricate designs and vivid colors, reflected their rich mythology and religious beliefs.
The Aztecs' cultural legacy continues to captivate and inspire modern audiences, serving as a testament to their enduring influence in the region.
Aztec Society and Governance
With the Aztecs' significant political and religious authority in mind, we can now explore the structure of Aztec society and governance.
The Aztec society was stratified, consisting of nobles, commoners, serfs, and slaves. At the top were the nobles, including the emperor, military leaders, and high-ranking priests, who held significant political and economic power. Below them were the commoners, who were artisans, merchants, and farmers. The lower strata included serfs who worked the land and slaves who were often prisoners of war. This social structure was tightly intertwined with the Aztec economy, which was primarily based on agriculture, tribute, and trade. The economy was largely controlled by the state, with tribute being collected from conquered territories and redistributed among the ruling class.
In terms of governance, the Aztecs had a complex system that combined elements of monarchy, aristocracy, and theocracy. The emperor held ultimate authority, but he was supported by a council of nobles and high-ranking priests who helped administer the empire. The governance structure was also closely linked to the religious practices of the Aztecs, with many aspects of governance being intertwined with religious rituals and beliefs. This holistic approach to governance and society was a defining feature of Aztec civilization.
Aztec Religious Practices
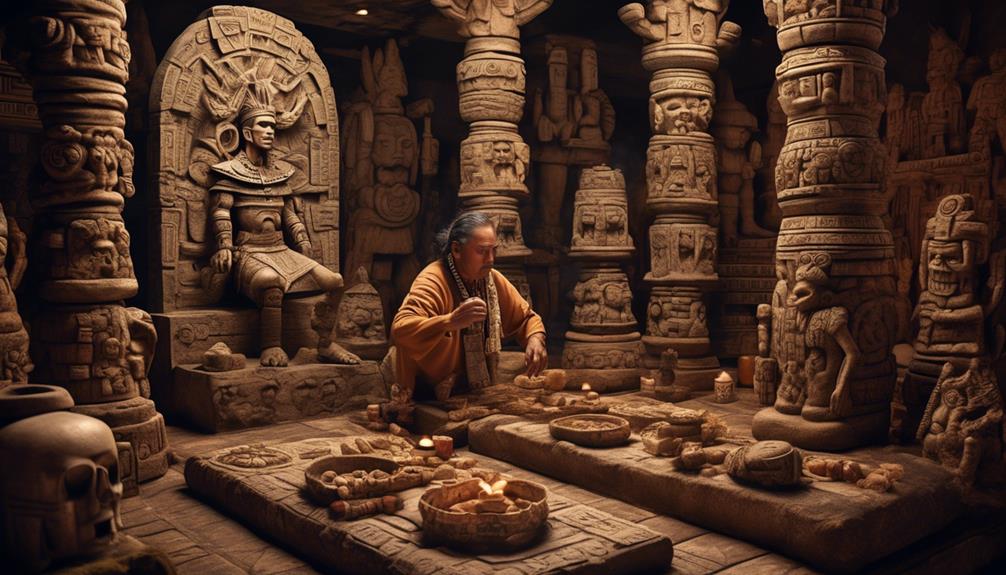

Evident throughout Aztec society, religious practices played a central role in shaping the cultural and spiritual life of the people.
- Spiritual Beliefs: The Aztecs believed in a complex pantheon of deities, each associated with different aspects of life and the natural world. Their spiritual beliefs were deeply intertwined with their everyday existence, influencing everything from agriculture to warfare. The sun god, Huitzilopochtli, held particular significance as the patron deity of the Aztecs, symbolizing power, warfare, and the sun's vital energy.
- Ceremonies: Aztec religious ceremonies were elaborate and diverse, often involving intricate rituals and vibrant performances. These ceremonies were held at specific times throughout the year to honor the gods and seek their favor. The Great Temple in the heart of Tenochtitlan was the center of these religious activities, where priests conducted ceremonies such as the New Fire Ceremony, which symbolized the renewal of the world.
- Ritual Sacrifices and Symbolism: Central to Aztec religious practices were ritual sacrifices, viewed as essential for maintaining the cosmic balance and ensuring the gods' benevolence. Symbolism played a crucial role in the offerings, with different sacrifices serving as potent symbols of devotion and renewal within the Aztec belief system.
Spanish Conquest and Aztec Resistance
Amidst the fervent upheaval sparked by the Spanish Conquest, Aztec resistance permeated the fabric of their society, embodying a steadfast determination to preserve their cultural heritage and sovereignty.
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire in the early 16th century brought about a tumultuous clash of civilizations. The Aztec resistance was multi-faceted, encompassing military, political, and cultural strategies.
Military leaders like Cuauhtémoc fiercely defended their land, and even after the fall of Tenochtitlan, the Aztecs continued to resist Spanish rule through guerrilla warfare.
Politically, some nobles sought to maintain a degree of autonomy under Spanish colonial rule, negotiating privileges and land rights.
Furthermore, the resistance extended to the preservation of Aztec cultural practices and beliefs, albeit often in syncretism with Catholicism.
This resistance, however, was met with severe repression by the Spanish, leading to immense loss of life and cultural heritage.
The resilience of the Aztec people in the face of the Spanish conquest and their enduring resistance serves as a testament to their unwavering commitment to their civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Other Indigenous Groups Besides the Aztecs Were Present in Mexico at the Time of the Spanish Arrival?
We know that besides the Aztecs, the Mayan civilization and Olmec culture were present in Mexico at the time of the Spanish arrival.
The indigenous resistance and population diversity showcased the rich tapestry of indigenous groups in Mexico.
This context illuminates the complexities of the indigenous landscape during that period and adds depth to our understanding of the indigenous experience in Mexico at that time.
How Did the Arrival of the Spaniards Impact Indigenous Groups Other Than the Aztecs?
The arrival of the Spaniards had a significant impact on indigenous groups other than the Aztecs. It led to a disruption of traditions, but also prompted the formation of new alliances and adaptation to the changing circumstances.
Despite the challenges, indigenous communities displayed resilience in the face of cultural and societal changes. Their ability to adapt and form new alliances showcases the strength and resourcefulness of these diverse groups during this transformative period.
What Were the Cultural and Religious Practices of Indigenous Groups in Mexico Besides the Aztecs?
We can explore the cultural practices and religious beliefs of indigenous groups in Mexico besides the Aztecs. Their diverse traditions and customs, including religious ceremonies, agricultural rituals, and artistic expressions, reflected their deep connection to the land and spiritual beliefs.
The Spanish arrival significantly impacted the diversity and population changes, leading to indigenous resistance and cultural assimilation.
Understanding these varied cultural practices and beliefs highlights the rich tapestry of indigenous heritage in Mexico.
How Did Indigenous Groups in Mexico Resist Spanish Conquest and Colonization?
We'll explore indigenous resistance and cultural preservation in Mexico during Spanish conquest and colonization.
Indigenous groups utilized various strategies, such as armed resistance, cultural adaptation, and preservation of traditions, to resist Spanish influence.
Some groups, like the Maya and Zapotec, maintained their cultural practices and language, while others, like the Yaqui and Mixtec, engaged in armed resistance.
This demonstrates the diverse ways indigenous communities in Mexico resisted and preserved their culture amidst Spanish colonization.
What Impact Did the Spanish Conquest Have on the Overall Population and Diversity of Indigenous Groups in Mexico?
The Spanish conquest had a significant impact on the overall population and diversity of indigenous groups in Mexico. Population changes were drastic due to disease, warfare, and forced labor. This led to a decline in the indigenous population.
Additionally, the Spanish colonization and imposition of their culture resulted in the suppression and assimilation of various indigenous groups, leading to a loss of diversity.
The lasting effects of these actions continue to shape Mexico's indigenous population today.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the arrival of the Spaniards in Mexico marked a significant shift in the power dynamics of the region. The Aztecs, a powerful and influential indigenous group, were concentrated in Mexico at the time of the Spanish arrival. Despite their resistance, the Aztecs eventually succumbed to Spanish conquest.
It's estimated that the population of the Aztec empire at the time of the Spanish arrival was around 5-6 million people, making them one of the largest and most advanced civilizations in the Americas.