Brought up in Mexico City, the phrase ‘roots run deep’ was often used when discussing the indigenous populations of Mexico. Like the intricate root systems that uphold a magnificent ceiba tree, indigenous groups across the Americas, including Mexico, have always been the foundation of vibrant cultures, traditions, and knowledge systems.
But what does it really mean to be indigenous in the context of modern Mexico? How has the historical legacy of indigenous peoples shaped the country's identity and values? These are questions that not only spark curiosity but also shed light on the complex and multifaceted nature of Indigenous Americas Mexico.
Key Takeaways
- Indigenous Americas Mexico is deeply rooted in centuries of rich cultural heritage and resilience, influenced by advanced civilizations like the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs.
- Cultural traditions and practices play a significant role in preserving indigenous heritage, with ceremonies like the Day of the Dead, Danza Azteca, and Temazcal being of utmost importance.
- The impact of indigenous cultures on modern Mexican society is evident through the integration of indigenous cultural practices into mainstream society, contributing to a more inclusive and diverse national identity.
- Despite economic challenges and the ongoing threats of globalization and modernization, indigenous communities in Mexico continue to demonstrate resilience in preserving their cultural heritage through sustainable livelihoods, advocacy, and the protection of ancestral lands and natural resources.
Historical Roots of Indigenous Americas Mexico
The historical roots of Indigenous Americas Mexico can be traced back through centuries of rich cultural heritage and resilience. The historical influences on Indigenous Americas Mexico are deeply intertwined with the ancestral connections to the land, traditions, and belief systems.
From the advanced civilizations of the Olmecs, Mayans, and Aztecs to the enduring legacy of indigenous communities today, the historical influences have shaped the identity of Indigenous Americas Mexico. The ancestral connections to the land are evident in the spiritual practices, agricultural traditions, and communal values that have been passed down through generations.
The historical influences on Indigenous Americas Mexico have been marked by periods of both triumph and struggle. The legacy of colonization and the enduring impact of European conquest continue to shape the contemporary challenges faced by indigenous communities. Despite these adversities, the resilience of the indigenous peoples has been a defining characteristic throughout history.
It's through an understanding of the historical influences and ancestral connections that we can truly appreciate the depth and significance of Indigenous Americas Mexico.
Cultural Traditions and Practices
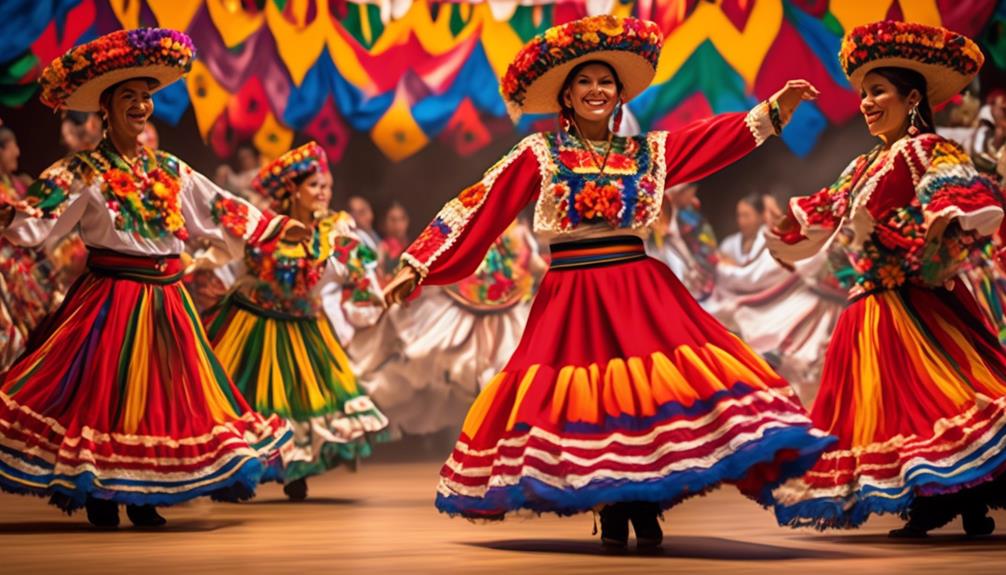

Engaging in traditional ceremonies and storytelling allows us to preserve and pass on our cultural heritage within Indigenous Americas Mexico. Cultural preservation is vital to maintaining our identity and connection to our ancestors.
Through traditional ceremonies such as the Day of the Dead, Danza Azteca, and Temazcal, we honor our past and instill a sense of pride in our cultural practices. These ceremonies provide a space for intergenerational knowledge transfer, ensuring that our customs and beliefs are upheld for future generations.
Storytelling is another integral component of our cultural preservation. Through oral traditions, myths, and legends, we impart wisdom, moral teachings, and historical accounts, keeping our heritage alive. These stories also serve as a means of connecting with our past and reinforcing our collective identity as Indigenous peoples of the Americas.
Impact on Modern Mexican Society
Participating in traditional ceremonies and storytelling has a profound impact on modern Mexican society, fostering cultural continuity and a deep sense of collective identity. The integration of indigenous cultural practices into mainstream society serves as a bridge between the country's rich heritage and its present-day reality.
This integration not only preserves ancient traditions but also enriches the cultural tapestry of Mexico, contributing to a more inclusive and diverse national identity. Furthermore, the economic disparities that have historically affected indigenous communities are being addressed through various initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable development and empowering these groups.
Challenges and Resilience
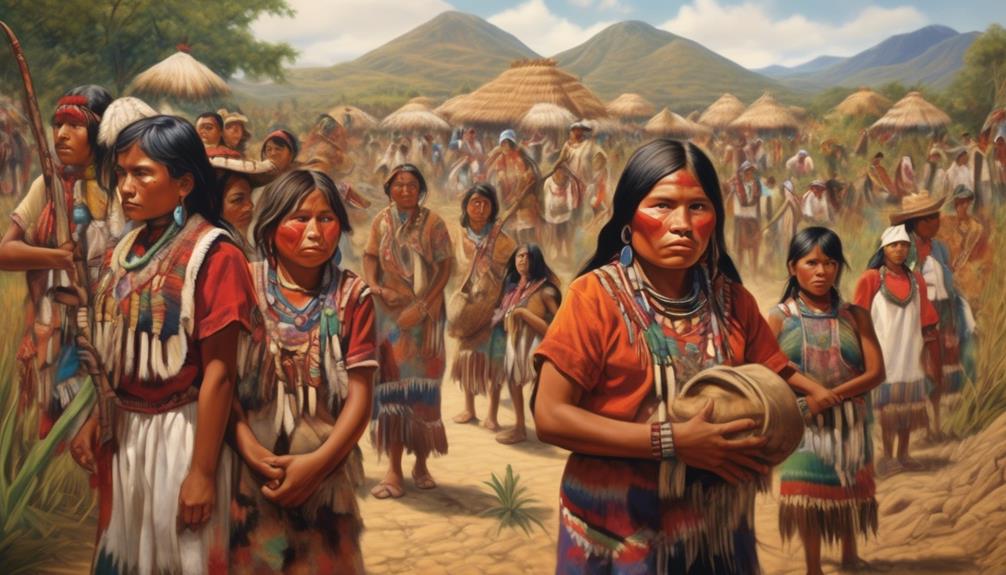

Amidst the ongoing societal and economic challenges, indigenous communities in Mexico demonstrate remarkable resilience and determination in preserving their cultural heritage and traditions. The challenges they face are multifaceted, yet their ability to adapt and overcome is a testament to their strength as a community.
Here are three key aspects highlighting the challenges and resilience of indigenous communities in Mexico:
- Economic Challenges: Indigenous communities often face significant economic hurdles, including limited access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Despite these obstacles, they exhibit resilience by creating sustainable livelihoods through traditional crafts, agriculture, and community-based enterprises.
- Cultural Preservation: The preservation of indigenous languages, customs, and spiritual practices is an ongoing challenge in the face of globalization and modernization. However, these communities showcase resilience by actively passing down their cultural heritage to younger generations and advocating for cultural preservation initiatives.
- Land Rights and Environmental Stewardship: Indigenous communities encounter challenges in protecting their ancestral lands and natural resources. Despite this, they exhibit resilience by engaging in advocacy efforts, sustainable land management practices, and environmental conservation projects to safeguard their territories for future generations.
The challenges faced by indigenous communities in Mexico are met with incredible resilience and a steadfast commitment to preserving their cultural identity and heritage.
Preserving Indigenous Heritage in Mexico
Preserving indigenous heritage in Mexico requires a steadfast commitment to sustaining traditional practices and advocating for cultural preservation initiatives amidst the economic and societal challenges faced by these communities. Heritage preservation is vital for maintaining the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures and traditions. Community engagement plays a pivotal role in this preservation effort, fostering a sense of collective responsibility and pride in safeguarding the intangible and tangible heritage of indigenous communities.
| Heritage Preservation Initiatives | Community Engagement | Traditional Practices Advocacy | Cultural Education |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revitalization of indigenous languages | Collaborative community projects | Advocacy for land rights and resource management | Indigenous history and art workshops |
| Preservation of traditional craftsmanship | Engaging youth in cultural events | Promotion of sustainable agricultural practices | Cultural exchange programs |
| Documentation of oral histories and traditional knowledge | Community-led heritage festivals | Support for traditional healing practices | Educational campaigns in schools |
Engaging with indigenous communities to understand their needs and perspectives is essential for the success of heritage preservation initiatives. By supporting these communities in their efforts to maintain their cultural identity, we can contribute to the enrichment and diversity of Mexico's cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Has the Concept of Indigenous Identity Evolved in Mexico Over Time?
We've seen the evolution of indigenous identity in Mexico over time through various stages. Indigenous representation has become more prominent, and there's been a push for the preservation of traditions.
However, modern challenges such as globalization and urbanization have impacted the traditional ways of life. Despite these challenges, there's a growing recognition and appreciation for indigenous cultures and their contributions to Mexican society.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Indigenous Cultures in Mexico?
Misconceptions about indigenous cultures in Mexico persist despite their rich history and resilience. The misrepresentation of these cultures overlooks their strong commitment to cultural preservation. Colonial influence has often obscured the true depth of indigenous identities.
It's ironic that these misconceptions exist in a country with such a vibrant indigenous heritage. Understanding these complexities is crucial for those seeking mastery in appreciating the indigenous Americas, Mexico included.
How Do Indigenous Communities in Mexico Adapt to Modern Societal Changes While Preserving Their Cultural Traditions?
Adapting to modern societal changes while preserving cultural traditions is crucial for indigenous communities in Mexico.
Through innovative adaptation strategies, they integrate traditional practices with modern tools and technologies. This includes sustainable agriculture methods and eco-friendly businesses.
Cultural preservation efforts involve passing down oral histories, reviving traditional art forms, and establishing community-led education programs.
What Are Some Examples of Cultural Appropriation of Indigenous Traditions in Modern Mexican Society?
Cultural appropriation in modern Mexican society involves the inappropriate adoption of Indigenous traditions by non-Indigenous communities. This phenomenon undermines the authenticity of these traditions and contributes to the erosion of Indigenous identity. It's like a vibrant tapestry being unraveled thread by thread.
This evolution of identity is complex, and understanding the impact of cultural appropriation is crucial for preserving the rich heritage of Indigenous communities in Mexico.
What Initiatives Are Being Taken to Empower Indigenous Communities and Promote Their Rights in Mexico?
We're seeing a range of empowerment initiatives in Mexico that focus on promoting indigenous rights. These efforts include:
- Educational programs
- Economic development projects
- Legal advocacy to address historical injustices
The aim is to empower indigenous communities by providing them with:
- Tools and resources to preserve their cultural heritage
- Access to economic opportunities
- Opportunities to participate in decision-making processes that affect their lives
These initiatives are vital in promoting the rights and well-being of indigenous peoples in Mexico.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the rich history and cultural traditions of Indigenous Americas Mexico, we can't help but be amazed by their resilience in the face of challenges. Their impact on modern Mexican society is undeniable, and their efforts to preserve their heritage are truly inspiring.
Let's continue to celebrate and honor the Indigenous peoples of Mexico, and work towards a future where their traditions and contributions are fully recognized and valued.