According to the latest census data, over 33% of Indigenous Australians live in major cities, showing a significant shift from their traditional rural and remote homes.
However, the distribution of Aboriginal people across the vast Australian landscape is far more complex than this statistic suggests. From the coastal regions to the outback settlements, Indigenous communities have unique living arrangements that reflect their cultural ties, historical connections, and contemporary challenges.
Understanding the diverse locations where Aboriginal people live in Australia provides a fascinating glimpse into their resilience and adaptation in the face of modern societal changes.
Key Takeaways
- Urban areas have a significant Aboriginal population, but they face challenges in accessing meaningful employment opportunities and quality education.
- Remote communities face unique challenges in accessing essential services and employment opportunities, but efforts towards sustainable economic development and local entrepreneurship are being made.
- Regional towns need to address issues of overcrowding and limited availability of suitable housing, while also considering traditional Aboriginal housing styles and communal living arrangements.
- Aboriginal communities in metropolitan cities reflect cultural integration, but still face socioeconomic challenges such as unemployment and inadequate access to education and healthcare. Grassroots initiatives and community engagement are important for addressing their diverse needs.
Urban Areas
In urban areas of Australia, Aboriginal communities are navigating a complex intersection of traditional cultural practices and modern urban living. The dynamics of urbanization have brought both challenges and opportunities for Aboriginal people.
One of the key challenges faced by Aboriginal communities in urban areas is accessing meaningful employment opportunities. Despite the growth of urban economies, Aboriginal Australians often encounter barriers to securing stable and well-paid jobs. This can be attributed to various factors including discrimination, lack of access to quality education, and cultural differences in the workplace. As a result, many Aboriginal individuals experience higher rates of unemployment and underemployment compared to the non-Indigenous population.
Moreover, urban education access remains a critical issue for Aboriginal communities. While urban areas may offer a wider range of educational institutions and resources, Aboriginal students often face systemic obstacles in accessing quality education. These barriers can manifest in the form of cultural insensitivity in educational curricula, a lack of support for Indigenous languages, and inadequate representation of Aboriginal history and knowledge. Additionally, socioeconomic disparities and limited access to educational support services contribute to lower educational attainment among Aboriginal students in urban areas.
In navigating these challenges, Aboriginal communities are actively seeking ways to promote greater inclusion in urban employment sectors and improve access to culturally responsive education. Initiatives aimed at fostering partnerships between Indigenous organizations and urban industries, as well as advocating for inclusive educational policies, are essential steps towards addressing these issues.
Remote Communities

Navigating the complexities of urban living has prompted Aboriginal communities to adapt to a contrasting way of life. This contrast is further exemplified in the unique challenges faced by Aboriginal people living in remote communities.
In these remote areas, community engagement and social infrastructure play crucial roles in maintaining the cultural fabric and well-being of the residents. The vast distances and isolation in remote communities create barriers to accessing essential services and opportunities. Despite these challenges, community engagement thrives through cultural practices and traditions, which foster a strong sense of belonging and collective identity.
Economic development and employment opportunities in remote communities are limited, often leading to financial hardship. The lack of industries and businesses means that many residents have to travel long distances for work, contributing to the economic strain and separation from their families and communities. However, initiatives focusing on sustainable economic development within these remote areas have shown promise. By supporting local entrepreneurship and traditional skills, there's potential to create employment opportunities that are closely tied to the cultural identity of the community.
The resilience and determination of Aboriginal people in remote communities are evident in their efforts to overcome these challenges. Despite the geographical barriers, there's a strong sense of unity and a deep connection to the land. It's essential to recognize and support the unique needs of these communities, ensuring that they have the resources and opportunities for sustainable development and prosperity.
Regional Towns
As we shift our focus to regional towns, it's important to consider the housing options available to Aboriginal communities, as well as the support services that are in place to ensure their well-being.
Additionally, our attention turns to the efforts being made to preserve the rich cultural heritage of Aboriginal people within these regional settings.
These aspects play a crucial role in understanding the experiences and challenges faced by Aboriginal individuals living in regional towns across Australia.
Aboriginal Housing Options
Amidst the vast expanse of regional towns in Australia, Aboriginal communities have a range of housing options that reflect their unique cultural and socio-economic circumstances.
In regional areas, many Aboriginal people live in government-provided housing or private rental properties. However, challenges persist, such as overcrowding due to limited availability of suitable housing and infrastructure. This situation is exacerbated by the migration of Aboriginal people from remote communities to regional towns in search of better opportunities.
The housing options in regional towns also face issues related to affordability and maintenance. Additionally, the cultural significance of housing is often overlooked, with traditional Aboriginal housing styles and communal living arrangements not being adequately considered in the current housing options.
Understanding and addressing these housing challenges in regional towns is crucial for ensuring that Aboriginal communities have access to safe, culturally appropriate, and affordable housing.
Community Support Services
In examining the provision of community support services in regional towns for Aboriginal communities, it becomes evident that a comprehensive understanding of their cultural and socio-economic needs is essential for effective and equitable assistance.
Community engagement and cultural support are crucial for developing services that respect and honor the traditions and values of Aboriginal peoples.
Health services play a significant role in addressing the specific health concerns and challenges faced by Aboriginal communities, while education opportunities are essential for empowering the younger generations and promoting long-term sustainability.
Cultural Preservation Efforts
Understanding the cultural and socio-economic needs of Aboriginal communities is integral to implementing effective cultural preservation efforts in regional towns. In regional areas, preservation initiatives play a crucial role in maintaining and celebrating traditional cultural practices. These efforts are vital for the continuation of Aboriginal heritage and knowledge, ensuring that future generations can access and honor their rich cultural traditions. Here's a snapshot of some of the cultural preservation initiatives in regional towns:
| Preservation Initiatives | Cultural Practices |
|---|---|
| Cultural festivals | Traditional dances |
| Indigenous language programs | Art and craft workshops |
| Land conservation projects | Storytelling sessions |
| Heritage centers and museums | Hunting and gathering demonstrations |
| Cultural exchange programs | Cultural knowledge sharing sessions |
These initiatives not only serve to preserve Aboriginal culture but also contribute to the cultural vibrancy and diversity of regional towns.
Coastal Regions

We have observed that many Aboriginal communities in coastal regions have a deep connection to the sea, which is reflected in their traditional fishing practices.
This connection extends beyond just sustenance, as the sea holds cultural significance and plays a vital role in spirituality for these communities.
Additionally, coastal regions provide abundant food sources such as shellfish and marine life, which have historically sustained Aboriginal populations.
Traditional Fishing Practices
Often practiced by Indigenous communities along the Australian coast, traditional fishing methods reflect a deep connection to the land and sea. The cultural significance of these techniques is profound, as they've been passed down through generations, preserving the knowledge and respect for the marine environment.
- Sustainable Practices: Indigenous fishing methods prioritize sustainability, ensuring that marine resources aren't overexploited.
- Community Bonding: Fishing activities foster a sense of community and shared responsibility, with knowledge and skills being shared among community members.
- Ceremonial Traditions: Fishing practices are often intertwined with ceremonial traditions, reinforcing cultural identity and spiritual connections to the sea.
The preservation of these traditional fishing practices not only sustains Indigenous communities but also offers valuable insights into sustainable living and environmental stewardship.
Connection to the Sea
In exploring the coastal regions, the enduring connection of Indigenous communities to the sea becomes strikingly evident through their traditional fishing practices, which embody a profound respect for the marine environment and sustainable living.
The traditional fishing practices of Aboriginal communities are deeply intertwined with their cultural and spiritual connection to the sea. Coastal food sources such as fish, shellfish, and marine plants have long been essential elements of the Aboriginal diet and are intricately linked to their traditional practices and knowledge systems.
These coastal communities have developed sustainable fishing methods that ensure the preservation of marine resources for future generations. The sea isn't just a source of sustenance; it holds deep cultural significance, with stories and traditions passed down through generations. The connection to the sea is an integral part of the identity and heritage of Aboriginal communities living in coastal regions.
Coastal Food Sources
The coastal regions of Australia are rich in traditional food sources for Aboriginal communities, including an array of fish, shellfish, and marine plants that have sustained their diets and cultural practices for generations. Traditional fishing practices are deeply ingrained in our coastal communities, with techniques passed down through oral traditions and practical demonstrations. The connection to the sea isn't solely about sustenance; it represents a profound spiritual and cultural tie to our ancestors and the land.
- Our coastal diet consists of a diverse range of seafood, such as barramundi, mullet, oysters, crabs, and sea snails.
- Fishing methods like spearfishing, netting, and trapping are still practiced, honoring the age-old techniques of our ancestors.
- Marine plants like samphire and sea spinach are foraged, adding unique flavors and nutritional diversity to our meals.
Outback Settlements

Nestled amidst the vast and rugged terrain of the Australian outback, Aboriginal settlements serve as focal points of cultural heritage and community resilience. The outback lifestyle for Indigenous communities is deeply intertwined with the land, reflecting a profound connection to traditions and customs. Despite the challenges posed by the remote location, these settlements offer unique opportunities for outback employment and economic sustenance.
The outback's infrastructure, although often rudimentary, has been gradually improving, facilitating greater access to essential services and enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
Outback employment opportunities within these settlements are primarily centered around industries such as mining, agriculture, and tourism. The rich natural resources of the outback provide employment avenues, enabling Indigenous communities to sustain their traditional lifestyle while participating in the modern economy. This integration fosters a sense of empowerment and self-determination, allowing the preservation of cultural heritage alongside economic prosperity.
The outback's community development is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of Aboriginal settlements. Despite geographical isolation, these communities have established strong social structures and support networks. The communal spirit is evident in the collective management of resources and the preservation of cultural practices. The outback lifestyle embodies a harmonious coexistence with nature, showcasing sustainable living practices that resonate with the global movement towards environmental consciousness.
Indigenous Reserves

Amidst the diverse landscapes of Australia, Indigenous reserves serve as vital spaces for preserving cultural heritage and fostering community cohesion. These reserves are more than just geographical areas; they represent the enduring connection of Indigenous peoples to their land and the ongoing struggle for indigenous land rights.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: Indigenous reserves play a crucial role in preserving the cultural heritage of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities. These areas are home to sacred sites, ancient rock art, and traditional knowledge that have been passed down through generations. By maintaining control over these lands, Indigenous communities can continue their cultural practices and ensure the survival of their traditions for future generations.
- Community Cohesion: The reserves provide a sense of belonging and identity for Indigenous communities. They offer a space where cultural practices can be freely celebrated, and traditional languages can be spoken without fear of erosion. The sense of community and connection to the land within these reserves is essential for the well-being of Indigenous peoples.
- Indigenous Land Rights: Indigenous reserves are a manifestation of the ongoing struggle for indigenous land rights. They represent the recognition of Indigenous peoples' rights to their traditional lands and the acknowledgment of their historical dispossession. Through these reserves, Indigenous communities can exercise control over their lands and protect them from exploitation or encroachment.
Metropolitan Cities

In metropolitan cities across Australia, we see a growing population of urban Aboriginal communities. This shift from traditional lands to urban areas has brought about changes in housing and urbanization patterns for many Aboriginal people.
Understanding the challenges and opportunities that arise from this urbanization process is essential for addressing the diverse needs of Aboriginal communities in metropolitan settings.
Urban Aboriginal Communities
Urban Aboriginal communities in metropolitan cities are vibrant and diverse, reflecting the rich cultural heritage and resilience of Indigenous Australians. As we engage with these communities, we witness the remarkable process of cultural integration within the urban development landscape. This integration is evident in the proliferation of Indigenous art, music, and cultural events that enrich the urban fabric.
However, alongside this cultural vibrancy, we also recognize the socioeconomic challenges faced by these communities. High rates of unemployment and inadequate access to education and healthcare persist, underscoring the need for sustained community engagement and support.
Despite these challenges, the strength and determination of the urban Aboriginal communities are evident in their grassroots initiatives and advocacy efforts, contributing to the broader narrative of Indigenous empowerment and self-determination.
- Vibrant cultural expressions enrich urban spaces
- Ongoing socioeconomic challenges require community support
- Grassroots initiatives demonstrate resilience and determination
Housing and Urbanization
Observing the vibrant cultural expressions and grassroots initiatives of urban Aboriginal communities, we can discern the impact of housing and urbanization on their daily lives in metropolitan cities.
Urbanization brings both opportunities and challenges for Aboriginal people. While metropolitan areas offer access to employment, education, and healthcare, housing affordability remains a pressing issue. As urbanization accelerates, the demand for housing often outstrips the availability of affordable options, leading to housing stress and homelessness within the Aboriginal population. This creates a cycle of disadvantage, impacting social and emotional well-being.
Additionally, rapid urbanization challenges the preservation of cultural connections to land and community, further exacerbating the struggle for identity and belonging.
Addressing housing affordability and urbanization challenges is crucial in ensuring that urban Aboriginal communities can thrive and preserve their cultural heritage within metropolitan cities.
Northern Territories

Located in the northeastern region of Australia, the Northern Territories encompass a diverse array of Aboriginal communities and traditional lands. As we explore this vast and culturally rich area, it becomes evident that Indigenous land rights and land management are crucial aspects of the Northern Territories. The Aboriginal people have a deep connection to the land, and it's inspiring to see their efforts in preserving and managing these ancestral lands for future generations.
- Indigenous Land Rights: The Northern Territories have been at the forefront of the Indigenous land rights movement in Australia. The Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 was a significant milestone, granting land rights to the Indigenous people. This legislation has paved the way for the establishment of Aboriginal land trusts, enabling communities to manage their traditional lands and resources.
- Cultural Traditions: The Northern Territories are home to a myriad of cultural traditions that have been upheld for generations. The preservation of these customs is fundamental to the identity and heritage of Aboriginal communities. From ancient ceremonies to art forms, the Northern Territories serve as a living repository of Aboriginal cultural richness.
- Language Preservation: The diverse linguistic landscape of the Northern Territories reflects the rich tapestry of Aboriginal languages. Efforts to preserve and revitalize these languages are ongoing, with many communities actively working towards language education and documentation.
In the Northern Territories, the resilience and determination of Aboriginal communities in upholding their cultural traditions and asserting their rights over ancestral lands serve as a testament to the enduring spirit of the Indigenous people.
Central Desert

Nestled within the heart of Australia, the Central Desert region offers a profound glimpse into the cultural richness and traditional heritage of Aboriginal communities. The Central Desert is a vast and arid landscape, covering traditional lands of various Aboriginal groups. These groups have inhabited the region for thousands of years, maintaining a deep connection to the land and preserving their cultural practices.
| Traditional Land Use | Cultural Practices |
|---|---|
| Hunting and Gathering | Dreamtime Stories |
| Nomadic Lifestyle | Rock Art and Ceremonies |
| Water Conservation | Kinship Systems |
The traditional land use in the Central Desert is characterized by hunting and gathering, reflecting the deep understanding of the environment and its resources. Aboriginal communities in the region have historically led a nomadic lifestyle, moving across the desert to follow food sources and seasonal changes. Water conservation has been a crucial aspect of traditional land use in this arid environment, with indigenous practices ensuring the sustainable management of this precious resource.
Cultural practices in the Central Desert are deeply rooted in the Dreamtime stories, which are narratives of creation, spiritual beliefs, and the origin of the natural world. Additionally, rock art and ceremonies are integral to preserving and passing down traditional knowledge and cultural heritage. The kinship systems, governing relationships and responsibilities within the community, play a significant role in maintaining social order and cultural continuity.
The Central Desert stands as a testament to the enduring connection of Aboriginal communities to their traditional lands and cultural practices, offering valuable insights into their way of life and spiritual beliefs.
Suburban Neighborhoods

We've noticed that suburban neighborhoods in Australia have become home to a growing number of Aboriginal communities. This shift is influenced by factors such as housing availability and the presence of crucial community support services.
As we examine these suburban areas, we aim to understand how these communities are thriving and the challenges they may face.
Suburban Housing Availability
In suburban Australia, housing availability varies widely, reflecting the diverse cultural and economic factors shaping these neighborhoods. Suburban housing affordability and community integration play crucial roles in determining the accessibility of housing for Aboriginal communities.
Cultural preservation is also a significant consideration, influencing the design and adaptation of suburban living arrangements to accommodate traditional practices and community cohesion. We've observed that some suburbs provide more affordable housing options, fostering a sense of inclusivity and belonging for Aboriginal families. However, there are still challenges in certain areas where housing availability is limited, impacting community integration and cultural preservation.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for promoting equitable access to suburban housing and nurturing diverse, thriving communities.
Community Support Services
Amidst the varied landscape of suburban housing availability for Aboriginal communities, the presence and accessibility of community support services are vital factors shaping the well-being and resilience of these neighborhoods. Community engagement and cultural preservation are central to the well-being of Aboriginal communities. Accessible healthcare and employment opportunities play a crucial role in ensuring the sustained development of these neighborhoods. Here, we present a snapshot of the community support services available in suburban Aboriginal neighborhoods:
| Support Services | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Services | Accessible healthcare facilities and programs | Improved health outcomes for community members |
| Employment Opportunities | Job training, placement programs | Economic stability and self-sufficiency |
| Cultural Preservation | Cultural centers, language programs | Preservation of traditions and identity |
These support services contribute to the overall resilience and prosperity of the Aboriginal suburban neighborhoods, fostering a sense of community and empowerment.
Western Australia

Located in the western part of Australia, the region of Western Australia is home to a diverse array of Aboriginal communities, each with its own unique cultural heritage and traditions. As we explore the indigenous communities of Western Australia, it's essential to acknowledge the rich tapestry of cultures and histories that have shaped this land for millennia.
- Cultural Diversity: One striking feature of Western Australia's indigenous communities is the remarkable diversity of cultures and languages. From the Noongar people of the southwest to the Yawuru and Bardi people of the Kimberley region, each community has a distinct cultural identity, language, and connection to the land.
- Connection to Country: The deep spiritual and cultural connection to the land, known as 'Country,' is a fundamental aspect of Aboriginal life in Western Australia. This profound relationship is expressed through art, storytelling, and traditional practices that have been passed down through generations.
- Challenges and Resilience: Like many indigenous communities around the world, Aboriginal peoples in Western Australia have faced historical injustices and ongoing socio-economic challenges. Despite this, there's a remarkable resilience and determination within these communities to preserve their cultural heritage and build a better future for their children.
The vibrant indigenous communities of Western Australia offer a window into the richness of Aboriginal culture and traditions. It's crucial to approach these communities with respect, openness, and a willingness to learn from their deep connection to the land and their enduring resilience.
Eastern States
Exploring the Eastern States of Australia reveals a rich tapestry of Aboriginal communities, each with its own distinct cultural heritage and enduring traditions. In our observations, we've noticed that Aboriginal employment opportunities vary across the Eastern States. While there are some success stories, many Aboriginal people face barriers to employment, such as limited access to education and training, as well as discrimination in the workforce. Addressing these issues is crucial for the liberation of Aboriginal communities, as meaningful employment can empower individuals and strengthen the entire community.
In terms of healthcare services, access remains a significant challenge for many Aboriginal communities in the Eastern States. Remote and rural areas often lack adequate healthcare facilities and professionals, resulting in limited access to essential medical services. This issue is compounded by cultural and linguistic barriers, making it difficult for Aboriginal people to seek and receive appropriate healthcare. Recognizing and addressing these disparities is essential for the liberation of Aboriginal communities, as access to quality healthcare is a fundamental human right.
As we continue to explore the Eastern States, it becomes evident that addressing Aboriginal employment opportunities and access to healthcare services is crucial for the empowerment and liberation of Aboriginal communities. By working towards eliminating barriers and implementing culturally sensitive policies, we can support the resilience and well-being of Aboriginal people across the Eastern States.
Indigenous Housing
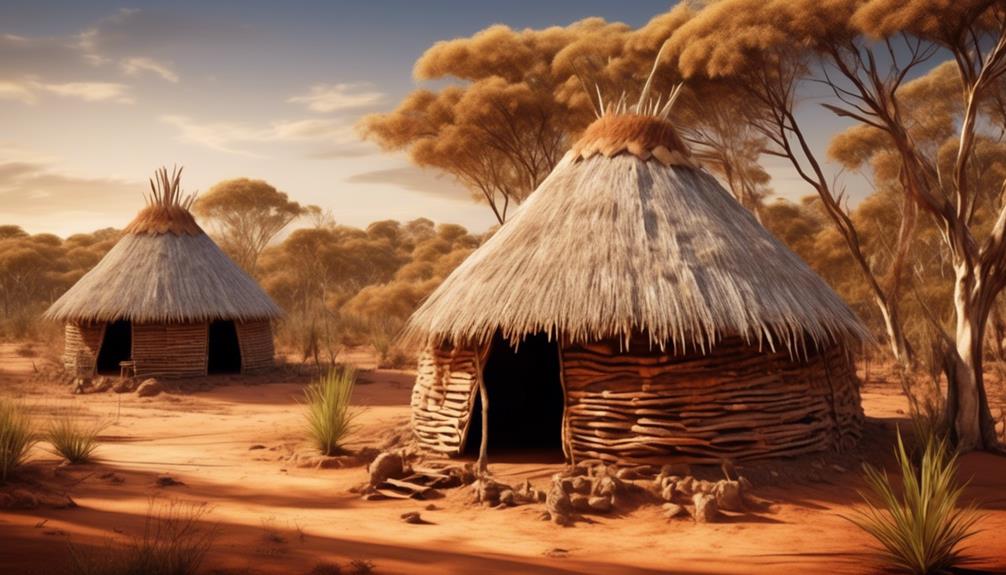

As we shift our focus to Indigenous housing, it becomes clear that the living conditions of Aboriginal communities in the Eastern States are intricately connected to their employment opportunities and access to healthcare services. The challenges of housing in remote areas are significant, contributing to overcrowding and inadequate infrastructure. This, in turn, affects the overall well-being and health of the community members.
- Housing Challenges: The lack of suitable housing in remote Aboriginal communities is a pressing issue. Many houses are overcrowded, leading to increased health risks and affecting the privacy and well-being of individuals and families. Additionally, limited access to essential amenities such as clean water and sanitation further exacerbates the housing challenges faced by Indigenous communities.
- Remote Areas and Traditional Architecture: In remote areas, there's a growing movement to incorporate traditional Aboriginal architecture into housing projects. This not only addresses the practical housing needs but also serves as a means of cultural preservation. By utilizing traditional building methods and materials, such as mud-brick and thatched roofing, communities can maintain their cultural identity while creating sustainable housing solutions.
- Cultural Preservation: Indigenous housing initiatives are increasingly recognizing the importance of cultural preservation. Efforts to involve local community members in the design and construction process help ensure that traditional knowledge and practices are integrated into housing projects, fostering a sense of pride and connection to their heritage.
Understanding the housing challenges and incorporating traditional architecture for cultural preservation is vital in addressing the housing needs of Aboriginal communities in the Eastern States.
Traditional Homelands
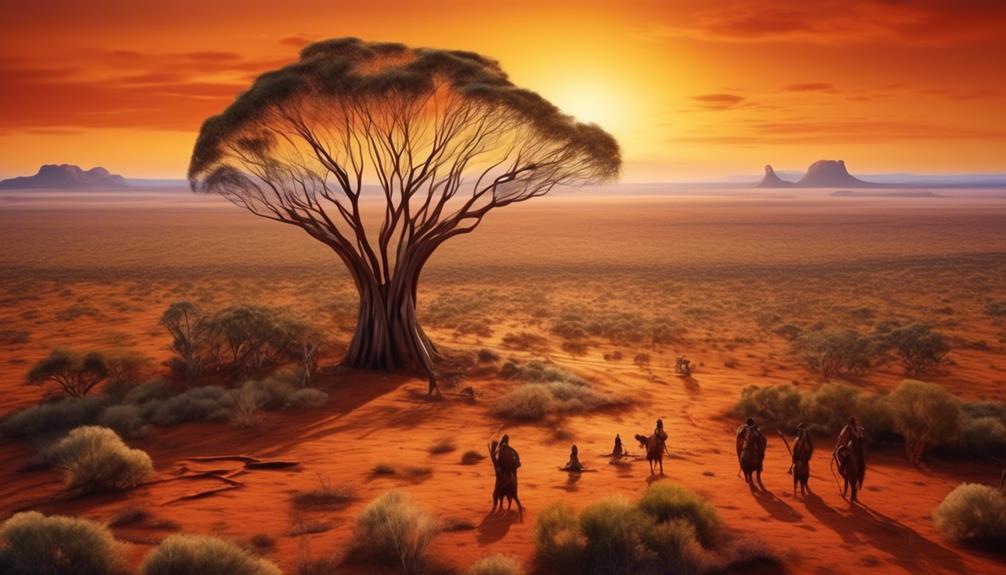

In our observations of Aboriginal communities in the Eastern States, the concept of traditional homelands holds significant cultural and historical importance. Traditional land ownership is deeply intertwined with the identity and spirituality of Aboriginal peoples. These homelands aren't just physical spaces; they're repositories of ancestral knowledge, cultural practices, and connections to the land. It's evident that the preservation of these homelands is crucial for the well-being of Aboriginal communities.
Cultural preservation efforts play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of traditional homelands. The ongoing struggle for recognition and protection of these lands is a testament to the resilience and determination of Aboriginal peoples. Through cultural events, storytelling, and artistic expressions, the significance of these homelands is kept alive. The passing down of traditional knowledge and practices from elders to the younger generations ensures the continuity of cultural ties to the land.
However, traditional homelands face numerous challenges, including encroachment by external developments and environmental degradation. The fight for land rights and the preservation of these homelands is an ongoing battle. It's crucial for broader society to recognize the significance of traditional homelands and support the efforts of Aboriginal communities in safeguarding these vital cultural and historical spaces.
The recognition and protection of traditional homelands are essential steps towards reconciliation and liberation for Aboriginal peoples across Australia.
Indigenous Housing Programs
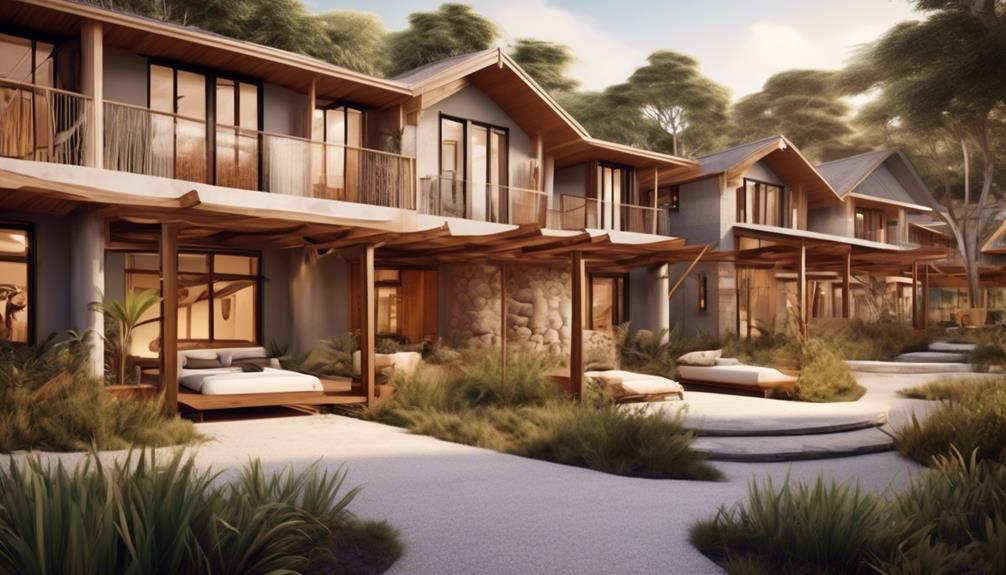

The significance of traditional homelands for Aboriginal communities underscores the critical need for effective Indigenous housing programs that not only address the current housing challenges but also respect and support the cultural and historical connections to the land. Indigenous housing programs play a pivotal role in addressing the housing challenges faced by Aboriginal communities. These programs are designed to not only provide adequate housing but also to foster a sense of community, belonging, and cultural identity.
- Community-Centered Approach: Indigenous housing programs often adopt a community-centered approach, involving local community members in the planning, construction, and maintenance of housing. This approach ensures that the housing reflects the cultural and social needs of the community, strengthening the connection to traditional lands and fostering a sense of ownership and pride.
- Sustainable and Affordable Housing Solutions: Many Indigenous housing programs focus on sustainable and affordable housing solutions that are tailored to the specific needs of Aboriginal communities. These programs aim to address overcrowding, inadequate infrastructure, and poor living conditions, thereby improving the overall quality of life for Indigenous peoples.
- Economic Opportunities: Effective Indigenous housing programs also create economic opportunities within Aboriginal communities. By engaging community members in construction, maintenance, and management of housing projects, these programs contribute to skill development, employment, and economic empowerment, thereby promoting self-sufficiency and resilience within the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Specific Cultural Practices and Traditions of the Aboriginal People in These Different Living Environments?
We observe that the specific cultural practices and traditions of the Aboriginal people in various living environments encompass a deep connection to the land, ceremonial rituals, and art as a form of storytelling.
These traditions are integral to their identity and survival, despite facing political challenges.
The preservation of traditional living and land connection is crucial for the Aboriginal people's cultural resilience and liberation.
How Do Aboriginal Communities in These Areas Access Healthcare and Education Resources?
Accessing healthcare and education resources in Aboriginal communities is crucial for their well-being and development. We've observed that some communities face challenges in accessing these resources due to geographical remoteness and limited infrastructure.
This impacts the quality of healthcare and education available. Understanding these barriers is essential for developing culturally sensitive and effective strategies to improve access for Aboriginal communities.
What Are the Economic Opportunities Available to Aboriginal People in These Different Living Environments?
Economic opportunities for Aboriginal people vary across different living environments. In urban areas, there are job markets and access to education and training.
In rural and remote areas, opportunities may be limited, impacting economic stability. Despite this, cultural practices often create avenues for economic development, such as through traditional arts, crafts, and tourism.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial to empowering Aboriginal communities and fostering economic growth while preserving cultural heritage.
How Do Aboriginal Communities in These Areas Maintain Connection to Their Traditional Lands and Cultural Heritage?
Maintaining connection to traditional lands and cultural heritage is vital for Aboriginal communities. Through traditional practices, storytelling, and art, we preserve our rich heritage.
However, accessing healthcare remains a challenge, impacting our ability to uphold these traditions. It's estimated that only 1 in 3 Aboriginal people have regular access to healthcare services.
This statistic underscores the ongoing struggle to balance cultural preservation with modern healthcare needs, a complex issue that demands attention and action.
What Are the Social and Political Challenges Faced by Aboriginal People in These Different Living Environments?
Social inequality and political representation are critical issues for Aboriginal people.
In our experience, these challenges manifest differently across living environments.
In urban areas, we face discrimination and lack of access to resources.
In remote communities, we struggle with limited infrastructure and services.
Both settings require tailored solutions to address these disparities.
Our cultural understanding informs the need for equitable opportunities and fair representation in decision-making processes.
Conclusion
After exploring where Aboriginal people live in Australia, it's clear that their connection to the land runs deep. In fact, over 20% of Indigenous Australians live in remote communities, maintaining their traditional way of life.
This statistic paints a picture of a resilient and enduring culture, rooted in the unique landscapes of the Australian continent. It's a testament to the strength and resilience of the Aboriginal people and their deep connection to their ancestral lands.