Looking back on the deep culture and resilient spirit of Indigenous communities in Australia, it’s difficult not to also recognize the difficult history of how they were mistreated.
The story of what happened to the Aboriginal in Australia is a complex and often distressing one. From the early interactions with European settlers to the impact of British colonization, the trajectory of the Aboriginal people has been profoundly shaped by a series of events that continue to reverberate today.
But what led to these events, and how have they impacted the Aboriginal communities over time?
Key Takeaways
- Arrival of British settlers in 1788 marked the beginning of cultural exchange and clashes over land, leading to the dispossession of Aboriginal communities and the alteration of their traditional way of life.
- Forced assimilation policies, including the forced removal of Indigenous children from families, resulted in cultural erasure and loss of Indigenous identity, causing intergenerational trauma and ongoing social and health issues within Aboriginal communities.
- Contemporary challenges faced by Aboriginal peoples include economic disparities, health and education inequalities, overrepresentation in the criminal justice system, and limited access to quality services, highlighting the importance of addressing these issues for their well-being and social inclusion.
- The ongoing struggle for land rights and sovereignty, including recognition of traditional ownership and Aboriginal connection to the land, the desire for meaningful involvement in decision-making processes and environmental conservation, and the need to address systemic discrimination, emphasize the importance of reconciliation efforts and ongoing commitment from the government and broader Australian society.

Dark Emu: Aboriginal Australia and the birth of agriculture
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Early Interactions and Colonization
As settlers arrived in Australia, the early interactions with Aboriginal peoples were marked by cultural misunderstandings and clashes over land. The arrival of the British in 1788 initiated a period of significant change for the Aboriginal peoples of Australia.
Early contact between the Indigenous Australians and the European settlers led to a complex cultural exchange. The Aboriginal people had a deep connection to the land, which was integral to their spirituality, culture, and way of life. However, the British colonial expansion resulted in land dispossession for the Aboriginal communities. This dispossession not only disrupted their traditional way of living but also led to the loss of their spiritual and cultural practices tied to the land.
In response to the challenges posed by colonization and land dispossession, resistance movements emerged among the Aboriginal peoples. They sought to protect their lands and resist the encroachment of the settlers. These movements varied in their nature and scope, ranging from small-scale localized resistance to larger, more organized efforts to assert their rights and sovereignty.
The early interactions and colonization also brought about social and economic changes within the Aboriginal communities. The imposition of foreign systems and laws had a profound impact on their social structures and traditional practices. Despite the hardships and challenges, the Aboriginal peoples demonstrated resilience and determination in the face of adversity. Their resistance movements laid the groundwork for the ongoing struggle for recognition, rights, and reconciliation in Australia.
Aboriginal land rights educational resources
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Impact of British Settlement
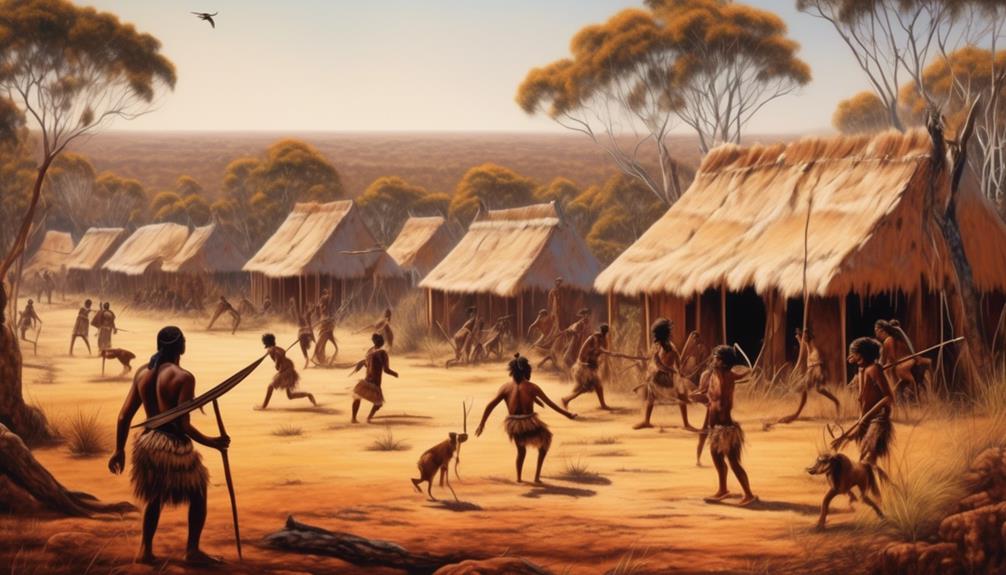

The British settlement in Australia significantly altered the traditional way of life for the Aboriginal peoples, causing widespread cultural upheaval and social dislocation. As the British established their colonies, they imposed their own legal and social systems, which directly conflicted with the existing structures of the Aboriginal communities. This led to a systematic erosion of Aboriginal cultural practices and beliefs, resulting in profound cultural displacement.
One of the most devastating impacts of the British settlement was the dispossession of Aboriginal land. The British disregarded the deep spiritual and cultural connections that Aboriginal people had with the land, leading to the forced removal of Indigenous communities from their traditional territories. This not only disrupted their way of life but also inflicted deep emotional and psychological wounds that continue to affect Aboriginal communities today.
Furthermore, the denial of land rights to the Aboriginal people perpetuated a cycle of social and economic disadvantage. Without ownership and control of their traditional lands, Aboriginal communities faced significant barriers to economic development and self-determination. This ongoing struggle for land rights has been a central issue in the fight for Indigenous rights and recognition in Australia.
The impact of British settlement on the Aboriginal peoples continues to reverberate through generations, shaping their experiences and perspectives. Recognizing and addressing the historical and ongoing consequences of cultural displacement and land rights denial is crucial for reconciliation and building a more equitable future for all Australians.

Dark Emu: Aboriginal Australia and the birth of agriculture
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Forced Assimilation Policies
The impact of British settlement on the Aboriginal peoples in Australia has led to the implementation of forced assimilation policies, aiming to reshape indigenous culture and traditions to align with European norms and values. This has resulted in a complex and troubling history that continues to affect Indigenous communities today.
Current Subtopic: Forced Assimilation Policies
Forced assimilation policies have had profound and lasting effects on the Indigenous peoples of Australia. Here are some key points to consider:
- Cultural Erasure: The forced assimilation policies aimed to eradicate Indigenous languages, traditions, and cultural practices. This systematic erasure of Indigenous culture has had long-lasting intergenerational impacts.
- Loss of Identity: The pressure to assimilate into European culture led to a profound loss of Indigenous identity for many Aboriginal people. This has created a sense of disconnection from their heritage and ancestry.
- Trauma and Displacement: The forced removal of Indigenous children from their families, known as the Stolen Generations, resulted in deep trauma and loss of connection to their communities and culture.
- Indigenous Resistance: Despite the devastating impact of forced assimilation policies, Indigenous communities have shown remarkable resilience and resistance. They've fought to reclaim and revitalize their languages, cultural practices, and traditions, asserting their identity and challenging the ongoing effects of assimilation policies.
Forced assimilation policies have left a painful legacy, but the ongoing Indigenous resistance and resilience demonstrate the strength and determination of Australia's First Nations peoples.
Reconciliation and Indigenous awareness kits
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Stolen Generations and Trauma
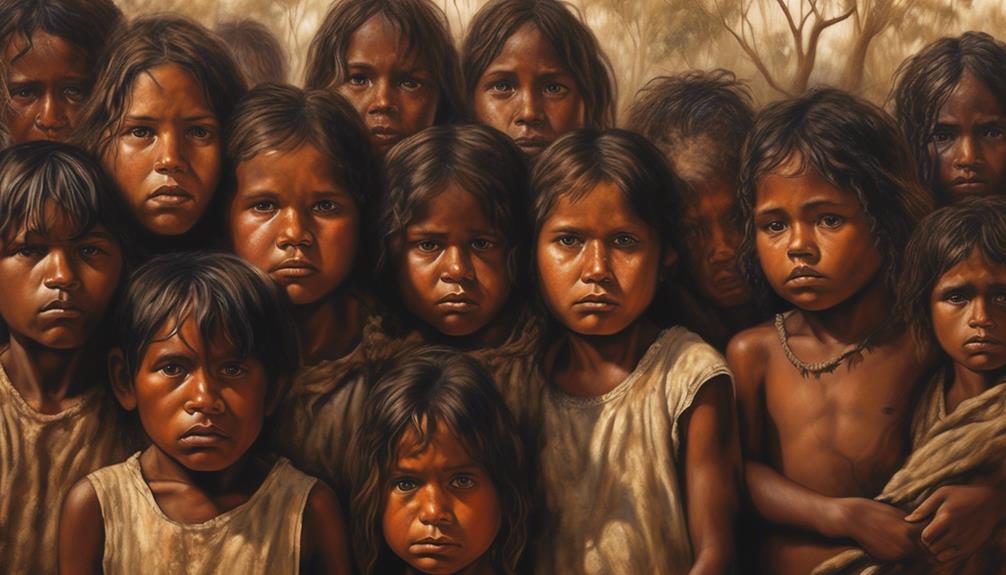

Experiencing the forced removal of Indigenous children from their families has left deep and lasting trauma within Aboriginal communities in Australia. The Stolen Generations refer to the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children who were forcibly taken from their families by government agencies and church missions between the early 1900s and the 1970s. This systematic removal was part of the government's assimilation policies, aiming to integrate Indigenous children into white society.
The impact of this traumatic practice has reverberated through generations, resulting in intergenerational trauma that continues to affect the social and emotional wellbeing of Indigenous Australians today.
The trauma experienced by those who were forcibly removed has been passed down through families, leading to ongoing cycles of pain, substance abuse, mental health issues, and disconnection from cultural heritage. Many Indigenous communities continue to grapple with the effects of this historical injustice, as the wounds of the Stolen Generations haven't fully healed.
However, there are ongoing efforts towards healing and reconciliation. Truth-telling processes, such as the national apology delivered by former Prime Minister Kevin Rudd in 2008, have been pivotal in acknowledging the trauma inflicted on the Stolen Generations. Additionally, culturally sensitive support services, community-led healing initiatives, and efforts to preserve and revitalize Indigenous languages and customs are crucial steps towards healing and reconciliation. These initiatives are essential in addressing the deep-seated trauma and fostering a sense of empowerment and cultural pride within Aboriginal communities.
Contemporary Challenges and Reconciliation Efforts
Amidst ongoing efforts towards healing and reconciliation, contemporary challenges persist for Aboriginal communities in Australia. It's important to understand the current landscape and the hurdles that continue to impact the lives of Aboriginal peoples. Here are some key points to consider:
- Economic Disparities: Despite various initiatives, Aboriginal communities still face significant economic challenges, including high unemployment rates and limited access to quality education and healthcare.
- Cultural Preservation: The preservation of Aboriginal culture and heritage remains a pressing concern. Efforts to revitalize and maintain traditional languages, customs, and practices are crucial for the well-being and identity of Aboriginal communities.
- Land Rights and Sovereignty: The ongoing struggle for land rights and sovereignty continues to be a critical issue. Aboriginal peoples seek recognition of their traditional ownership and connection to the land, as well as meaningful involvement in decision-making processes concerning natural resources and environmental conservation.
- Social Inequality and Discrimination: Despite progress, social inequality and discrimination persist, impacting the everyday lives of Aboriginal individuals and communities. Addressing systemic discrimination and promoting social inclusion are essential for achieving meaningful reconciliation.
In the face of these contemporary challenges, reconciliation efforts are vital. It requires ongoing commitment from both the government and the broader Australian society to address the injustices of the past and work towards a more equitable and harmonious future for all Australians.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Did the Early Interactions Between Aboriginal People and European Settlers Impact the Development of Australia?
Early interactions between Aboriginal people and European settlers had a significant impact on the development of Australia. The cultural exchange between the two groups influenced art, language, and traditions.
However, the impact on the economy was largely negative for Aboriginal people, as their lands were taken, disrupting their traditional way of life. This led to significant economic and social disparities that continue to affect Aboriginal communities today.
What Were the Long-Term Effects of British Settlement on the Aboriginal Population in Terms of Land Ownership and Cultural Preservation?
Cultural displacement, land rights, intergenerational trauma, and assimilation policies have had long-term effects on the Aboriginal population. These issues have led to severe challenges in preserving their traditions and connection to their ancestral lands.
The impact of British settlement has been devastating, causing ongoing struggles for Aboriginal communities. It's crucial to recognize and address these historical injustices to work towards healing and reconciliation.
What Were the Specific Policies and Practices Used to Force Assimilation of Aboriginal People Into European Society, and How Did It Impact Their Communities?
Forced assimilation policies aimed to erase Aboriginal culture and replace it with European ways. These practices severely impacted their communities, leading to profound cultural trauma.
The impact on generations has been significant, with lasting effects on the preservation of traditions and land ownership.
The historical trauma resulting from these policies continues to affect Aboriginal communities today, highlighting the ongoing struggle for cultural preservation and healing.
How Did the Stolen Generations and the Trauma Experienced by Aboriginal People During This Time Continue to Affect Their Communities Today?
Inter generational trauma continues to impact Aboriginal communities today, stemming from the Stolen Generations. The ongoing effects of this trauma are profound, influencing mental health, family dynamics, and cultural identity.
However, healing and reconciliation efforts are steadily progressing, offering hope for the future. It's crucial to understand the lasting repercussions of historical injustices and support initiatives that promote healing and empowerment within Aboriginal communities.
What Are Some Current Challenges Facing Aboriginal People in Australia, and What Efforts Are Being Made Towards Reconciliation and Addressing These Challenges?
We're witnessing ongoing challenges for Aboriginal people in Australia, including disparities in health, education, and socio-economic opportunities. However, there are commendable efforts towards reconciliation and addressing these challenges.
Initiatives promoting cultural preservation and empowerment, alongside government policies and community-led programs, are making strides. These efforts are vital for fostering understanding, healing past injustices, and creating a more equitable future for Aboriginal communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of Aboriginal people in Australia has been marked by colonization, forced assimilation, and trauma. Despite the challenges they've faced, Aboriginal communities continue to strive for reconciliation and healing.
It's time to turn the page and work towards a brighter future, where we can all walk hand in hand. After all, it's never too late to mend fences and build bridges for a better tomorrow.