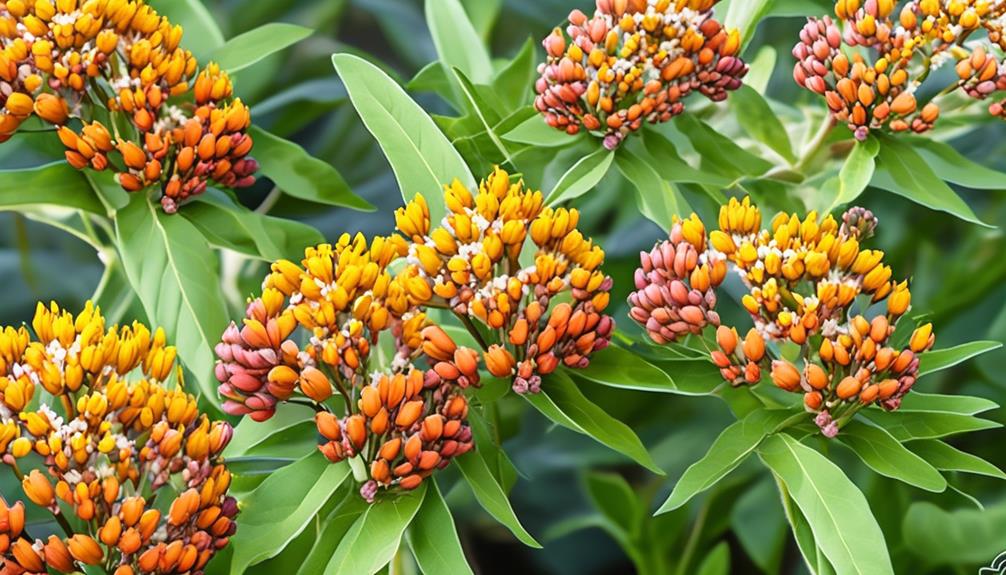
We, as passionate plant enthusiasts, have often pondered the ongoing debate of whether to plant native or tropical milkweed. This subject has sparked much debate among gardeners, leading to confusion over which type is the best choice for their gardens.
While both native and tropical milkweed have their own unique attributes, the impact on monarch butterflies and potential ecological consequences weigh heavily in the decision-making process.
Join us as we explore the characteristics of each, the interaction with the iconic monarch butterfly, and the best practices for planting, to uncover the intricacies of this captivating conundrum.
Key Takeaways
- Native milkweed is indigenous to North America and plays a crucial role in the life cycle of monarch butterflies as the primary host plant for their larvae.
- Tropical milkweed, while fast-growing and attractive, can disrupt monarch migration patterns if not managed carefully and used in conjunction with native milkweed.
- The prolonged presence of tropical milkweed can impact the timing of monarch migration and reproductive cycles.
- Planting practices for both native and tropical milkweed include paying attention to planting depth, soil fertility, moisture levels, and sunlight requirements.
Native Milkweed Characteristics
Native milkweed, also known as Asclepias syriaca, is a perennial plant that's indigenous to North America and plays a crucial role in the life cycle of monarch butterflies.
The benefits of native milkweed are manifold. It serves as the primary host plant for monarch butterfly larvae, providing essential food and habitat for their development. Additionally, native milkweed offers nectar for a variety of pollinators, aiding in the conservation of diverse insect species.
Conservation efforts focused on native milkweed are vital due to its declining population. Factors such as urbanization, agricultural practices, and herbicide use have significantly reduced the abundance of native milkweed in its natural habitat. As a result, initiatives promoting the cultivation and preservation of native milkweed have been established to restore its population and support the conservation of monarch butterflies.
Tropical Milkweed Characteristics
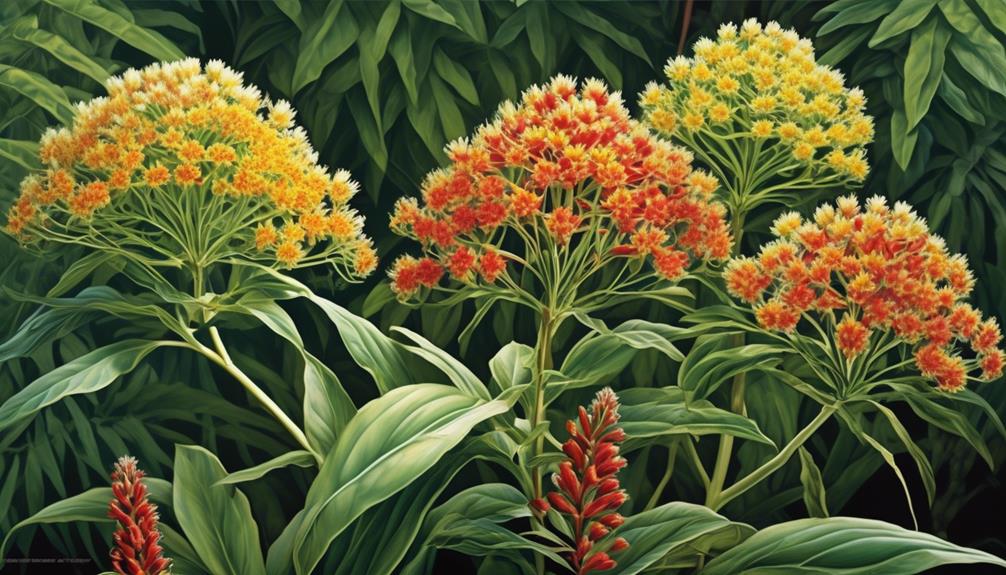

Characterized by its vibrant flowers and fast growth, tropical milkweed, also known as Asclepias curassavica, is a popular non-native species cultivated in many regions. When considering tropical milkweed characteristics, it's important to note its unique growth and propagation methods:
- Rapid Growth: Tropical milkweed is renowned for its fast growth, making it an appealing option for gardeners and conservationists seeking to establish milkweed patches quickly.
- Vibrant Flowers: This species is distinguished by its striking, brightly colored flowers, which make it an attractive addition to gardens and landscapes, while also serving as a nectar source for various pollinators.
- Multiple Propagation Methods: Tropical milkweed can be propagated through seeds, cuttings, or division. Its adaptability to various propagation techniques contributes to its widespread cultivation.
- Year-Round Blooms: Unlike some native milkweed species, tropical milkweed has the capability to bloom year-round in warmer climates, providing a consistent nectar source for pollinators.
Understanding the growth and propagation characteristics of tropical milkweed is essential for individuals considering its cultivation, as it allows for informed decision-making in garden planning and conservation efforts.
Monarch Butterfly Interaction
The interaction between tropical milkweed and monarch butterflies has been the subject of significant research and observation due to its potential impact on the butterflies' behavior and migration patterns.
Monarch behavior can be influenced by the presence of tropical milkweed, as it provides a nectar source and serves as a breeding site for the butterflies.
However, the prolonged presence of tropical milkweed in certain regions can disrupt monarch migration patterns. This is because tropical milkweed can lead to a deviation from their natural migratory instincts, causing them to remain in an area longer than they should. This can affect the timing of their migration and reproductive cycles, ultimately impacting the overall population.
On the other hand, when used cautiously and in conjunction with native milkweed species, tropical milkweed can provide essential resources for monarch butterflies during their reproductive and migratory phases.
Thus, it's crucial to carefully manage the presence of tropical milkweed to ensure that it supports monarch butterflies' natural behavior and migration patterns without causing long-term disruptions.
Potential Ecological Impacts

Studying the potential ecological impacts of tropical milkweed on native ecosystems involves assessing its role in altering plant communities and influencing the behavior of pollinators and other wildlife. The implications of introducing tropical milkweed into native ecosystems are complex and require careful consideration.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Displacement of Native Plants: Tropical milkweed has the potential to outcompete native plant species, leading to a decline in the diversity of plant communities.
- Altered Pollinator Behavior: The availability of tropical milkweed throughout the year can disrupt the natural migratory behavior of monarch butterflies, potentially affecting their population dynamics.
- Impacts on Other Wildlife: Changes in plant composition due to the presence of tropical milkweed may influence the availability of resources for other wildlife, such as nectar-feeding insects and birds.
- Challenges for Ecological Restoration: The spread of tropical milkweed in native habitats can pose challenges for ecological restoration efforts aimed at conserving native plant diversity and restoring natural ecosystem functions.
Understanding the potential ecological impacts of tropical milkweed is crucial for informed decision-making in biodiversity conservation and ecological restoration initiatives. It requires a balanced approach that considers both the needs of threatened species like monarch butterflies and the broader goals of conserving native biodiversity.
Best Practices for Planting
Considering the potential ecological impacts of tropical milkweed, it's important to establish best practices for planting this species to minimize potential disruptions to native ecosystems.
When planting tropical milkweed, it's crucial to pay attention to the planting depth and soil fertility. The ideal planting depth for tropical milkweed is around 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch. It's essential to ensure that the soil is well-draining and fertile, as this will promote healthy growth and development of the plant.
In terms of watering frequency, tropical milkweed generally prefers consistently moist soil. However, it's important to avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot and other issues. Therefore, it's recommended to water the plant deeply but infrequently, allowing the soil to partially dry out between waterings.
Regarding sunlight exposure, tropical milkweed thrives in full sun to partial shade. It's advisable to plant it in an area where it can receive at least 6 hours of sunlight per day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Differences in Plant Care Between Native and Tropical Milkweed?
In caring for native and tropical milkweed, differences arise in growing conditions, impact on wildlife, and soil requirements. Both offer unique benefits and drawbacks.
Understanding the distinct needs of each variety ensures successful growth. Factors such as climate requirements and the impact on pollinators must be considered when deciding whether to grow them together or separate.
It's essential to research and understand the specific care required for each type of milkweed.
Are There Any Potential Risks or Drawbacks to Planting Either Native or Tropical Milkweed in a Home Garden?
There are potential drawbacks to planting either native or tropical milkweed in a home garden. Risks include potential harm to monarch butterflies, as tropical milkweed can disrupt their natural migration patterns.
Additionally, both types of milkweed can spread aggressively, impacting the local environment.
When considering garden compatibility, it's important to weigh the benefits of attracting pollinators against the potential risks of planting milkweed.
It's crucial to carefully manage and monitor these plants in a home garden setting.
Can Native and Tropical Milkweed Be Grown Together in the Same Garden, or Should They Be Kept Separate?
Growing conditions for native and tropical milkweed are similar, making it feasible to grow them together. Cohabitation benefits include attracting a wider variety of pollinators and providing continuous nectar sources. However, it's essential to monitor for potential issues, such as the spread of parasites or pathogens, and take appropriate measures if necessary.
How Do Native and Tropical Milkweed Impact Other Pollinators and Wildlife, Aside From Monarch Butterflies?
In our study, we observed that native and tropical milkweed impact pollinator diversity and wildlife habitat in various ways beyond their influence on monarch butterflies.
The ecological impact of these milkweeds can either promote or inhibit the presence of other pollinators and wildlife species.
When integrating them into gardens, it's crucial to consider their potential effects on the overall ecosystem and strive for a balanced approach that supports biodiversity.
Are There Any Specific Soil or Climate Requirements for Successfully Growing Native or Tropical Milkweed?
For successful growth of native or tropical milkweed, it's crucial to consider soil composition and climate requirements.
Soil should be well-draining, rich in organic matter, and slightly acidic.
Both native and tropical milkweed thrive in full sun and warm climates. They prefer temperatures above 70°F and are sensitive to frost.
Adequate moisture is also essential, but they can tolerate periods of drought.
Understanding these requirements is key to successfully cultivating native or tropical milkweed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when considering whether to plant native or tropical milkweed, it's important to weigh the potential ecological impacts and the needs of the monarch butterfly. Are we willing to risk disrupting the natural balance for the sake of convenience?
With careful consideration and best practices in planting, we can support monarch populations while minimizing negative effects on the environment. It's a delicate balance, but one worth striving for in our efforts to protect these beautiful creatures.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.