Have you ever considered the deep historical connection that Indigenous Australians have with their land?
Take for example the discovery of Mungo Man and Mungo Lady, whose remains were found in New South Wales and have been dated to over 40,000 years ago. It's a staggering figure, but it also raises a multitude of questions about the timeline of Aboriginal presence in Australia.
How did they arrive? What were their lives like? And what does this mean for our understanding of human history? These are just a few of the mysteries that we'll explore as we unravel the complex and captivating story of the Aboriginal people and their enduring legacy on this ancient continent.
Key Takeaways
- Aboriginal people have been in Australia for approximately 65,000 years, as supported by archaeological evidence and genetic studies.
- Indigenous oral histories provide a unique perspective on Aboriginal history, offering insights into historical events and the enduring connection to the land.
- Transmission of cultural traditions and historical knowledge through generations fosters a sense of belonging and identity within Indigenous communities.
- Coastal migration played a significant role in the settlement of Australia by early Aboriginal populations, influencing cultural practices, societal integration, and settlement patterns.
Theories of Aboriginal Arrival
One of the theories about the arrival of Aboriginal people in Australia suggests that they migrated to the continent around 65,000 years ago. This theory is based on archaeological evidence, including the discovery of ancient tools and remains, as well as genetic studies. It's believed that the ancestors of the Aboriginal people traveled from Southeast Asia, possibly using boats to cross the waters that separated the landmasses. This theory is supported by the presence of similar stone tool technologies found in both Southeast Asia and Australia.
Another theory proposes that the migration was part of a series of waves, with groups of people arriving at different times over thousands of years. This theory is based on the diversity of Aboriginal cultures and languages across the continent. It suggests that different groups may have taken different routes and arrived in Australia at different periods, leading to the rich tapestry of Aboriginal societies observed by European settlers.
The study of Aboriginal migration and arrival theories is crucial in understanding the deep history of Australia and the enduring connection of the Aboriginal people to the land. These theories also contribute to the appreciation of the diverse cultures and traditions that have evolved over tens of thousands of years. By exploring these theories, we gain insight into the remarkable resilience and adaptability of the Aboriginal people in the face of significant environmental and social changes.
Indigenous Oral Histories

We trust Indigenous oral histories as they've been passed down through generations, preserving the stories of our ancestors.
These narratives not only offer insights into historical events, but also provide a deeper understanding of the enduring connection Aboriginal peoples have with their land.
As we explore Indigenous oral histories, we uncover a rich tapestry of knowledge that continues to shape our understanding of Australia's ancient past.
Oral History Reliability
Indigenous oral histories provide valuable insights into the rich cultural heritage and historical experiences of Australia's Aboriginal communities. When assessing the reliability of these oral histories, it's crucial to consider the storytelling techniques and cultural perspectives embedded within them.
While these narratives may not align with Western historical accuracy, they offer a different lens through which to view the past. The reliability of oral histories lies in their ability to convey the lived experiences and collective memory of Indigenous communities across generations.
It's essential to approach these narratives with respect for their cultural significance and recognize that historical truths can be conveyed through oral traditions, offering a more holistic understanding of Australia's Aboriginal history.
Transmission Through Generations
Passed down through generations, Indigenous oral histories in Australia have served as a vital means of preserving cultural traditions and historical knowledge.
The richness of our oral traditions is remarkable:
- Elders gathered around the fire, their faces illuminated by the dancing flames, sharing stories of the Dreamtime, passing on wisdom about the land, and recounting the struggles and triumphs of our people.
- The intricate hand gestures and facial expressions that accompany the stories, adding depth and emotion to the narratives.
- Children sitting at the feet of their elders, absorbing the knowledge and traditions that have been passed down through countless generations.
These moments of generational transmission not only preserve our cultural heritage but also foster a deep sense of belonging and identity within our communities.
Connection to Land
Preserving our cultural heritage and fostering a deep sense of belonging, the connection to land in Indigenous oral histories is deeply intertwined with the transmission of wisdom and traditions across generations.
The connection to land holds immense cultural significance for Indigenous communities, serving as a fundamental aspect of our identity and spirituality.
Our oral histories intricately weave narratives that highlight the profound spiritual connection to the land, emphasizing its role as a source of sustenance, healing, and guidance.
Furthermore, the concept of land rights is deeply embedded within our oral traditions, reflecting the ongoing struggle for recognition and protection of Indigenous lands.
Through the storytelling and passing down of oral histories, we impart the significance of the land to future generations, ensuring the perpetuation of our spiritual and cultural connection to the land.
Archaeological Discoveries

Recent archaeological discoveries have provided remarkable insights into the ancient Aboriginal history in Australia. Through advanced excavation techniques and preservation methods, researchers have unearthed a treasure trove of cultural artifacts, shedding light on the dietary habits, societal structures, and technological advancements of the Aboriginal people.
Excavation Techniques:
- Cutting-edge ground-penetrating radar technology has enabled archaeologists to uncover hidden artifacts and structures without disturbing the surrounding environment, preserving the integrity of the sites for future study.
- The use of 3D laser scanning and drone technology has allowed for precise mapping and documentation of archaeological sites, providing a comprehensive understanding of the layout and spatial relationships within ancient Aboriginal settlements.
Preservation Methods:
- Preservation through non-invasive techniques such as controlled environment storage and digital scanning has ensured the long-term conservation of delicate artifacts, including tools, rock art, and ceremonial objects, offering a window into the material culture of the Aboriginal people.
- Collaboration with Aboriginal communities has facilitated the development of preservation strategies that respect the cultural significance of the artifacts, integrating traditional knowledge with modern conservation practices.
These discoveries haven't only deepened our understanding of the Aboriginal history in Australia but also underscored the enduring cultural legacy of the world's oldest continuous civilization.
Genetic Studies and Findings
Recent archaeological discoveries have provided remarkable insights into the ancient Aboriginal history in Australia, and genetic studies and findings have further enriched our understanding of the origins and migrations of the Aboriginal people.
Genetic diversity studies have revealed a complex tapestry of ancient ancestry among Aboriginal populations. These studies have shown that Aboriginal Australians are one of the oldest continuous populations outside Africa, with an ancestry spanning more than 50,000 years. DNA analysis of modern Aboriginal populations has also provided evidence of multiple waves of migration and settlement across the Australian continent, shedding light on the intricate patterns of population movement and interaction over millennia.
Moreover, genetic research has uncovered significant diversity among different Aboriginal groups, reflecting the complex and varied history of population migration and interaction within Australia. This diversity underscores the rich tapestry of Aboriginal cultures and traditions, each shaped by unique historical and environmental contexts.
Additionally, genetic studies have highlighted the deep connections between Aboriginal communities and their ancestral lands, reinforcing the profound spiritual and cultural significance of country for Aboriginal peoples.
Megafauna and Early Settlement

Uncovering evidence of megafauna interactions and early human settlement provides valuable insights into the ancient Aboriginal history in Australia. As we delve into the megafauna extinction and early migration patterns, it becomes apparent that the landscape of Australia was once inhabited by massive creatures such as the Diprotodon, a giant wombat-like marsupial, and the Genyornis, a large flightless bird. These megafauna roamed the land in the Pleistocene era, coexisting with the early Aboriginal inhabitants.
Imagine the vast grasslands where herds of Diprotodons grazed peacefully, their heavy footsteps leaving imprints in the soft earth. The air is filled with the echoing calls of the Genyornis, their imposing figures dominating the skyline.
The early Aboriginal people, with their primitive tools and communal hunting strategies, navigated this landscape, forging a delicate balance with the megafauna as they sought sustenance and shelter.
However, as the climate shifted and the continent underwent significant environmental changes, the megafauna faced extinction. This period of transition also influenced the early migration patterns of the Aboriginal people, as they adapted to new terrains and sought out new food sources.
These interactions between the ancient Aboriginal inhabitants and the megafauna not only shaped the physical landscape but also influenced cultural practices and belief systems. Understanding how these early settlers coexisted with and eventually outlasted the megafauna provides a compelling narrative of resilience and adaptation in the face of environmental challenges.
Coastal Migration Hypotheses
We've come across fascinating evidence pointing to the possibility of coastal migration playing a significant role in the settlement of Australia.
The coastal route hypothesis offers compelling insights into how early Aboriginal populations may have navigated and settled the continent.
This has the potential to reshape our understanding of the impact of coastal migration on the cultural and historical development of Aboriginal communities.
Coastal Route Evidence
Examining the coastal route evidence provides valuable insights into the hypotheses of Aboriginal coastal migration. The archaeological evidence along the coastal areas offers compelling support for the theory of early human migration.
- Shell Middens: These ancient heaps of discarded shells along the coast indicate prolonged human occupation and exploitation of marine resources.
- Rock Art Sites: Depictions of maritime activities and sea creatures in coastal rock art sites suggest a deep connection to the sea and maritime skills.
- Stone Tools and Artefacts: The discovery of specialized marine-oriented tools and artefacts in coastal areas provides concrete evidence of a culture adapted to coastal living and seafaring.
These compelling archaeological findings paint a vivid picture of the Aboriginal coastal migration, showcasing their deep-rooted connection to the coastal environment and maritime activities.
Impact on Settlement
The impact of coastal migration on Aboriginal settlement patterns reveals a significant influence on the development of early human communities in Australia.
The availability of marine resources along the coast facilitated a shift in the Aboriginal culture, impacting their societal integration and settlement patterns.
The coastal migration hypothesis suggests that as the Aboriginal people migrated along the coast, they adapted to new environmental conditions and developed specialized technologies for exploiting marine resources, such as fishing tools and watercraft.
This shift not only impacted their diet and subsistence strategies but also influenced their cultural practices and social organization.
The proximity to the coast allowed for increased interaction with neighboring groups, leading to the exchange of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices, ultimately shaping the diversity and complexity of Aboriginal societies in different regions of Australia.
Climate Change Impacts

Experiencing significant changes in our environment, the Aboriginal communities in Australia are actively adapting to the impacts of climate change. As custodians of the land for thousands of years, our cultural adaptation and traditional knowledge have been instrumental in addressing the challenges posed by climate change.
- Resilient Agricultural Practices: Our communities have been utilizing traditional farming techniques that are resilient to extreme weather conditions, ensuring food security and sustainability. This includes the implementation of sophisticated water management systems and the cultivation of climate-resilient crops, preserving biodiversity and traditional food sources.
- Cultural Heritage Conservation: Climate change impacts have led us to actively engage in the preservation of our cultural heritage sites, which hold immense historical and spiritual significance. Through traditional land management practices and environmental stewardship, we're safeguarding these sites from erosion and degradation caused by changing climatic patterns.
- Adaptive Resource Management: Our deep understanding of the land and its resources has enabled us to adapt our resource management strategies in response to climate change impacts. By integrating traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches, we're ensuring sustainable utilization of natural resources while mitigating the effects of environmental changes.
Rock Art and Cultural Signifiers
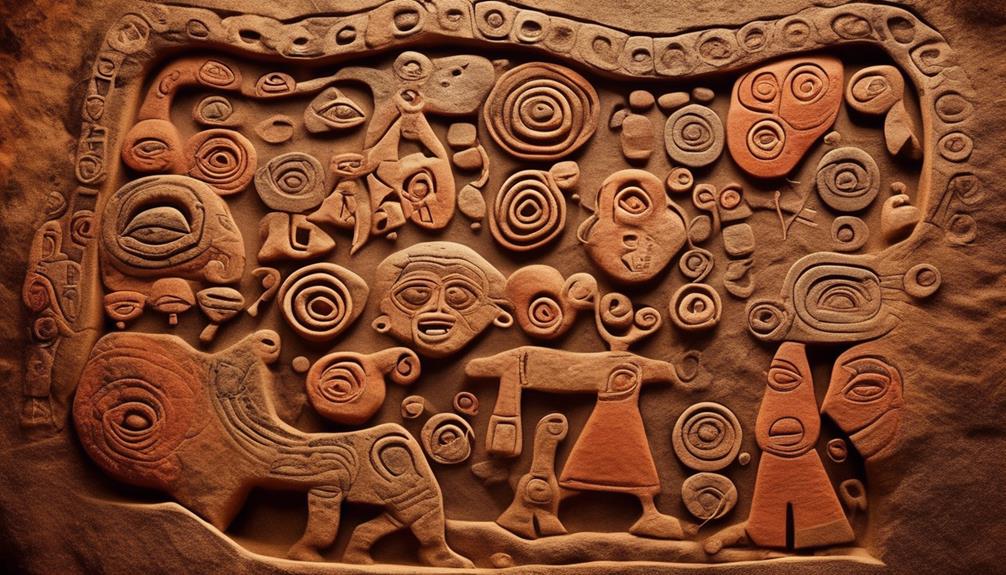

Embracing our ancestral legacy, we incorporate traditional rock art as a vital cultural symbol and means of communication within our community. Our rock art serves as a profound connection to our past, preserving our cultural heritage and Indigenous storytelling traditions. These ancient depictions on cave walls, rock shelters, and boulders convey our spiritual beliefs, sacred rituals, and significant events, reflecting the essence of our existence as Aboriginal people. The intricate patterns, symbols, and figures represent a form of visual language, carrying narratives that have been passed down through generations.
Cultural preservation is at the core of our rock art, as it encapsulates the richness of our traditions, customs, and knowledge systems. Each stroke and pigment used in the creation of these artworks holds profound meaning, a testament to our enduring presence on this land. Through these visual expressions, we communicate our profound connection to the land, the animals, and the celestial realms, fostering a deep sense of belonging and identity within our community.
Furthermore, our rock art serves as a touchstone for the continuation of Indigenous storytelling traditions. It provides a tangible link to our oral histories, reinforcing the importance of passing down knowledge through verbal narratives and visual representations. As custodians of this ancient legacy, we recognize the significance of preserving and interpreting these cultural signifiers, ensuring that our stories and traditions endure for generations to come.
Colonization and Displacement
When colonization began in Australia, it had a profound impact on Aboriginal communities. The forced displacement caused by colonization led to the loss of traditional lands, disrupting centuries-old connections to the land and culture.
The effects of this displacement continue to resonate within Aboriginal communities today, shaping their ongoing struggle for recognition and restitution.
Impact of Colonization
Upon the arrival of European settlers, the indigenous peoples of Australia faced significant displacement and colonization, leading to profound and lasting impacts on their communities and cultures.
This impact of colonization resulted in forced displacement, as indigenous communities were forcibly removed from their traditional lands, disrupting their connection to the land and their traditional way of life.
The colonization also brought about the imposition of foreign laws and customs, eroding the autonomy and self-governance of indigenous societies.
Additionally, the introduction of diseases and violence led to a significant decline in the indigenous population, further destabilizing their communities.
These factors combined to create a legacy of trauma, loss, and ongoing socio-economic challenges for indigenous peoples in Australia, shaping their experiences and realities to this day.
Forced Displacement Effects
The forced displacement caused by colonization significantly impacted the indigenous peoples of Australia. This led to profound and lasting changes in their communities and traditional way of life.
The displacement disrupted established social structures and cultural practices. It resulted in the loss of ancestral lands and connection to sacred sites. This forced relocation also led to the breakdown of intergenerational knowledge transfer and traditional governance systems.
As a result, many Aboriginal communities experienced a loss of cultural identity and struggled to preserve their heritage in the face of external pressures.
Despite these challenges, efforts to reclaim and revitalize traditional languages, customs, and spiritual beliefs have been ongoing. Initiatives aimed at cultural preservation, such as land rights movements and cultural heritage programs, play a crucial role in restoring and safeguarding the rich cultural heritage of Australia's indigenous peoples.
Loss of Traditional Lands
Due to colonization and forced displacement, our indigenous communities suffered the profound loss of their traditional lands, disrupting centuries-old connections to their ancestral territories and sacred sites. This loss has had devastating effects on our people, as our traditional knowledge and cultural practices are deeply intertwined with the land.
The impact of this displacement is palpable, with our communities facing immense challenges in maintaining our cultural heritage and passing down traditional knowledge to future generations. The loss of land rights has also resulted in economic hardships, as our ability to sustain ourselves through traditional means has been severely compromised.
Our people continue to fight for recognition of our land rights, seeking to regain control over our ancestral lands and preserve our traditional knowledge for the benefit of all humanity.
- We remember the vibrant landscapes that once sustained us, now lost to the relentless march of colonization.
- The rivers that once teemed with life now stand as silent witnesses to our displacement.
- Our sacred sites, once imbued with the wisdom of our ancestors, now stand desolate, severed from our spiritual connection.
European Contact and Impact

European explorers and settlers arrived in Australia in the late 18th century, profoundly impacting the lives and cultures of the Aboriginal people. The contact with Europeans brought about significant changes in the traditional way of life for the Aboriginal communities. Cultural assimilation was a common approach employed by the European settlers, aiming to integrate the Aboriginal people into the European way of life. This had a profound impact on the traditions of the Aboriginal people as they were coerced into adopting European customs, language, and religion. The imposition of European laws and governance also greatly affected the traditional systems of land ownership and land use, leading to the erosion of Aboriginal land rights. The dispossession of traditional lands had devastating consequences for the Aboriginal people, disrupting their spiritual connection to the land and severing ties to their cultural heritage.
The introduction of European diseases also had a catastrophic impact on the Aboriginal population, leading to a significant decline in their numbers. The loss of lives, combined with the displacement from their traditional lands, resulted in immense suffering and trauma for the Aboriginal communities.
The enduring legacy of European contact and its impact on the Aboriginal people continues to shape the socio-cultural landscape of Australia today. It remains a poignant reminder of the resilience and perseverance of the Aboriginal people in the face of immense adversity.
Continuity of Traditional Practices

Despite the significant impact of European contact, Aboriginal communities have continued to maintain and pass down their traditional practices, demonstrating resilience and cultural vitality. Cultural preservation has been a cornerstone of our identity, allowing us to navigate societal changes while staying rooted in our heritage. The generational knowledge inherited from our ancestors has enabled us to adapt traditional practices to the modern world, ensuring their relevance and sustainability.
- *Connection to the Land*: Our traditional practices are deeply intertwined with the land, reflecting our profound connection to the natural environment. Through rituals, storytelling, and art, we continue to honor and celebrate the landscapes that have shaped our culture for millennia. This enduring connection serves as a testament to our commitment to preserving our ancestral ways.
- *Passing Down Oral Traditions*: Despite the challenges posed by societal changes, the oral traditions of our elders persist as a vital means of transmitting knowledge and wisdom to younger generations. These stories, myths, and legends embody the essence of our cultural identity, fostering a sense of continuity and belonging within our communities.
- *Adaptation to Contemporary Lifestyles*: While upholding our traditional practices, we've also embraced modern adaptation, integrating new tools and techniques into age-old customs. This adaptive approach ensures that our cultural heritage remains relevant and accessible to younger members of our community, bridging the gap between the past and the present.
The continuity of our traditional practices serves as a living testament to our resilience, perseverance, and commitment to preserving our rich cultural heritage in the face of societal changes.
Connection to Country

Rooted in our cultural identity, our deep connection to the land, known as 'Country,' is a fundamental aspect of Aboriginal heritage and spirituality. Connection to land is more than just a physical presence; it encompasses a spiritual and cultural significance that has been passed down through generations. Our relationship with the land is defined by mutual respect, responsibility, and reciprocity. We've a profound understanding of the interconnectedness of all living things, and this understanding forms the basis of our cultural identity.
Our connection to Country isn't merely about ownership or possession; it's about custodianship and belonging. The land isn't seen as a commodity but as a part of our identity, a source of spiritual sustenance, and a repository of cultural memory. It's where our stories, traditions, and laws originate, and where they continue to thrive. Our profound connection to Country is evident in the way we care for the land, using sustainable practices that have been honed over millennia. This deep-rooted connection also underpins our spiritual beliefs, ceremonies, and rituals, which are intrinsically linked to the land.
The cultural significance of our connection to Country can't be overstated. It shapes our worldview, our sense of belonging, and our understanding of our place in the world. Our connection to land isn't just historical; it's a living, dynamic relationship that continues to define and sustain us as Aboriginal people.
Legal Recognition and Rights
Asserting our legal recognition and rights as Aboriginal people has been an ongoing struggle rooted in our history and shaped by our enduring connection to Country. Our fight for legal recognition is like a river carving its path through rugged terrain, constantly pushing against barriers erected by historical injustices. We stand firm, like the ancient trees in our forests, seeking to secure our rightful place within the legal framework of our land.
In the courtrooms, we've tirelessly pursued legal avenues to affirm our rights, seeking recognition of our inherent connection to the land and the protection of our cultural heritage. Like skilled navigators, we chart a course through complex legal systems, striving to uphold our traditions and secure our future.
Our legal battles are intertwined with the preservation of our cultural identity. Like guardians of an ancient flame, we advocate for laws that safeguard our traditions, languages, and sacred sites. Our aim is to ensure that our cultural heritage remains vibrant and intact for generations to come.
Legal recognition isn't just a theoretical concept for us; it's a means to empower our communities. Like master craftsmen shaping raw materials into something enduring, we seek legal mechanisms that enable self-governance, economic development, and the well-being of our people.
In this ongoing struggle for legal recognition and rights, our commitment to cultural preservation remains unwavering. We continue to navigate the legal landscape, striving for justice and empowerment while safeguarding our rich heritage.
Contemporary Aboriginal Communities

We see that contemporary Aboriginal communities are diverse and dynamic, with a significant portion living in urban areas. These communities continue to hold onto traditional cultural practices while adapting to the modern world, showcasing resilience and strength.
Understanding the complexities and richness of contemporary Aboriginal communities is crucial for appreciating the ongoing legacy and contributions of Australia's First Nations people.
Urban Aboriginal Populations
Contemporary Aboriginal communities in urban areas have experienced significant cultural, social, and economic changes over the past century.
- The sounds of didgeridoos blend with the bustling city noises, reflecting the fusion of traditional music with modern urban rhythms.
- Aboriginal art adorns the cityscape, with vibrant murals and sculptures showcasing the resilience and creativity of urban Aboriginal artists.
- Indigenous cuisine has found its place in urban settings, offering a fusion of traditional bush tucker with contemporary gastronomy, creating a unique culinary experience.
The urban Aboriginal lifestyles are a testament to the resilience and adaptability of Indigenous cultures in the face of cultural assimilation in cities. Despite the challenges, contemporary Aboriginal communities continue to thrive, preserving their heritage while embracing the opportunities and diversity present in urban environments.
Traditional Cultural Practices
In contemporary urban settings, traditional cultural practices of Aboriginal communities continue to thrive, adapting to the dynamic landscape of modern life while maintaining their rich heritage. Cultural preservation remains a top priority for many Aboriginal groups, as these practices hold immense heritage significance. The table below illustrates some traditional cultural practices that are still actively embraced and practiced within Aboriginal communities today.
| Traditional Cultural Practices | Description |
|---|---|
| Dreamtime Stories | Oral traditions passing down creation myths, beliefs, and cultural values. |
| Bush Tucker | Gathering and preparing native food sources, connecting people to the land. |
| Art and Symbolism | Expressing cultural stories and beliefs through intricate designs and symbols. |
| Ceremonial Practices | Rituals and gatherings for spiritual, social, and cultural purposes. |
The continuation of these traditional practices not only strengthens the Aboriginal identity but also fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of their rich cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Current Population of Aboriginal People in Australia?
The current population of Aboriginal people in Australia is estimated to be around 800,000.
Population statistics show that efforts have been made to preserve their rich cultural heritage. Cultural preservation is a priority to ensure the traditions, languages, and customs are passed down to future generations.
This is crucial for maintaining the unique identity and history of the Aboriginal people within Australia.
What Are Some Traditional Aboriginal Practices That Are Still Maintained Today?
As we explore traditional Aboriginal practices maintained today, we encounter a rich tapestry of cultural heritage.
Traditional ceremonies, such as corroborees and initiation rites, continue to be cherished and passed down through generations.
Additionally, Aboriginal art traditions, like rock paintings and dot paintings, serve as a testament to their enduring connection to the land.
These practices reflect the resilience and profound spirituality of Aboriginal culture, offering a glimpse into their timeless traditions.
How Have Aboriginal Communities Adapted to Modern Society?
We've observed that Aboriginal communities have adapted to modern society through a delicate balance of cultural preservation and social integration. By maintaining traditional practices while also embracing technological advancements and educational opportunities, they've navigated the complexities of modern life.
This has allowed them to honor their heritage while actively participating in broader social and economic systems. Such adaptation showcases the resilience and dynamism of Aboriginal communities in the face of ongoing societal changes.
What Legal Rights and Recognition Do Aboriginal People Have in Australia Today?
Aboriginal land rights and cultural preservation are critical issues in Australia today. Legal recognition has been a major step forward, but there's still work to be done.
The struggle for land rights and cultural preservation continues as we navigate complex legal frameworks. Aboriginal people have made significant progress in gaining legal rights and recognition, but the fight is ongoing.
We must stay vigilant in supporting these important causes.
What Are Some Current Issues Facing Aboriginal Communities in Australia?
We face significant social inequality and land rights issues within Aboriginal communities in Australia. These challenges impact access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities.
Our people continue to fight for recognition and rights over traditional lands, facing ongoing injustices. It's crucial to address these issues to create a more equitable and inclusive society.
We must work together to advocate for change and support the empowerment of Aboriginal communities.
Conclusion
Just as the roots of a mighty tree run deep into the earth, the Aboriginal people have been in Australia for thousands of years, intertwined with the land and its stories.
Through oral histories, archaeological evidence, and genetic studies, their ancient connection to this country is undeniable.
Like the timeless ebb and flow of the tides, their presence in Australia is an enduring part of the natural landscape, shaping the rich tapestry of this ancient land.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.