Many people are unaware that Australia houses over 250 distinct Indigenous language groups, and each one includes a unique word for ‘family.’ This diversity not only highlights an interesting fact but also showcases the richness of Aboriginal cultures. It underscores the deep and complex nature of their sense of kinship.
However, it's not just about the linguistic diversity; the Aboriginal word for 'family' holds profound cultural and spiritual significance that offers us a glimpse into a worldview that is fundamentally different from our own.
As we explore the Aboriginal word for 'family,' we'll uncover the deep-rooted cultural concepts, values, and connections that shape the Aboriginal understanding of kinship, leaving us with a deeper appreciation for their heritage.
Key Takeaways
- The Aboriginal word for family reflects deep connections to kinship, community, and ancestral traditions.
- It encompasses a profound sense of belonging and interconnectedness, extending beyond immediate blood relations to include the broader community and the land itself.
- Aboriginal communities have an extended family structure with shared responsibilities and specific roles and responsibilities for each member.
- The cultural concepts and values within Aboriginal communities emphasize respect, responsibility, reciprocity, community support, and traditional practices of cooperation and sharing.
Origin and Significance
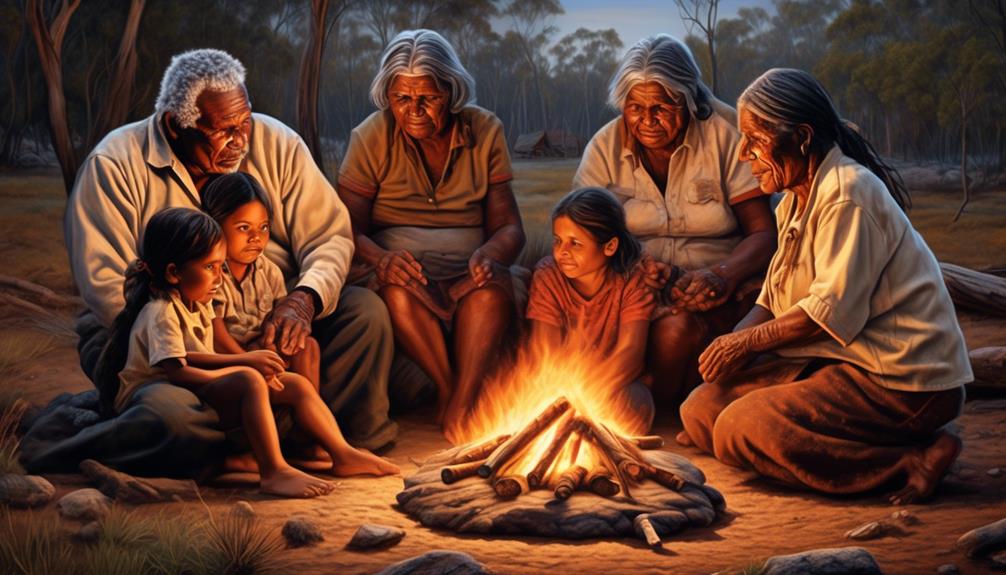
The origin and significance of the Aboriginal word for family can be traced back to the rich cultural and spiritual heritage of the indigenous people, reflecting their deep connections to kinship, community, and ancestral traditions. The word for family in Aboriginal culture has evolved over thousands of years, shaped by the social dynamics and roles within the community. It encompasses a profound sense of belonging and interconnectedness, extending beyond immediate blood relations to include the broader community and the land itself.
Social dynamics and roles within Aboriginal communities have played a pivotal role in shaping the concept of family. The extended family structure, where responsibilities and care are shared among members, has been integral to the evolution of the Aboriginal word for family. Each member has specific roles and responsibilities, contributing to the well-being and harmony of the family unit. This collective approach underscores the deep-rooted values of cooperation, reciprocity, and mutual support within the Aboriginal concept of family, reflecting the interconnectedness of all members within the community.
Cultural Concepts and Values

Cultural concepts and values within Aboriginal communities intricately intertwine with the evolution of the word for family, reflecting the deep-rooted interconnectedness and collective approach that underpin the Aboriginal concept of kinship and community. Intergenerational wisdom plays a significant role in shaping these cultural values.
Elders hold a revered position within Aboriginal communities, serving as the custodians of traditional knowledge and cultural practices. Their wisdom and guidance are instrumental in shaping the values associated with family, emphasizing respect, responsibility, and reciprocity within the community.
Community support is another fundamental aspect of Aboriginal cultural concepts and values. The concept of family extends beyond biological relationships to encompass the broader community. Collective responsibility and mutual support are deeply ingrained in Aboriginal cultural values, fostering a sense of belonging and interconnectedness.
This communal approach to family and community reflects the traditional practices of cooperation and sharing that have sustained Aboriginal societies for generations.
Extended Kinship Networks
Reflecting the intricate web of relationships and connections, extended kinship networks form a foundational aspect of Aboriginal communities, encompassing a wide array of familial and communal ties. These networks are characterized by intergenerational support, where elders play a pivotal role in transmitting cultural knowledge, traditions, and values to younger generations. Additionally, community relationships within extended kinship networks foster a sense of belonging and interconnectedness, shaping the social fabric of Aboriginal societies.
- Intergenerational Support: Elders are revered for their wisdom and experience, providing guidance and imparting traditional knowledge to younger members of the community.
- Community Relationships: Aboriginal communities are interconnected through a complex system of relationships that extend beyond immediate family, creating a supportive and cohesive social structure.
- Cultural Transmission: Extended kinship networks serve as conduits for the transmission of cultural practices, oral histories, and spiritual beliefs, ensuring the preservation of Aboriginal traditions across generations.
These intricate networks not only contribute to the well-being of individuals within the community but also serve as mechanisms for the preservation and continuation of Aboriginal cultural heritage.
Spiritual and Ancestral Connections

Embedded within the extended kinship networks of Aboriginal communities are profound spiritual and ancestral connections that shape the collective identity and worldview of the community members. Ancestral reverence forms the cornerstone of Aboriginal spirituality, fostering a deep sense of connection to the land, the environment, and the cosmos. The spiritual bonds between the living and the ancestors are integral to the Aboriginal understanding of family and community. These connections are upheld through rituals, ceremonies, and oral traditions that have been passed down through generations, serving as a bridge between the past, present, and future.
The Aboriginal concept of family extends beyond the living members to include the ancestors who continue to influence and guide the community. This interconnectedness with the spiritual realm creates a profound sense of belonging and responsibility towards the ancestors and future generations. It fosters a deep respect for the wisdom and teachings of those who've come before, enriching the collective consciousness and shaping the values and traditions of the community.
Thus, spiritual and ancestral connections are interwoven into the fabric of Aboriginal family life, providing a sense of continuity, belonging, and purpose.
Contemporary Interpretations
In contemporary Aboriginal communities, the concept of family continues to evolve and adapt to the changing social and cultural landscapes, reflecting the resilience and dynamism of Aboriginal kinship structures. Modern perspectives on family within Aboriginal communities recognize the importance of maintaining traditional connections while also embracing contemporary societal changes.
Cultural evolution has led to a reimagining of family that encompasses diverse family structures and relationships, acknowledging the fluidity and complexity of familial bonds in today's world.
- Recognition of diverse family structures: Contemporary Aboriginal perspectives on family acknowledge and embrace a wide range of family structures, including nuclear families, extended families, chosen families, and non-traditional familial relationships.
- Adaptation to societal changes: Aboriginal communities have shown resilience in adapting to societal changes, such as urbanization and globalization, while still preserving the core values and beliefs that underpin their understanding of family.
- Empowerment of future generations: Modern interpretations of family prioritize the empowerment and well-being of future generations, emphasizing the transmission of cultural knowledge and values to ensure the continuity of Aboriginal kinship structures.
These modern perspectives and cultural evolution demonstrate the ongoing vitality and relevance of Aboriginal understandings of family in contemporary society.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Has the Aboriginal Word for Family Evolved Over Time?
Over time, the evolution of terminology reflects the cultural influence on language. The shifts in meaning and usage often mirror the societal changes and values.
As a result, the aboriginal word for family has undergone significant changes, marking the transformations within the community and its understanding of kinship.
This evolution of terminology is a testament to the dynamic nature of language and its ability to adapt to the shifting cultural landscape.
Are There Variations of the Aboriginal Word for Family Based on Different Aboriginal Cultures?
Variations in language and cultural significance among different Aboriginal cultures have led to diverse words for family. Like branches on a tree, these variations reflect the richness and complexity of Aboriginal languages and traditions.
The significance of family in Aboriginal cultures is deeply rooted in connection and kinship, with each variation of the word for family carrying its own unique history and meaning.
How Do Aboriginal Communities Incorporate the Concept of Family Into Their Everyday Lives?
In Aboriginal communities, family values are deeply ingrained in cultural practices, fostering intergenerational bonding and community support. These values are upheld through storytelling, ceremonies, and shared responsibilities.
Elders play a crucial role in passing down traditions and wisdom, strengthening family ties and preserving cultural heritage. The concept of family extends beyond blood relations, encompassing a sense of belonging and mutual respect.
These practices promote resilience and unity within Aboriginal communities.
What Role Do Elders Play in Teaching the Importance of Family in Aboriginal Culture?
Elders' wisdom is integral in teaching family values within Aboriginal culture. Through intergenerational learning, elders pass down traditions and knowledge, preserving our cultural heritage.
Their guidance fosters a deep understanding of the importance of family, connecting us to our roots. This transmission of wisdom reinforces the significance of family bonds, ensuring that our traditions endure.
The elders' role in imparting these values is fundamental to the preservation of our cultural identity.
How Do Aboriginal Communities Address Challenges to Traditional Family Structures in Contemporary Society?
In contemporary society, challenges to traditional family structures in Aboriginal communities are addressed through a variety of support systems. These challenges include modern influences that may impact cultural preservation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the aboriginal word for family, with its deep cultural and spiritual significance, reflects the interconnectedness and interdependence of all members.
The extended kinship networks and ancestral connections underscore the importance of community and heritage.
This word captures the essence of familial bonds and the enduring values of love, support, and unity.
It serves as a timeless reminder of the rich cultural heritage and traditions of the aboriginal people.