When examining the native peoples who lived in Mexico, it is often assumed that there was only one dominant civilization. But the reality is much more complex and fascinating.
Mexico was home to a diverse array of indigenous groups, each with their own unique cultures, languages, and traditions. From the Olmecs, who are considered the earliest known civilization in Mesoamerica, to the Maya, who built advanced cities in the Yucatán Peninsula, the history of indigenous groups in Mexico is rich and multifaceted.
But what about the lesser-known groups like the Zapotecs, Mixtecs, and Tarahumara? These indigenous peoples have their own compelling stories that deserve our attention.
Key Takeaways
- Olmecs were the earliest known civilization in Mexico
- Maya civilization thrived in the Yucatán Peninsula and excelled in various fields such as architecture, art, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture
- Zapotecs built the city of Monte Albán and were known for impressive architecture, art, and urban planning
- Mixtecs were skilled artisans and traders, renowned for their intricate metalwork and textiles

Olmec Head Clay Statue, Ancient Mesoamerican Inspired Sculpture, Decorative Artifact Replica
AUTHENTIC OLMEC DESIGN: Hand-crafted clay statue featuring the iconic Olmec head design with distinctive facial features, carved headdress…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Olmecs: Earliest Known Civilization
The Olmecs were the earliest known civilization in Mesoamerica, laying the foundation for the complex societies that followed. They flourished from around 1400 BCE to 400 BCE in what's now present-day Mexico. The Olmecs are renowned for their monumental architecture, particularly their large stone heads, and ancient artifacts, including intricate jade carvings and pottery. Their most famous legacy is the colossal basalt heads, which are believed to depict rulers or deities and showcase the Olmec's remarkable sculptural skills and cultural sophistication.
The ancient artifacts of the Olmecs provide valuable insights into their religious beliefs, social structure, and artistic achievements. These artifacts, such as the jade masks and figurines, reflect the Olmec's advanced craftsmanship and their use of symbolic imagery in their cultural and religious practices. Furthermore, the Olmecs' monumental architecture, including their ceremonial centers and colossal stone heads, indicate a highly organized society capable of monumental construction and engineering feats.
Studying the Olmec civilization and their ancient artifacts not only sheds light on their own culture but also provides a crucial understanding of the cultural and technological advancements that laid the groundwork for subsequent Mesoamerican civilizations.

LQPFBSM El Castillo Pyramid Building Blocks Sets Mexico Architecture Building Block Toys for Adults and Kids Mayan Pyramid Model Gift for Boys and Girls 1346+PCS
Pyramid Building Model:This building set precisely reproduces El Castillo Pyramid, the iconic Maya masterpiece at Chichén Itzá, featuring…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Maya: Advanced Civilization in the Yucatán Peninsula
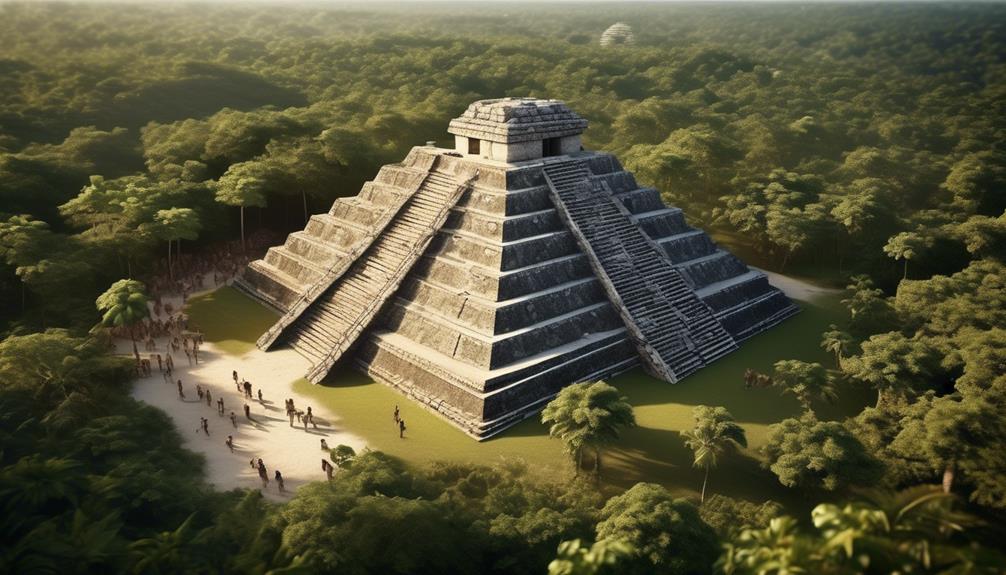

Arriving in the Yucatán Peninsula, we find the Maya civilization, known for its advanced cultural and technological achievements. The Maya excelled in various fields, including architecture, art, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture, making them one of the most sophisticated pre-Columbian civilizations. Their architectural marvels, such as the iconic stepped pyramids, palaces, and temples, reflect a deep understanding of mathematics and celestial alignments. The city of Chichen Itza, with its renowned pyramid known as El Castillo, is a testament to the Maya's architectural prowess and their complex understanding of astronomy.
The Yucatán culture, shaped by the Maya civilization, was rich and diverse. The Maya developed a sophisticated writing system, hieroglyphic inscriptions, and codices that provided insights into their history, rituals, and astronomical knowledge. Their agricultural techniques, including the use of terracing and irrigation systems, allowed for sustainable food production to support their growing population. The Maya's intricate understanding of the cosmos is evident in the layout of their cities and the precise orientation of their structures to celestial events, demonstrating their advanced knowledge of astronomy and mathematics.
The enduring legacy of the Maya in the Yucatán Peninsula continues to fascinate and inspire modern-day researchers and enthusiasts.

Ancient Greek Bronze Museum Statue Replica of Pegasus (176)
Ancient Greek Bronze Museum Statue Replica Of Pegasus
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Zapotecs: Builders of Monte Albán
Shaping the cultural landscape of ancient Mesoamerica, the Zapotecs, known for their remarkable achievements in architecture, art, and urban planning, established the impressive city of Monte Albán. This ancient civilization, flourishing from 500 BCE to 750 CE, left a lasting legacy as master builders and urban planners.
Their architectural prowess is evident in the construction of grand pyramids, intricate tombs, and expansive plazas, showcasing their advanced understanding of engineering and design. The Zapotecs' utilization of the landscape and topography in the layout of Monte Albán highlights their sophisticated urban planning skills. Their ability to harmoniously blend the city with its natural surroundings is a testament to their ingenuity as ancient architects.
Furthermore, the Zapotecs' artistic contributions to Mesoamerican culture are exemplified through their intricate carvings, pottery, and jewelry, reflecting their rich artistic traditions. Their mastery in creating elaborate works of art further solidifies their position as influential cultural innovators.
The enduring impact of the Zapotecs as the builders of Monte Albán is a testament to their significant role in shaping the cultural and architectural heritage of ancient Mesoamerica.

Across The Puddle, Historical Jewelry Collection, 24k Gold Plated Pre-Columbian Aztec Solar Calendar Earrings
HISTORICAL JEWELRY COLLECTION. Our Pre-Columbian Collection draws inspiration from the goldwork created by Pre-Hispanic Cultures. It is based…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Mixtecs: Skilled Artisans and Traders

Mixtecs demonstrate exceptional skill in craftsmanship and trade within ancient Mesoamerica, leaving a profound influence on the cultural and economic landscape of the region. Renowned for their intricate metalwork and textiles, the Mixtecs were highly skilled artisans, producing elaborate jewelry, ornaments, and finely woven textiles.
Their mastery of metallurgy enabled them to create intricate gold and copper ornaments, showcasing their advanced craftsmanship. Additionally, the Mixtecs were active participants in ancient trade routes and commerce, utilizing their expertise in crafting and trading to establish strong economic networks throughout Mesoamerica.
Their valuable goods, including fine ceramics and exquisite feathers, were highly sought after, leading to their involvement in extensive trade relationships with neighboring regions, further enhancing their influence and prosperity.
The Mixtecs' ability to produce exceptional goods and their active involvement in trade not only contributed to their own thriving economy but also played a significant role in the broader economic dynamics of ancient Mesoamerica.
Tarahumara: Indigenous People of the Sierra Madre
Nestled within the rugged terrain of the Sierra Madre, the Tarahumara people have long inhabited this picturesque region, maintaining a unique cultural heritage and traditional way of life. The Tarahumara, also known as the Rarámuri, are renowned for their long-distance running ability, a tradition that has been passed down through generations. Their resilience and connection to the land are evident in their sustainable agricultural practices, which have sustained them in the challenging mountainous environment. The Tarahumara's traditional dwellings, known as "cave houses," are built into the cliffs of the Sierra Madre, showcasing their ingenuity and adaptation to the natural surroundings. Additionally, their vibrant crafts, such as intricately woven baskets and colorful textiles, reflect their rich artistic traditions.
| Tarahumara Traditions | Sierra Madre Culture |
|---|---|
| Long-distance running | Sustainable agriculture |
| Cave houses | Artistic traditions |
| Intricately woven baskets | |
| Colorful textiles |
The Tarahumara's deep connection to their heritage and environment makes them an integral part of the rich tapestry of Indigenous cultures in Mexico.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Olmecs and Their Society?
We've found that there are several common misconceptions about the Olmec society, leading to a misunderstood portrayal.
Some of these misconceptions include the belief that the Olmecs were a homogeneous society, when in fact they were diverse and composed of various social groups.
Additionally, there's a misconception that the Olmecs were solely focused on monumental architecture, neglecting their rich cultural and artistic expressions.
Understanding these misconceptions is crucial in gaining a comprehensive view of Olmec society.
How Did the Maya Civilization Impact the Development of Other Indigenous Groups in Mexico?
The Maya civilization had a significant impact on the development of other indigenous groups in Mexico. Their influence can be seen in the architecture, art, and complex social structures of subsequent societies.
The interactions between the Maya and other indigenous groups fostered the exchange of knowledge, technology, and cultural practices, contributing to the rich and diverse heritage of Mexico's indigenous peoples.
This dynamic interplay shaped the development of various groups and their unique contributions to Mexican history.
What Are Some Lesser-Known Achievements of the Zapotecs at Monte Albán?
At Monte Albán, the Zapotecs achieved remarkable advancements in architecture, art, and astronomy.
Their intricate stonework, including the famous carved stone slabs, displayed their skill and craftsmanship.
Additionally, their understanding of celestial bodies is evident in the alignment of their structures with astronomical events.
These achievements not only showcased the Zapotecs' ingenuity but also contributed to the cultural and scientific legacy of indigenous groups in Mexico.
How Did the Mixtecs Contribute to Trade and Commerce in Ancient Mexico?
Contributing to trade and commerce in ancient Mexico, the Mixtecs established extensive networks and excelled in craftsmanship. Their intricate gold, silver, and turquoise jewelry adorned elites across Mesoamerica, enhancing their prestige.
Mixtec trade routes extended across the region, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas. Their artisanal skills and entrepreneurial spirit played a pivotal role in the economic and cultural development of ancient Mexico.
What Are Some Unique Cultural Practices and Traditions of the Tarahumara People in the Sierra Madre?
The Tarahumara people in the Sierra Madre have unique cultural practices and traditional beliefs that have been preserved for generations. Their deep connection to nature is reflected in their spiritual ceremonies and traditional dances.
The use of long-distance running for hunting and religious purposes is also a distinctive aspect of their culture.
These traditions provide insight into the rich and complex heritage of the Tarahumara people in the rugged terrain of the Sierra Madre.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it's fascinating to think about the rich history and contributions of indigenous groups in Mexico. From the Olmecs to the Maya, the Zapotecs to the Mixtecs, each group left a lasting impact on the region.
It's ironic that despite their advanced civilizations, many of these indigenous groups faced oppression and marginalization. As we reflect on their history, it's important to recognize and honor the resilience and cultural legacy of these communities.