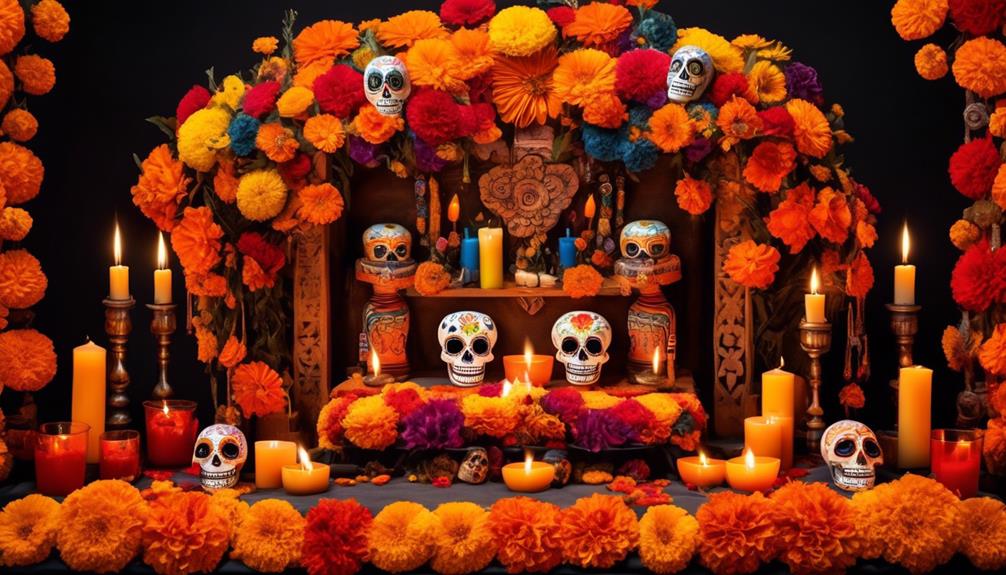
While strolling through the bustling streets of Mexico during the festive Day of the Dead celebration, we are enveloped in a mesmerizing blend of Spanish and indigenous traditions that unite to honor the departed.
This unique fusion of beliefs and customs creates a rich tapestry of cultural significance and symbolism. But how exactly do these two distinct influences come together to shape this deeply meaningful commemoration?
Join us as we unravel the intricate layers of El Día De Los Muertos and discover the fascinating interplay between Spanish Catholicism and Mesoamerican rituals that have shaped this beloved tradition.
Key Takeaways
- El Día de los Muertos combines pre-Columbian indigenous traditions and Spanish customs, resulting in a unique cultural fusion.
- Spanish Catholicism heavily influenced the celebration, with the integration of Catholic practices and beliefs into indigenous rituals.
- Mesoamerican rituals and beliefs, such as honoring and communicating with deceased ancestors, form a fundamental part of El Día de los Muertos.
- Symbolism and traditions, such as the creation of ofrendas and sugar skulls, are used to honor and remember the deceased during the celebration.

Dia De Los Muertos Decorations, Ofrenda Decorations for Altar, 2Pcs Papel Picado, Linen Mexican Table Runner, 50Pcs Marigold Garland for Day of The Dead
What you will get – 1Pcs Linen Mexican Table Runner, 2Pcs Papel Picado, 50Pcs Marigold Flowers with stem
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Origins of El Día De Los Muertos
The origins of El Día De Los Muertos can be traced back to pre-Columbian indigenous traditions and beliefs, which were later combined with Spanish customs and practices. The influence of colonization and the cultural fusion that occurred during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire played a significant role in shaping the traditions and rituals associated with El Día De Los Muertos.
When the Spanish arrived in the 16th century, they encountered the indigenous people's rituals honoring the dead. Rather than eradicating these customs, the Spanish sought to integrate them into their own traditions, leading to the fusion of indigenous beliefs with Catholicism.
This cultural fusion gave rise to the modern celebration of El Día De Los Muertos, blending elements of indigenous Aztec traditions with Catholicism. The holiday's practices, such as creating ofrendas (altars) and offering marigolds and favorite foods of the deceased, reflect this blending of cultures.
The result is a unique and vibrant celebration that honors the memories of loved ones who've passed away, showcasing the rich tapestry of Mexican heritage and history.

Dia De Los Muertos Table Runner Cinco de Mayo Rustic Linen Mexican Sugar Skull Day of The Dead Altar Decoration for Home Kitchen Dining Room (13" x 72")
Material: 100% linen fabric, no shrink, no fading.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Influence of Spanish Catholicism

In combining Spanish and indigenous beliefs for El Día De Los Muertos, we integrated Catholic practices with the rituals of honoring the dead that were already present in the indigenous traditions. The influence of Spanish Catholicism on this tradition is profound.
When the Spanish conquistadors arrived in the Americas, they brought with them their own religious beliefs and customs. The Spanish influence on El Día De Los Muertos is evident in the way it merged with the indigenous traditions to create a unique cultural and religious syncretism. One prominent example is the timing of the celebration, which aligns with the Catholic All Saints' Day and All Souls' Day. This demonstrates the integration of indigenous beliefs with Catholic traditions.
Furthermore, the use of altars, candles, and incense in El Día De Los Muertos mirrors practices found in Catholicism. The concept of praying for the souls of the departed also reflects a clear influence of Spanish Catholicism. These elements highlight the religious syncretism that took place, blending Spanish and indigenous beliefs to form the rich tapestry of traditions observed during this commemoration.

Hananona 50 Pcs Marigold Flower Heads Bulk, Silk Marigolds with Stems Artificial Mexican Flowers for Diwali Day of The Dead Dia De Los Muertos Ofrenda Decor
ARTIFICIAL MARIGOLD: These artificial marigold flowers bring you the feeling of fresh and elegant, they are beautiful and…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Mesoamerican Rituals and Beliefs
Drawing from our indigenous heritage, Mesoamerican rituals and beliefs play a significant role in shaping the traditions and practices associated with El Día De Los Muertos. Mesoamerican practices, deeply rooted in ancient civilizations such as the Aztec, Maya, and Zapotec, contribute to the spiritual connection that's central to this celebration.
One of the most prominent Mesoamerican beliefs integrated into El Día De Los Muertos is the concept of honoring and communicating with deceased ancestors. This is reflected in the construction of altars adorned with offerings like marigolds, favorite foods, and mementos of the departed.
Additionally, the use of copal incense during the festivities is a direct link to Mesoamerican rituals, where it was burned as an offering to the gods. The symbolism of death as a natural part of the cycle of life, prevalent in Mesoamerican cosmology, also permeates the observance of El Día De Los Muertos.
The fusion of Spanish and indigenous beliefs in this celebration has created a unique tapestry of traditions that beautifully encapsulates the cultural richness of Mexico.
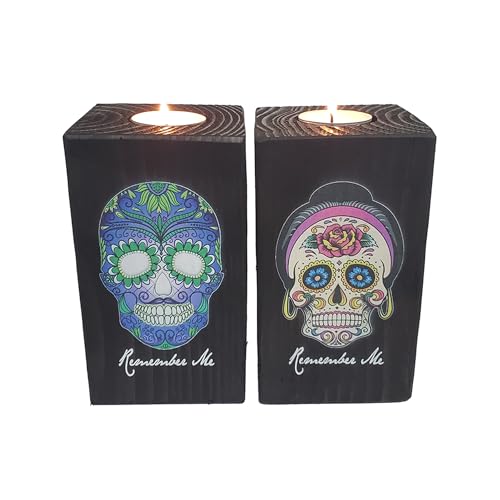

Remember Me Celebration Candle Holders for Day of The Dead Set of Two Blue with Green Skull and Pink Rose Skull – Dia De Los Muertos – Printed in Full Color, 6 Inches Tall
Set of two Remember Me Candle Holders for Day of the Dead (Dia De Los Muertos)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Symbolism and Traditions

Rooted in our indigenous heritage, Mesoamerican rituals and beliefs deeply influence the symbolism and traditions of El Día De Los Muertos. One of the most prominent traditions is the creation of symbolic offerings, or ofrendas, that honor the deceased and strengthen the ancestral connection.
These ofrendas typically include items such as marigolds, known as the 'flower of the dead,' which are believed to guide the spirits back to the living world. Additionally, families often place the favorite foods and drinks of their departed loved ones on the ofrendas, as well as personal belongings or photos. These offerings are meant to provide comfort and sustenance to the spirits during their visit.
Another significant tradition is the creation of intricately crafted sugar skulls, which serve as a reminder of the cycle of life and death. These skulls are often adorned with the names of the deceased and are displayed as a way to honor and remember them.
Evolution of Modern Celebrations
Reflecting the influence of globalization and cultural exchange, the modern celebrations of El Día De Los Muertos have evolved to encompass a blend of traditional customs and contemporary elements. This evolution has led to a cultural fusion, where modern practices intertwine with age-old traditions.
Cross cultural influences have played a significant role in shaping contemporary expressions of this revered holiday. One notable change is the incorporation of technology, with social media platforms being used to share artistic renditions of altars and calaveras. Additionally, the commercialization of the festival has led to an increase in themed merchandise and products that cater to the modern celebrants.
While some may argue that these changes dilute the authenticity of the celebration, they also serve as a means of preserving and spreading awareness of this rich tradition to a global audience. The evolution of modern celebrations has thus demonstrated the adaptability and resilience of El Día De Los Muertos, showcasing how it continues to thrive and evolve in a rapidly changing world.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Modern Celebrations of El Día De Los Muertos Differ From Traditional Mesoamerican Rituals and Beliefs?
Modern celebrations of El Día de los Muertos differ from traditional Mesoamerican rituals and beliefs through cultural fusion.
Contemporary practices incorporate elements from Spanish colonization, such as the use of marigolds and sugar skulls.
Indigenous customs, like building ofrendas and honoring ancestors, remain central.
This blending reflects the evolving nature of the holiday, embracing both historical roots and present-day influences to create a rich and vibrant tradition.
Are There Any Regional Variations in How El Día De Los Muertos Is Celebrated, and How Do These Variations Reflect Spanish and Indigenous Influences?
In terms of regional variations, we've found that El Día de los Muertos celebrations differ across Mexico and even within specific communities. These variations reflect the cultural fusion of indigenous traditions and Spanish influence.
For instance, in the Yucatán Peninsula, there's a strong Mayan influence, while in the Lake Pátzcuaro region, pre-Hispanic traditions are prominent. These regional differences highlight the rich tapestry of El Día de los Muertos and the blending of Spanish and indigenous beliefs.
What Role Do Food and Offerings Play in El Día De Los Muertos, and How Has This Tradition Evolved Over Time?
We've witnessed an evolution of offerings and modern food traditions during El Día de los Muertos.
The role of food and offerings has transformed over time, blending Spanish and indigenous influences. Traditional offerings like pan de muerto and sugar skulls now accompany modern favorites such as favorite foods and drinks of the departed.
This evolution reflects a harmonious fusion of Spanish and indigenous beliefs, creating a rich and diverse celebration of remembrance.
How Has the Commercialization of El Día De Los Muertos Impacted the Authenticity and Meaning of the Celebration?
We've witnessed a transformation of El Día de los Muertos due to the impact of consumerism and cultural commodification. The soul of this tradition, once deeply rooted in honoring ancestors, now contends with commercial interests.
It's akin to a vibrant garden overrun by weeds, as the essence of our celebration risks being overshadowed by materialism. The struggle lies in preserving the authenticity and meaning of a sacred commemoration amidst modern commercial pressures.
Are There Any Controversies or Debates Surrounding the Appropriation or Misrepresentation of El Día De Los Muertos in Popular Culture?
We've encountered appropriation debates and misrepresentation controversies surrounding El Día de los Muertos in popular culture. These discussions often revolve around the commercialization and commodification of this sacred tradition.
Many argue that the true meaning and significance of the celebration are being diluted or misrepresented for profit. It's essential to recognize and address these concerns to ensure that the authenticity and cultural significance of El Día de los Muertos are preserved and respected.
Conclusion
In conclusion, El Día de los Muertos beautifully blends Spanish and indigenous beliefs, creating a rich tapestry of tradition and symbolism.
Like two sides of the same coin, these cultural influences have come together to form a celebration that's both deeply rooted in history and ever-evolving.
As they say, 'two heads are better than one,' and the fusion of these beliefs has created a unique and vibrant celebration of life and remembrance.