When thinking about the indigenous communities in Ecuador, one cannot overlook the significant cultural heritage that has influenced the country for generations. Have you ever pondered on the primary regions where the indigenous population in Ecuador mainly lives?
It's a question that may seem straightforward, but the answer is far more complex than one might expect. From the highlands to the Amazon rainforest and even within urban centers, the indigenous communities of Ecuador have carved out unique spaces that reflect their traditions and way of life.
But where exactly do most of them call home? Let's explore the diverse landscapes and settlements that serve as the backdrop for Ecuador's indigenous population.
Key Takeaways
- Ecuador's Indigenous population is diverse, comprising various cultures, traditions, and languages.
- Highland Indigenous communities practice terraced farming, weaving, and celebrate colorful festivals blending pre-Columbian rituals and Catholic traditions.
- Amazon Rainforest Indigenous groups have a vibrant cultural heritage rooted in their ancestral connection to the natural world, practicing sustainable livelihoods and facing challenges from extractive industries and deforestation.
- Coastal Indigenous settlements rely on fishing, agriculture, and trade, preserving cultural heritage through art, music, dance, and oral traditions, while facing challenges from modernization and environmental changes.
Overview of Ecuador's Indigenous Population
The Indigenous population of Ecuador comprises a rich tapestry of cultures, traditions, and languages, each contributing to the vibrant mosaic of the country's social fabric. Indigenous cultures in Ecuador are incredibly diverse, with each group maintaining its unique traditional practices, languages, and customs.
These cultures have a deep-rooted connection to the land, and the preservation of their language and ancestral territories is of utmost importance to them. In recent years, there's been a significant push for the recognition of Indigenous land rights, as many communities have faced threats from industrial development and resource extraction.
Additionally, the quest for political representation has been a focal point for Indigenous groups in Ecuador, as they seek to have their voices heard in the national decision-making process. The government has taken steps to support these efforts, with the inclusion of Indigenous representatives in political institutions.
Despite the challenges they've faced, Ecuador's Indigenous population continues to strive for the preservation of their rich cultural heritage and the protection of their rights.
Highland Indigenous Communities
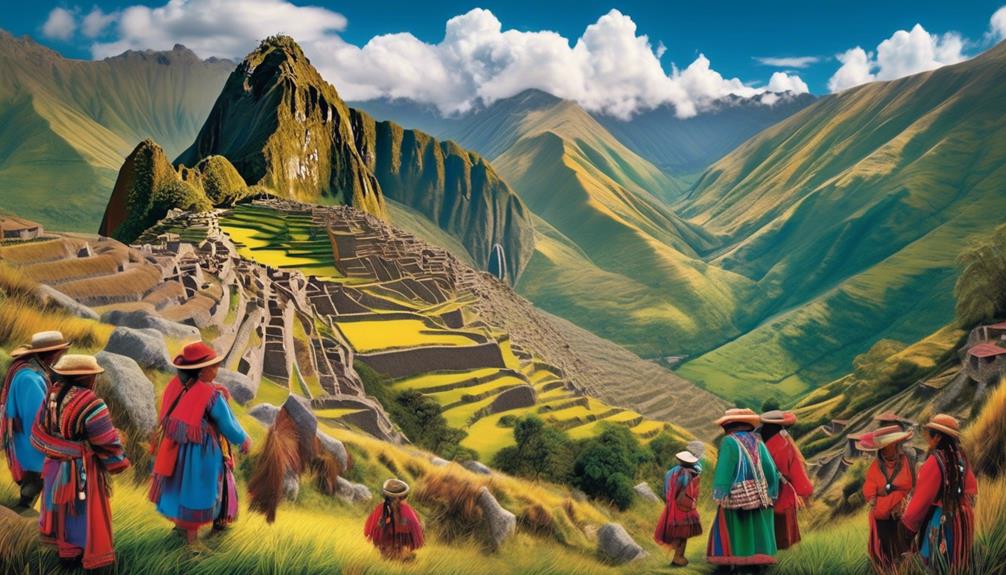

Nestled amidst the majestic Andes, the highland Indigenous communities of Ecuador thrive in a landscape that has shaped their traditions, customs, and way of life for centuries. These communities are rich in Andean traditions, with a deep connection to the land and a profound respect for nature.
The following aspects provide a glimpse into the unique culture and lifestyle of these highland Indigenous communities:
- Terraced Farming: The highland Indigenous communities are renowned for their intricate terraced farming systems, allowing them to cultivate crops such as quinoa, potatoes, and maize on steep mountain slopes.
- Traditional Textiles: The art of weaving is integral to the cultural identity of these communities, with vibrant textiles reflecting their history, beliefs, and daily life.
- Community Festivals: Highland Indigenous communities celebrate a myriad of colorful festivals, blending pre-Columbian rituals with Catholic traditions, showcasing their deep spiritual connection and festive spirit.
- Herbal Medicine Practices: These communities have a profound knowledge of natural remedies, utilizing native plants and herbs for healing, a practice deeply rooted in their cultural heritage.
Highland agriculture and the preservation of Andean traditions are fundamental to the identity of these Indigenous communities, fostering a harmonious relationship with the breathtaking mountain environment they call home.
Amazon Rainforest Indigenous Groups
Amidst the lush expanse of the Amazon rainforest, the Indigenous groups of Ecuador maintain a vibrant and diverse cultural heritage deeply rooted in their ancestral connection to the natural world. These communities, including the Waorani, Shuar, Achuar, and Sapara, have thrived in the Amazon for centuries, preserving their traditional ways of life and closely intertwining their existence with the rainforest.
Their sustainable livelihood practices, such as hunting, fishing, and agriculture, are harmonious with the delicate balance of the ecosystem, ensuring minimal impact on the environment.
Cultural preservation is at the core of their existence, with unique languages, belief systems, and rituals being passed down through generations. The intimate knowledge of the rainforest's medicinal plants and natural resources is an integral part of their cultural identity, contributing to their well-being and resilience in the face of modern challenges.
These Indigenous groups have faced increasing pressures from extractive industries and deforestation, threatening their traditional territories and ways of life. However, their strong sense of community and connection to the land continue to drive their efforts in safeguarding their cultural heritage and promoting sustainable practices, ensuring that future generations can continue to thrive in harmony with the Amazon rainforest.
Coastal Indigenous Settlements

Respecting the cultural diversity and historical significance of the coastal Indigenous settlements in Ecuador, we recognize their enduring connection to the maritime environment and the rich traditions that have shaped their way of life.
- Coastal Indigenous Economy: The coastal Indigenous communities in Ecuador have traditionally relied on fishing, agriculture, and trade as the mainstays of their economy. The abundance of marine resources has been crucial to sustaining their livelihoods for generations.
- Cultural Preservation in Coastal Communities: These settlements have preserved their cultural heritage through vibrant art, music, dance, and oral traditions. The distinct craftsmanship of their traditional clothing and intricate jewelry reflects their deep-rooted cultural identity.
- Maritime Lifestyle: The coastal Indigenous people maintain a close relationship with the ocean, utilizing traditional fishing techniques and maritime skills that have been passed down through centuries.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While these communities face challenges from modernization and environmental changes, there are ongoing efforts to promote sustainable development and preserve their unique way of life.
The coastal Indigenous settlements in Ecuador offer a captivating insight into a cultural tapestry woven through centuries of maritime heritage, economic resilience, and the preservation of rich traditions.
Urban Indigenous Presence
The urban landscape of Ecuador is increasingly marked by the growing presence of Indigenous communities, reflecting the dynamic intersection of traditional heritage and modern urban life.
Urban migration has led to significant cultural assimilation, with Indigenous people adapting to city living while striving to preserve their cultural identity.
Quito, the capital, is home to a large urban Indigenous population, particularly in neighborhoods like La Mariscal and La Floresta. These areas showcase a blend of traditional Indigenous practices and modern urban amenities, such as Indigenous-owned shops selling artisanal crafts and traditional foods alongside trendy cafes and boutiques.
Similarly, in Guayaquil, the largest city in Ecuador, there's a noticeable urban Indigenous presence, with communities maintaining their cultural traditions through events like the Inti Raymi festival.
The influx of Indigenous people into urban areas has also led to the establishment of cultural centers and organizations aiming to support and promote Indigenous heritage within the urban landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Traditional Customs and Practices of Indigenous Communities in Ecuador?
Traditional ceremonies and spiritual beliefs are integral to indigenous communities in Ecuador. These customs vary among different groups, such as the Kichwa, Shuar, and Waorani. Traditional ceremonies, like Inti Raymi, honor the sun god, and Pawkar Raymi celebrate the harvest.
Indigenous crafts play a vital role in cultural preservation. Indigenous crafts, such as weaving and pottery, are essential for passing down cultural knowledge. These customs are central to our identity and heritage.
How Do Indigenous Communities in Ecuador Access Healthcare and Education?
Accessing healthcare is a significant challenge for indigenous communities in Ecuador due to geographical barriers and limited resources. Many lack proper facilities and face language barriers when seeking medical help.
In terms of education, remote locations and lack of infrastructure make it difficult for indigenous children to attend school regularly.
These challenges require innovative solutions and government support to ensure that indigenous communities have equal access to healthcare and education.
What Are the Main Economic Activities of Indigenous People in Ecuador?
Main agricultural activities of indigenous people in Ecuador revolve around farming, particularly of crops like maize, potatoes, and quinoa.
Additionally, artisanal crafts such as weaving and pottery play a significant role in their economic activities.
These traditions have been passed down through generations and continue to be important sources of income for indigenous communities.
The economic activities reflect their strong cultural ties and connection to the land.
How Do Indigenous Communities in Ecuador Address Environmental Conservation and Protection?
In Ecuador, indigenous communities actively engage in environmental conservation and protection. They implement sustainable living practices, such as reforestation and organic farming, to preserve their ancestral lands.
Community engagement is crucial, as they work together to safeguard natural resources. An interesting statistic is that over 90% of indigenous people in Ecuador live in the Andean and Amazon regions, where they play a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance through their conservation efforts.
What Role Do Indigenous Languages Play in Everyday Life and Communication Within These Communities?
Indigenous languages play a crucial role in everyday life within these communities. Their importance goes beyond communication; they're integral to preserving cultural heritage and traditions.
Language is a key tool for passing down knowledge and wisdom from generation to generation. Its preservation is essential for maintaining the unique identity and values of indigenous groups.
In our experience, language connects us to our roots and strengthens our community bond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the indigenous people of Ecuador are found in various regions across the country, including the highlands, Amazon rainforest, coastal areas, and urban centers.
Their rich cultural heritage and traditions are an integral part of Ecuador's diverse society.
As we continue to explore the unique ways of life of these indigenous communities, we're reminded of the interconnectedness of all people and the importance of preserving and celebrating cultural diversity.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.