The saying goes, “The past is a prelude,” and this holds true, particularly when considering the ancient indigenous populations of Peru.
When we think of Peru, many of us immediately conjure up images of the mighty Inca Empire, but there is so much more to the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures that have thrived in this region.
From the enigmatic Chavín civilization to the intricate artistry of the Moche culture, and the mysterious geoglyphs of the Nazca civilization, Peru is a treasure trove of ancient history.
But what about the other indigenous groups that have left their mark on this land? Well, the answer might surprise you.
Key Takeaways
- The Inca Empire was known for its advanced engineering, agricultural terraces, and iconic structures like Machu Picchu.
- The Chavín Civilization was recognized for its sophisticated temples with intricate stonework and complex ventilation systems in their architecture.
- The Moche Culture showcased impressive artistic expressions, advanced agricultural techniques, and a complex societal structure.
- The Nazca Civilization left a lasting legacy with their iconic geoglyphs known as the Nazca lines, fine craftsmanship in pottery, and stylized figures of humans, animals, and mythological beings.
The Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, known for its advanced engineering and impressive agricultural terraces, was a powerful and sophisticated civilization that thrived in ancient Peru. The architectural marvels of the Incas, such as the iconic Machu Picchu, stand as a testament to their engineering feats.
The Incas were masters of agricultural innovation, utilizing a system of terraces and irrigation to cultivate crops at high altitudes where farming would otherwise be impossible. This intricate understanding of agriculture allowed them to sustain an empire that spanned over 2,500 miles along the Andes Mountains.
Moreover, the Inca road system, known as Qhapaq Ñan, was an engineering marvel that facilitated communication, trade, and the swift movement of troops across vast and varied terrain. This network of roads, built with precision and skill, connected the far reaches of the empire, allowing for efficient travel and communication.
The Inca Empire's architectural and engineering prowess is a testament to their ingenuity and mastery of their environment. Their ability to construct magnificent structures and develop innovative agricultural techniques in challenging terrains speaks volumes about their advanced civilization and enduring legacy.
The Chavín Civilization

Thriving amidst the diverse landscapes of ancient Peru, the Chavín civilization left a lasting impact on the region's cultural and religious developments, building upon the engineering and agricultural achievements of the Inca Empire. The Chavín people are renowned for their sophisticated architecture and religious practices. Their temples, such as the Chavín de Huántar, were constructed with intricate stonework and complex ventilation systems, showcasing their architectural prowess. These temples served as ceremonial centers where religious rituals and gatherings took place, reflecting the significance of spirituality in Chavín society.
The Chavín civilization also wielded substantial influence in the realm of artistic achievements. Their intricate carvings, sculptures, and pottery were adorned with stylized motifs and symbols, depicting mythological creatures and deities. The most iconic of these is the Lanzón, a granite monolith featuring a fanged deity, which is a testament to the Chavín people's mastery of stone carving and their spiritual beliefs.
| Chavín Architecture | Religious Practices |
|---|---|
| – Sophisticated temples | – Ceremonial gatherings |
| – Intricate stonework | – Spiritual significance |
| – Complex ventilation | – Rituals and spirituality |
The enduring legacy of the Chavín civilization continues to fascinate scholars and enthusiasts alike, as their cultural and artistic contributions remain an integral part of Peru's rich heritage.
The Moche Culture
Amidst the diverse cultural landscape of ancient Peru, the Moche Culture emerged as a significant civilization, known for their impressive artistic expressions and advanced agricultural techniques. The Moche, also known as the Mochica, thrived on the north coast of Peru from about 100 to 700 CE. Their society was characterized by intricate social structures, advanced technology, and a rich religious tradition.
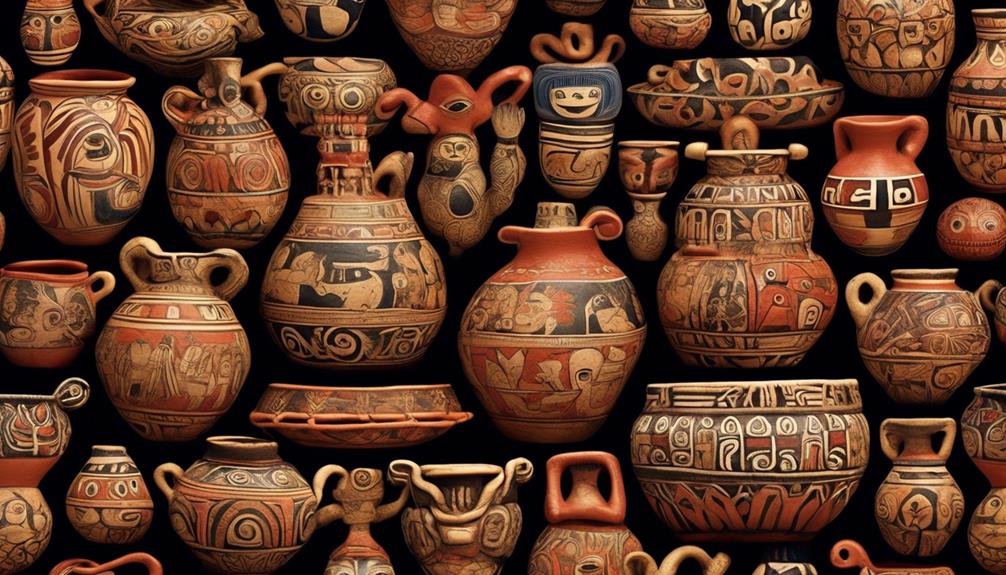
Moche art: The Moche people were accomplished artists, known for their detailed pottery, elaborate metalwork, and expressive murals. Their art often depicted scenes of everyday life, as well as rituals and ceremonies, providing invaluable insights into their culture and beliefs.
Moche pottery: Renowned for their ceramic work, the Moche created stunning pottery depicting a wide range of subjects, including animals, deities, and various aspects of daily life. These pottery pieces served both practical and ceremonial purposes, reflecting the Moche's skilled craftsmanship and artistic sophistication.
Moche technology: The Moche were adept at irrigation and engineering, allowing them to harness the arid coastal environment for agriculture. Their expertise in canal systems and agricultural practices enabled them to sustain a complex society with significant population centers.
The Moche culture's intricate artwork, advanced technology, and complex societal structure illustrate their significant contributions to ancient Peruvian civilization.
The Nazca Civilization

Emerging from the rich cultural tapestry of ancient Peru, the Nazca Civilization stands as a testament to the ingenuity and artistry of indigenous peoples in the region, known for their iconic geoglyphs and intricate pottery.
The most famous aspect of the Nazca civilization is the Nazca lines, a series of large ancient geoglyphs formed by depressions or shallow incisions made in the soil of the Nazca Desert. These geoglyphs, depicting a variety of creatures, plants, and shapes, are best viewed from the air, leading to much speculation about how the Nazca people were able to create such precise and massive designs.
The Nazca pottery is another remarkable aspect of their culture, characterized by its fine craftsmanship and distinct iconography featuring stylized figures of humans, animals, and mythological beings. The pottery often exhibits a rich variety of designs and vibrant colors, showcasing the artistic sophistication of the Nazca civilization.
Through their geoglyphs and pottery, the Nazca people left a lasting legacy that continues to captivate and intrigue people around the world.
Other Indigenous Groups
Numerous other indigenous groups in Peru have left a significant mark on the country's history and cultural heritage through their unique traditions, technological advancements, and artistic achievements.
These diverse groups have contributed to the rich tapestry of indigenous traditions and cultural practices in Peru. Some of the notable indigenous groups include:
- The Chachapoyas: Known for their intricate stone architecture, the Chachapoyas constructed massive fortresses and mausoleums in the cloud forests of the Andes. Their complex funerary practices, including the use of sarcophagi and elaborate burial sites, reflect their reverence for the afterlife.
- The Moche: Renowned for their advanced metalworking and pottery techniques, the Moche civilization produced exquisite artifacts that provide insights into their societal structure and religious beliefs. Their elaborate ceramic vessels depict scenes of everyday life, mythology, and ritualistic practices.
- The Chimu: Recognized for their engineering marvels, the Chimu people constructed elaborate irrigation systems and massive adobe complexes, such as the city of Chan Chan. Their expertise in hydraulic engineering enabled them to thrive in the arid coastal regions of northern Peru.
These indigenous groups, among others, have significantly shaped the cultural landscape of Peru through their distinctive traditions and practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Was the Daily Life Like for Ancient Indigenous People in Peru?
Daily routines of ancient indigenous people in Peru revolved around agricultural activities, such as cultivating maize, potatoes, and quinoa.
Cultural traditions included elaborate ceremonies to honor nature and their deities. These rituals often involved music, dance, and offerings.
The people's livelihood depended on their close connection to the land, and their daily lives were intricately woven with spiritual beliefs and practices.
This connection to the land and their spiritual beliefs shaped a rich and vibrant tapestry of indigenous culture in Peru.
How Did Ancient Indigenous People in Peru Interact With Their Environment and Natural Resources?
Interactions with nature were fundamental to ancient indigenous people in Peru. Resource utilization was deeply intertwined with their daily lives, shaping their culture and traditions.
The intricate knowledge of the environment allowed us to thrive, fostering sustainable practices and a deep respect for the land. Our interactions with nature weren't only a means of survival but also a reflection of our profound connection to the natural world.
What Were the Religious and Spiritual Beliefs of Ancient Indigenous People in Peru?
Religious rituals and spiritual practices were integral to the ancient indigenous people of Peru. Their beliefs were deeply intertwined with nature, leading to ceremonies and offerings to honor the land and its resources.
These rituals were central to their worldview, reflecting a harmonious relationship with the environment. The spiritual practices encompassed a reverence for sacred sites and a strong connection to the natural world, shaping their understanding of the cosmos and their place within it.
What Were the Social Structures and Hierarchies Within Ancient Indigenous Communities in Peru?
Social structures in ancient indigenous communities in Peru were complex, reflecting power dynamics and social hierarchies. Leadership roles were often hereditary, with chiefs or priests holding significant authority.
These societies valued religious practices and cultural traditions, which played a crucial role in shaping their social fabric. Individuals' roles were defined by their lineage and contributions to the community, creating a dynamic and interconnected social system.
How Did Ancient Indigenous People in Peru Contribute to the Development of Agriculture and Technology in the Region?
Innovations in agriculture and technological advancements by ancient indigenous people in Peru were pivotal in the region's development. Their mastery of irrigation systems, terracing, and crop diversification transformed the landscape, allowing for sustainable farming practices in challenging terrains.
Additionally, they developed sophisticated tools and techniques for metalworking, textiles, and pottery, showcasing their advanced technological prowess.
These contributions laid the foundation for the flourishing civilizations that thrived in Peru's diverse landscapes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ancient indigenous people of Peru, such as the Inca, Chavín, Moche, and Nazca, left behind a rich legacy of art, architecture, and cultural practices that continue to fascinate and inspire us today.
From the mysterious lines of the Nazca to the impressive stone structures of the Inca, these ancient civilizations have left an indelible mark on the history and culture of Peru, inviting us to explore and uncover the secrets of their remarkable achievements.