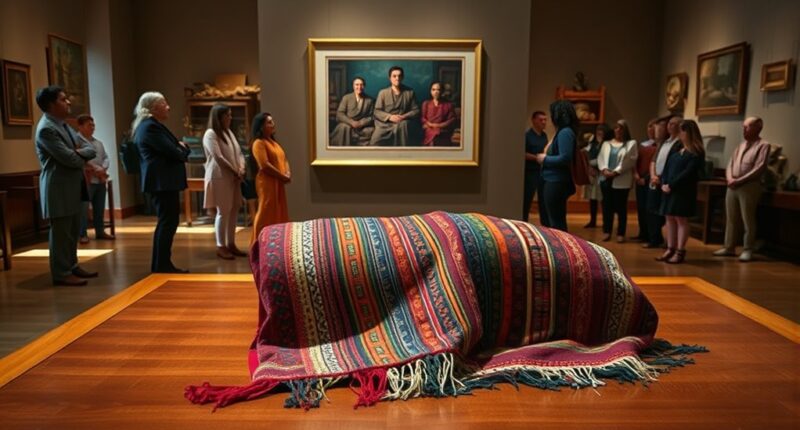
Museums are actively working to right past injustices by returning sacred remains and cultural artifacts to their original communities. This process helps restore cultural identity, honor spiritual practices, and acknowledge the wrongs of theft and exploitation. By collaborating with communities and adopting respectful procedures, museums aim to rebuild trust and respect cultural sovereignty. If you want to understand how these efforts are transforming museums into guardians of heritage, there’s more to explore.
Key Takeaways
- Museums are collaborating with communities to facilitate respectful repatriation of ancestors’ remains and cultural artifacts.
- They are adopting transparent policies to acknowledge past wrongs and ensure ethical, culturally sensitive processes.
- Repatriation helps restore cultural identity, spiritual practices, and ancestral connections for marginalized communities.
- Institutions recognize their moral obligation to rectify historical thefts and misappropriations through repatriation efforts.
- These actions promote justice, reconciliation, and cultural empowerment, reaffirming indigenous sovereignty and heritage.
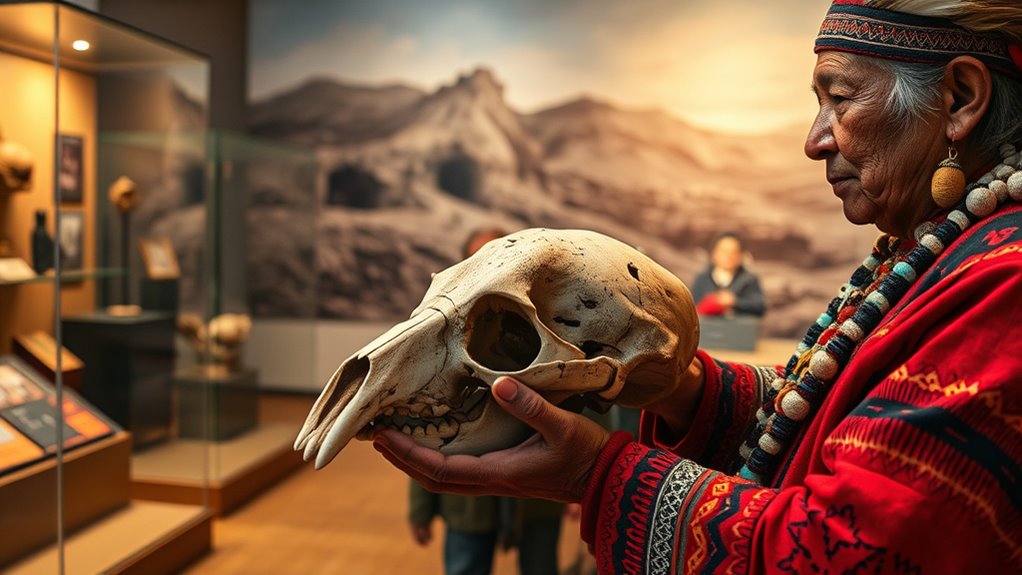

Repatriation of ancestors refers to the process of returning sacred remains, artifacts, or cultural items to their original communities or homelands. This act holds profound significance, not just as a matter of physical return, but as a step toward restoring cultural identity. When museums and institutions engage in repatriation, they acknowledge the importance of respecting the cultural heritage that was often taken without proper consent. You might see this as a way to address past wrongs, but more importantly, it’s about empowering communities to reconnect with their history and traditions. These efforts serve as a form of ethical restitution, recognizing that many objects in collections were acquired through colonial exploitation, theft, or misappropriation. By returning these items, museums help repair the damage inflicted on indigenous and marginalized communities, fostering a sense of justice and reconciliation.
As you explore this process, you realize that repatriation isn’t simply about physical objects. It’s about restoring a sense of ownership and dignity to communities whose cultural expressions and ancestors were disrupted or displaced. When sacred remains are returned, communities can perform traditional ceremonies, honor their ancestors, and preserve their spiritual practices. This reaffirmation of cultural identity is crucial, especially when historical traumas have threatened the continuity of indigenous customs. Museums, historically seen as custodians of knowledge and artifacts, are increasingly recognizing their role in rectifying historical injustices by collaborating with communities to ensure that repatriation aligns with their cultural values and needs. Additionally, proper repatriation processes help ensure that cultural heritage preservation is maintained and respected throughout the process.
Ethical restitution guides these efforts, emphasizing that the return of cultural items shouldn’t be seen as a favor but as a moral obligation. It’s about acknowledging the harm caused by past acquisitions and working to rectify it. Many institutions now have policies and protocols designed to facilitate respectful, transparent, and culturally sensitive repatriation processes. You can appreciate that this shift isn’t just administrative; it’s a profound moral stance that recognizes communities as rightful owners of their heritage. Repatriation fosters trust, rebuilds relationships, and helps heal wounds inflicted by centuries of cultural dispossession. Ultimately, it’s about more than objects—it’s about restoring the integrity of cultural identities and affirming the sovereignty of indigenous peoples and other communities whose histories have been marginalized or stolen.

Cultural Artifact Repatriation: Symbolic Diplomacy
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Museums Identify Which Artifacts Belong to Specific Communities?
You can find out which artifacts belong to specific communities through a combination of methods. Museums often use DNA analysis to match remains or items with ancestral groups. They also conduct community consultations, engaging with community members to guarantee cultural accuracy and respect. These approaches help museums accurately identify artifacts, fostering trust and ensuring that repatriation efforts honor the rightful communities.
What Legal Challenges Exist in Repatriating Cultural Artifacts?
You face legal challenges like maneuvering complex legal jurisdiction and complying with international treaties. These hurdles can delay or block repatriation efforts, as laws vary across countries and treaties may lack enforcement mechanisms. You must also address ownership disputes and cultural heritage laws, which complicate the process. Overcoming these legal obstacles requires careful negotiation, legal expertise, and international cooperation to guarantee that artifacts are returned ethically and legally.
How Do Museums Handle Disputes Over Ownership of Ancestral Remains?
When disputes over ancestral remains arise, museums prioritize cultural sensitivity and community consultation to address concerns respectfully. You’re encouraged to see how they actively engage with communities, listening to their perspectives and honoring their wishes. These institutions often establish collaborative agreements, ensuring that the handling and repatriation processes reflect cultural values. By fostering open dialogue, museums aim to resolve disputes ethically, promoting healing and mutual understanding.
What Ethical Considerations Guide Repatriation Decisions?
You face complex ethical dilemmas when making repatriation decisions, balancing respect for cultural sensitivities with legal and moral obligations. You consider the wishes of descendant communities, acknowledge historical injustices, and aim to honor cultural significance. It’s essential to approach these decisions with transparency, humility, and an understanding of the broader implications, ensuring that respect and dignity guide your actions to right past wrongs and foster trust.
How Do Repatriation Efforts Impact Museum Collections and Exhibitions?
You might find that about 90% of museums have increased their focus on cultural sensitivity and collection diversification due to repatriation efforts. These efforts can lead to more inclusive exhibits, showcasing a wider range of cultural narratives. Repatriation can temporarily reduce collections but ultimately enrich museum displays, fostering respect and understanding. You’ll notice that embracing these changes helps museums serve diverse communities better while preserving cultural heritage.
indigenous ancestral remains display
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
By embracing repatriation, you actively help correct historical injustices, restoring dignity to communities. Think of it like returning a lost scroll from the Library of Alexandria—bringing pieces of history home that were once thought lost forever. This act isn’t just about objects; it’s about healing wounds, fostering understanding, and rewriting the narrative. As museums open their doors to this new chapter, you become part of a movement that truly respects ancestors and their legacy.

Field Guide to Emergency Response: A Vital Tool for Cultural Institutions
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

Tikimaster Primitive Idol Artifact- 20 in – Ceremonial Primitive Art | #ksa902850
Ceremonial Artifact: Handcrafted Primitive Piece
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.