The Hopi tribe, an indigenous community rich in history, lives in a region of great cultural significance. To grasp the location of the Hopi tribe, it is essential to explore the unique landscape that has shaped their traditions and way of life.
Understanding the geographic context of the Hopi tribe provides valuable insight into the factors that have influenced their cultural practices and beliefs. This exploration will shed light on the enduring connection between the Hopi people and their ancestral homeland, offering a deeper understanding of their heritage and customs.
Key Takeaways
- The Hopi Tribe was located in the Southwestern United States, specifically in northeastern Arizona.
- The Hopi Tribe's villages were perched atop First, Second, and Third Mesas, which provided natural protection and held spiritual significance.
- The Hopi Tribe's location on mesas with fertile lands and a strategic defense position allowed for the development of sustained communities and distinct traditions.
- The arid climate in the region necessitated the development of sophisticated farming techniques, such as dry farming and intricate irrigation systems, which shaped the Hopi Tribe's traditions, diet, and social structure.

Native American Tribes: The History and Culture of the Hopi (Pueblo)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Origins of the Hopi Tribe
The origins of the Hopi Tribe can be traced back to ancient times, where their ancestors settled in the Southwestern United States. The Hopi people have a rich cultural heritage that's deeply rooted in their ancient settlements. Their traditions and way of life are closely tied to the land they've inhabited for centuries. The ancient Hopi settlements were strategically built on mesas, high above the desert floor, providing natural defense and fertile lands for agriculture. This allowed the Hopi to sustain their communities and develop distinct traditions that have been passed down through generations.
The origins of Hopi traditions are intertwined with their spiritual beliefs, agricultural practices, and communal lifestyle. The ancient Hopi settlements were designed to foster a sense of unity and cooperation among the tribe members. Each village had its own religious ceremonies, social structures, and responsibilities that contributed to the overall well-being of the tribe. The traditions established in these ancient settlements continue to shape the Hopi way of life today, emphasizing the importance of harmony with nature, community, and spirituality.

Eastern Print Native American Wall Art, Set Of 9 Pcs Unframed Posters, Native American Tribal Artwork, Indigenous Indian Pictures, America Indian Decor for Bedroom, Livingroom, UNFRAMED
💥UNFRAMED PRINTS💥: The preview images are examples of what the art prints will look like when framed: We…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
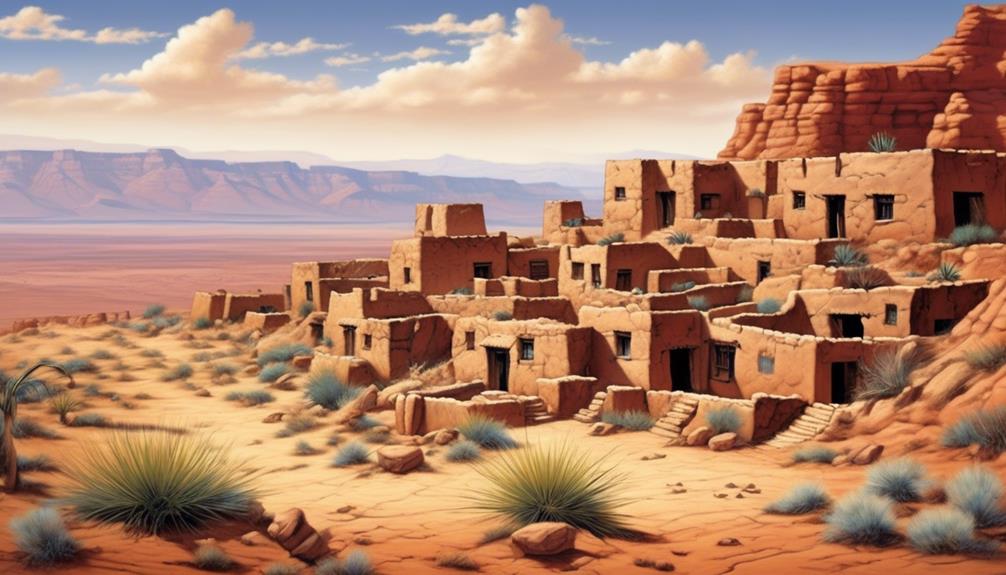
Geographic Location of the Hopi Tribe
Located in northeastern Arizona, the geographic location of the Hopi Tribe is characterized by its mesas and villages, which have been integral to their cultural heritage and way of life for centuries. The Hopi people have inhabited this region for over a millennium, and their villages are perched atop three mesas: First Mesa, Second Mesa, and Third Mesa. These mesas not only provide natural protection but also hold immense spiritual significance for the Hopi, shaping their traditions and ceremonies.
Hopi migration: The Hopi Tribe's migration to the present-day northeastern Arizona occurred around the 12th century, where they settled and established their villages on the mesas, maintaining a deep connection to the land and its resources.
Tribal boundaries: The Hopi Tribe's reservation covers approximately 2,531 square miles in northeastern Arizona, encompassing the villages atop the mesas and the surrounding lands. The boundaries of their reservation are defined by the Hopi Tribal Council and have evolved over time, reflecting the tribe's historical and cultural ties to the region.
The Hopi Tribe's geographic location hasn't only shaped their physical surroundings but also profoundly influenced their cultural practices, traditions, and spiritual beliefs.

Designs On Prehistoric Hopi Pottery (1919)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Landscape and Environment of Hopi Territory
Nestled within the northeastern Arizona landscape, the Hopi Tribe's territory boasts a unique and diverse environment that has played a pivotal role in shaping their cultural traditions and way of life for centuries. The landscape of the Hopi territory varies from high desert mesas to low-lying valleys, creating a rich tapestry of natural resources that have sustained the Hopi people for generations. This environment has not only influenced the tribe's agricultural practices but also served as the backdrop for their traditional ceremonies and rituals.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Hopi Agriculture | Reliant on dry farming techniques, utilizing terraced fields |
| and a unique irrigation system called "puddling" | |
| Traditional Ceremonies | Intricately linked to the agricultural calendar, with rituals |
| & Rituals | performed to ensure successful harvests and bountiful crops |
Hopi agriculture is deeply intertwined with the land, as the tribe practices dry farming using traditional terraced fields and a unique irrigation technique known as "puddling." The landscape also serves as the backdrop for the tribe's traditional ceremonies and rituals, which are intricately linked to the agricultural calendar and are performed to ensure successful harvests and bountiful crops.

ENSIANTH My Tribe Gift Celebrate Friendship Gift Find Your Tribe Love Them Hard Tribe Jewelry Tribal Bracelet Sorority Sister Gift (tribe s bra)
Tribe Bracelet – Find Your Tribe Love Them Hard. This simple and meaningful gift is a perfect best…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Influence of Location on Hopi Culture
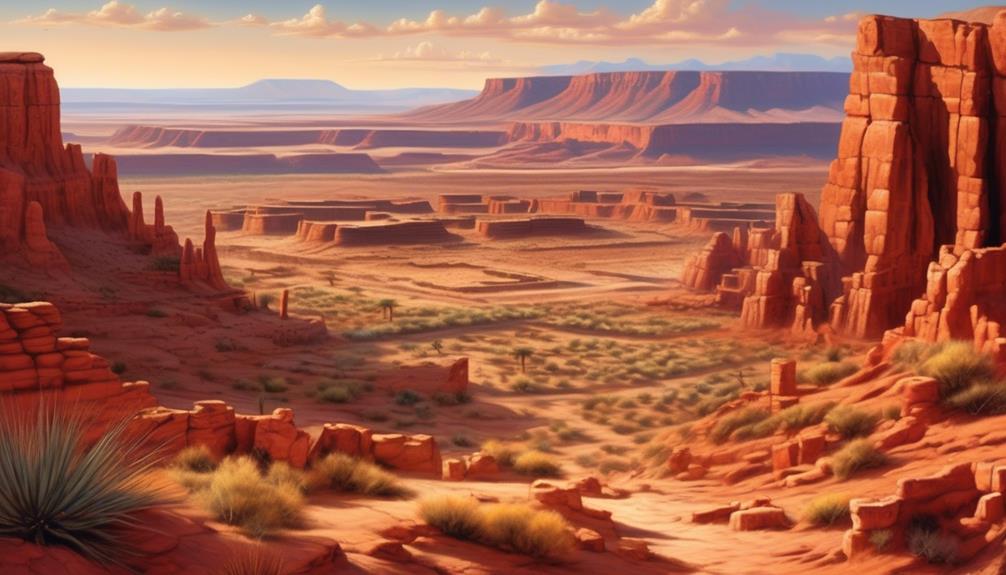

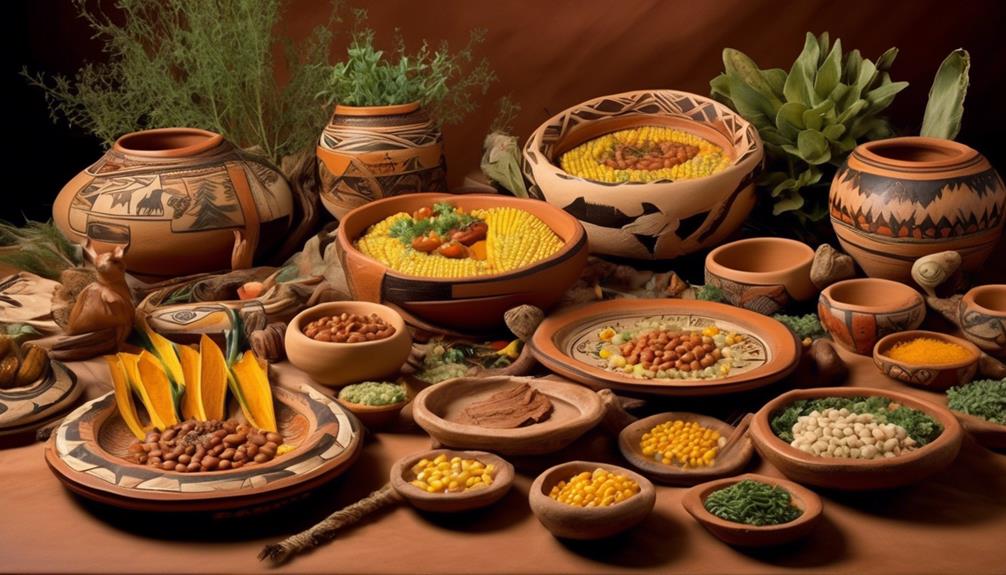
Perched atop a landscape of high desert mesas and low-lying valleys, the Hopi Tribe's cultural practices have been profoundly influenced by the natural resources and terrain of their territory. The impact of climate on the Hopi culture is significant, as the arid environment necessitated the development of sophisticated farming techniques, such as dry farming and the construction of intricate irrigation systems, to cultivate crops like corn, beans, and squash. Agriculture is deeply woven into the fabric of the Hopi way of life, shaping their traditions, diet, and social structure.
- Impact of Climate on Hopi Culture
- The arid climate necessitated the development of sophisticated farming techniques.
- Dry farming and intricate irrigation systems were crucial for cultivating crops.
- Agriculture is deeply woven into the fabric of the Hopi way of life.
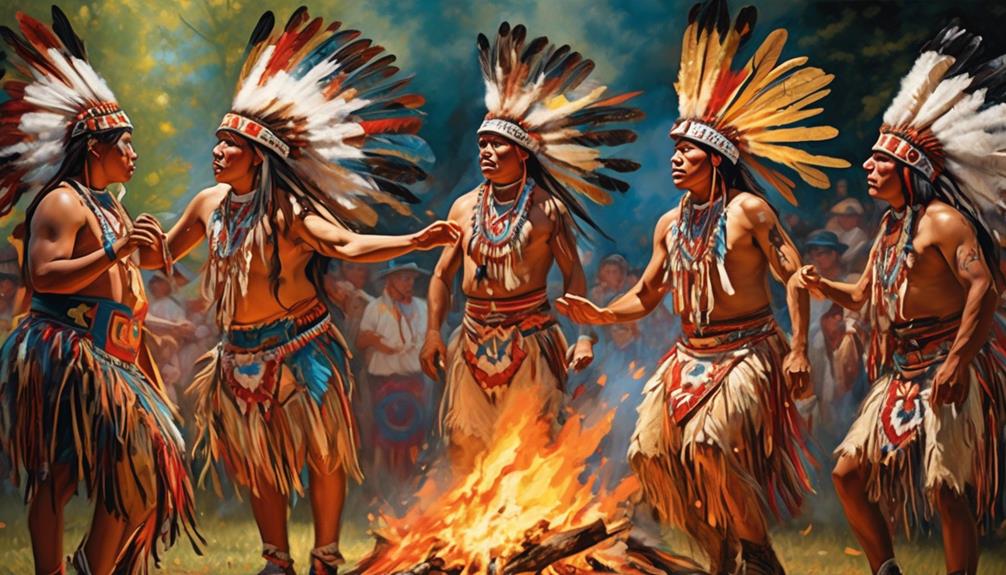
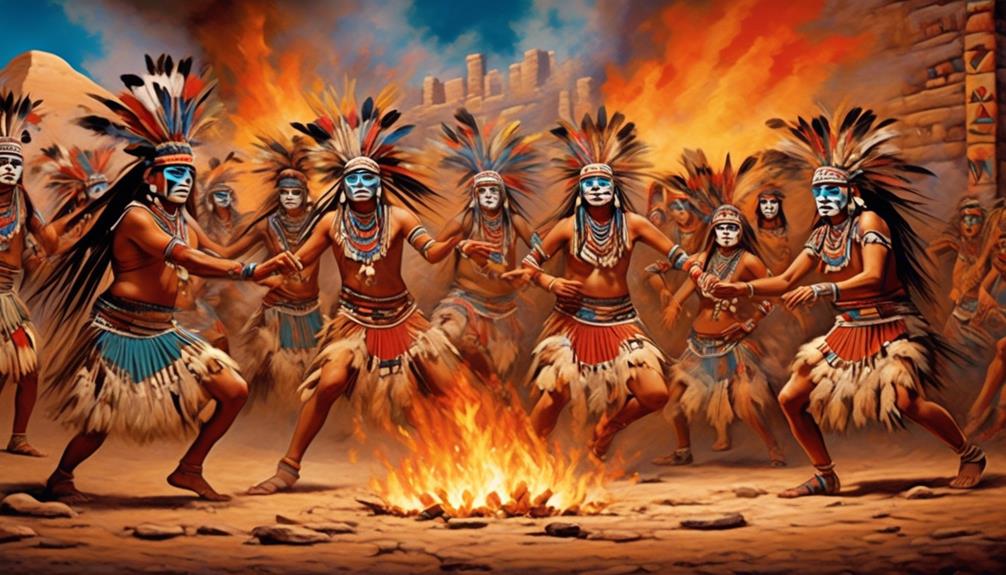
The traditional ceremonies of the Hopi tribe, deeply rooted in agriculture, reflect the tribe's spiritual connection to the land. These ceremonies, including the Hopi Snake Dance and the Powamu Festival, are integral to the tribe's spiritual practices and serve as expressions of gratitude for the land's bounty.
The spirituality of the Hopi tribe is intimately linked to their agricultural practices, and their reverence for the natural world is evident in their traditional ceremonies.
Contemporary Presence of the Hopi Tribe
The contemporary presence of the Hopi Tribe is characterized by a dynamic interplay between traditional cultural practices and engagement with the modern world. The tribe actively seeks to balance economic development with the preservation of its cultural heritage, striving to maintain a sustainable way of life. Economic development initiatives are approached with careful consideration for their impact on the environment and traditional Hopi values. The tribe has embraced opportunities for tourism, art sales, and agricultural ventures, while also emphasizing the importance of maintaining a deep connection to the land and the teachings of their ancestors.
Tribal sovereignty remains a cornerstone of the Hopi Tribe's contemporary presence. The tribe works tirelessly to assert its rights to self-governance and maintain control over its lands and resources. This commitment to tribal sovereignty is evident in the tribe's efforts to protect sacred sites, negotiate with government entities, and uphold traditional laws and customs.
Despite the challenges posed by modernity, the Hopi Tribe continues to navigate the complexities of the contemporary world while safeguarding its unique cultural identity and legacy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Traditional Hopi Tribal Ceremonies and How Do They Relate to Their Geographic Location?
Traditional ceremonies of the Hopi tribe are deeply connected to their geographic location. These rituals reflect their cultural and agricultural practices, as well as their relationships with neighboring tribes.
The ceremonies, such as the Snake Dance and the Powamu Ceremony, are tied to agricultural cycles and invoke blessings for successful harvests.
The tribe's geographic location in the arid desert of the American Southwest greatly influences their ceremonial practices and sustenance.
What Is the Significance of Specific Geographic Landmarks to the Hopi Tribe?
Significance of specific geographic landmarks to the Hopi tribe lies in their deep connection to cultural practices. These landmarks aren't just physical; they're woven into our traditions, influencing our agricultural methods and food sources.
The mesas and buttes shape our ceremonies, guiding our spiritual connection to the land. Their significance is immeasurable, grounding us in our heritage and providing a sense of belonging and purpose.
How Has the Geographical Location of the Hopi Tribe Influenced Their Agricultural Practices and Food Sources?
The geographical location of the Hopi tribe has significantly influenced our agricultural practices and food sources.
The arid environment has led us to develop innovative farming techniques such as terrace farming and water conservation methods.
Our food sources primarily consist of corn, beans, and squash, which are crucial for sustaining our community.
Additionally, the unique landscape has also shaped the spiritual significance of certain areas for our tribal ceremonies.
Are There Any Specific Natural Resources in the Hopi Territory That Have Played a Significant Role in Their Culture and Traditions?
In the Hopi territory, the land and natural resources have played a significant role in our culture and traditions.
The role of the land is central to our way of life, as it provides the resources for our traditional ceremonies and sustains our agricultural practices.
Natural resources like water, clay, and plants hold great cultural significance, used in crafting and in traditional ceremonies that have been passed down through generations.
How Has the Geographical Location of the Hopi Tribe Impacted Their Interactions With Neighboring Tribes or Communities?
Living in a region characterized by geographical barriers, the Hopi tribe's interactions with neighboring communities were influenced by the unique terrain. The rugged landscape limited direct contact, shaping distinct cultural practices.
However, strategic trade routes facilitated exchanges with nearby tribes, allowing for the sharing of resources and ideas.
This geographical location fostered both independence and interdependence, impacting the tribe's relationships with neighboring communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Hopi tribe's location was absolutely crucial to their unique culture and way of life.
Their homeland provided the perfect backdrop for their agricultural practices and spiritual beliefs, shaping their traditions and values for generations.
Today, the Hopi tribe continues to thrive in their ancestral territory, keeping their rich heritage alive in the beautiful landscape of the American Southwest.









