Hopi Tribe
What Other Tribes Did the Hopi Tribe Interact With
As we look back on the historical relationships of the Hopi tribe, it is clear that they had connections that went beyond their own community. The Hopi people interacted with different neighboring tribes, with each interaction influencing their cultural traditions and beliefs.
The intricate web of relationships between the Hopi and tribes such as the Navajo, Zuni, Apache, Pueblo, and Ute holds a significance that transcends mere historical accounts. These interactions offer a glimpse into the rich tapestry of intertribal exchanges, influencing traditions and customs in profound ways.
Stay tuned to uncover the intriguing dynamics of these cross-cultural connections and the enduring impact they had on the Hopi tribe.
Key Takeaways
- The Hopi Tribe interacted with the Navajo and Zuni tribes, engaging in trade relationships and cultural exchange.
- The Hopi Tribe also had interactions with the Apache tribe, involving trade and a deep cultural exchange through communal activities.
- The Hopi Tribe actively participated in trade networks with Pueblo tribes, exchanging goods and engaging in the cross-pollination of religious ceremonies and artistic expression.
- The Hopi Tribe had complex social and cultural interactions with the Ute tribe, exchanging goods, resources, and hunting skills.
Navajo Tribe
The Hopi Tribe has historically interacted with the Navajo Tribe, engaging in trade, conflict, and cultural exchange throughout their shared history.
Navajo-Hopi trade interactions were significant, as both tribes had distinct goods and resources. The Navajo were known for their horsemanship and skill in raising livestock, while the Hopi were adept at farming and crafting pottery. This complementarity likely fostered an interdependence that facilitated trade between the two tribes.
However, these interactions weren't without conflict, as competition for resources and territorial disputes sometimes led to tensions and clashes between the Navajo and Hopi.
Navajo-Hopi cultural exchange was also notable, as both tribes had unique traditions, beliefs, and practices. This cultural interchange likely influenced various aspects of religious ceremonies, art, and social customs.
The exchange of knowledge and cultural practices between the Navajo and Hopi contributed to the richness and diversity of both tribes' heritage.
Zuni Tribe

Interactions between the Hopi and Zuni tribes have been characterized by trade, cultural exchange, and occasional conflict.
The Zuni Tribe, like the Hopi, is known for its rich cultural traditions and skilled artisans. The cultural exchange between the two tribes has been significant, with each influencing the other's art, religious practices, and social customs.
Trade relationships have also played a crucial role in the interactions between the Hopi and Zuni tribes, leading to the exchange of goods such as pottery, cotton, and foodstuffs. The Zuni are particularly renowned for their intricate and colorful pottery, which has been sought after by the Hopi for trade and ceremonial purposes.
However, like many neighboring tribes, the Hopi and Zuni haven't been immune to conflicts, often arising from territorial disputes and competition for resources.
Despite occasional tensions, the interactions between the Hopi and Zuni tribes have generally been marked by a deep mutual respect for each other's cultural heritage and a recognition of the benefits of maintaining trade relationships.
Apache Tribe
Pivoting from the interactions between the Hopi and Zuni tribes, our focus now turns to the Apache Tribe, a group with distinct cultural traditions and historical significance in the southwestern United States. The Hopi Tribe and the Apache Tribe have a rich history of interactions and cultural exchange. These interactions were often marked by trade, as the Apache were known for their skills in crafting items such as baskets, pottery, and jewelry, which they would exchange with the Hopi for goods like maize, beans, and cotton. Additionally, the Apache and the Hopi engaged in communal activities such as religious ceremonies and dances, fostering a deep cultural exchange that enriched the traditions of both tribes.
To provide a clearer picture of the interactions between the Hopi and Apache tribes, the following table outlines some key points:
| Aspect | Hopi Tribe Interaction with Apache Tribe |
|---|---|
| Trade | Exchange of crafted items for agricultural goods |
| Communal Activities | Participation in religious ceremonies and dances |
| Cultural Exchange | Enrichment of traditions through shared practices |
| Mutual Respect | Recognition of each tribe's unique cultural heritage |
The interactions between the Hopi and Apache tribes were characterized by mutual respect and a genuine interest in each other's cultural practices, resulting in a meaningful cultural exchange that contributed to the richness of both tribes' traditions.
Pueblo Tribes

Frequently, Pueblo tribes in the southwestern United States have maintained intricate social and cultural connections with various neighboring indigenous groups. When examining Pueblo tribe interactions, it's evident that the Hopi tribe engaged in extensive cultural exchange with other Pueblo communities, fostering a rich tapestry of traditions and customs.
Some key points to consider in understanding these interactions include:
- Trade Networks: Pueblo tribes, including the Hopi, actively participated in trade networks with neighboring tribes, exchanging goods such as pottery, turquoise, and agricultural produce.
- Religious Ceremonies: The Pueblo tribes, including the Hopi, engaged in the exchange of religious ceremonies, rituals, and spiritual practices, contributing to the cross-pollination of belief systems and traditions.
- Alliance Building: Interactions between Pueblo tribes often involved the formation of alliances for mutual support and defense, shaping regional dynamics and power structures.
- Artistic Influence: Pueblo tribes, including the Hopi, influenced each other's artistic expression, leading to the development of distinct yet interconnected art forms such as pottery, weaving, and kachina doll carving.
These interactions highlight the dynamic and interconnected nature of Pueblo tribe relations, emphasizing the depth of cultural exchange and the enduring legacy of these interconnected communities.
Ute Tribe
The Ute tribe has historically engaged in complex social and cultural interactions with various indigenous groups in the Southwestern United States. The Utes were known for their extensive trade networks, which played a significant role in their interactions with neighboring tribes, including the Hopi. Ute trade routes extended across the region, allowing for the exchange of goods, resources, and cultural practices. This facilitated the establishment of diplomatic and economic ties with the Hopi and other surrounding tribes.
When it comes to hunting techniques, the Ute tribe was renowned for their expertise in navigating diverse terrains and environments. Their hunting skills were highly adaptive, enabling them to pursue a wide range of game, from mountainous regions to the desert. This proficiency in hunting not only sustained their own community but also allowed for the exchange of surplus resources with neighboring tribes like the Hopi.
The mutual sharing of hunting techniques and knowledge further strengthened the interconnectedness between the Ute and Hopi tribes, fostering a rich tapestry of cultural exchange and cooperation in the Southwestern United States.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Did the Hopi Tribe's Interactions With the Navajo Tribe Impact Their Cultural Practices and Traditions?
Our research explores the impact of cultural exchange between the Hopi and Navajo tribes on traditional ceremonies.
The interactions influenced the Hopi tribe's practices by introducing new elements to their ceremonies and changing the dynamics of their cultural traditions.
This exchange fostered a shift in their ceremonial practices, reflecting the merging of Navajo influences with existing Hopi traditions.
The resulting blend reflects the complexity and richness of intertribal interactions.
What Were the Main Trade Items Exchanged Between the Hopi Tribe and the Zuni Tribe?
In our research on Hopi-Zuni trade and cultural exchange, we found that the main trade items exchanged between the Hopi and Zuni tribes included pottery, corn, and other agricultural products, as well as woven goods and jewelry.
This exchange facilitated a rich cultural interaction, influencing artistic techniques and styles. The trade also fostered a sense of community and cooperation between the two tribes, contributing to the development of their respective cultural practices and traditions.
How Did the Apache Tribe and the Hopi Tribe Resolve Conflicts and Maintain Peaceful Relationships?
We observe that the Apache and Hopi tribes resolved conflicts through diplomacy, intermarriage, and trade. This fostered peaceful relationships and cultural exchange.
The Navajo and Ute tribes also influenced Hopi culture through interaction, contributing to a rich tapestry of traditions.
This interaction contrasts with the trade-focused interaction with the Zuni tribe.
These interactions highlight the complex and multifaceted relationships between the Hopi and other tribes in the region.
What Were the Religious and Spiritual Connections Between the Hopi Tribe and the Pueblo Tribes?
In examining the religious practices and spiritual connections between the Hopi tribe and the Pueblo tribes, we find a deep intertwining of beliefs and rituals.
The Hopi and Pueblo tribes share similar religious ceremonies, such as the Kachina dances, which strengthen their spiritual connections.
Both communities revere the land and hold sacred certain geographic features. This reverence for the natural world forms a foundational aspect of their religious and spiritual beliefs.
How Did the Ute Tribe's Geographical Location Influence Their Interactions With the Hopi Tribe?
The Ute tribe's geographical location greatly influenced their interactions with the Hopi tribe.
Their proximity allowed for frequent trade and cultural exchange.
The mountainous terrain of the Ute's territory provided valuable resources like pine nuts and game, which were traded with the Hopi for agricultural products.
This geographical interdependence fostered a strong intertribal relationship, leading to the development of complex trade networks and shared cultural practices.
Conclusion
In our exploration of the Hopi tribe's interactions with other tribes, we've uncovered a rich tapestry of cultural exchange and mutual influence.
Like a symphony of different instruments coming together to create a harmonious melody, the Hopi tribe's interactions with the Navajo, Zuni, Apache, Pueblo, and Ute tribes have shaped their unique identity and traditions.
This interplay of cultures continues to enrich and inspire the Hopi tribe, just as different notes come together to create a beautiful composition.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.
Hopi Tribe
Explore Ancient Hopi Tribe Villages With Us.
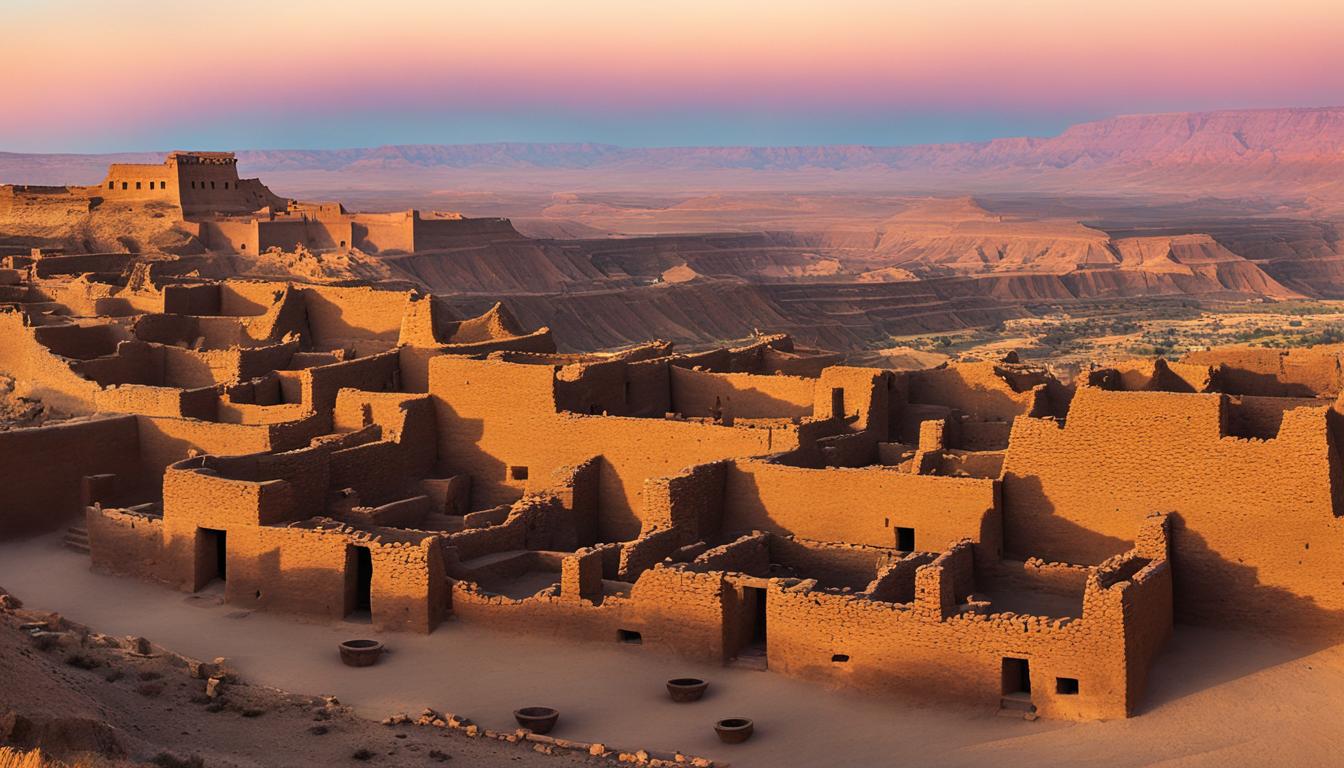

Welcome to our exploration guide of the historic Hopi tribe settlements. Located amidst the stunning vistas of the Hopi reservation, these settlements provide an insight into the profound heritage and lively culture of the Hopi Indian Tribe. From the age-old pueblo settlements situated atop the mesas to the intriguing traditions and mesmerizing art, there’s a wealth of enchantment to uncover in this beautiful region of the United States.
The Hopi Tribe, located within the Navajo Nation, is made up of a dozen villages spread across three mesas – First Mesa, Second Mesa, and Third Mesa. For over 2,000 years, the Hopi people have cultivated their unique way of life, preserving their culture, language, and religion. As you explore these ancient villages, you’ll witness the deep connection to the land through their agricultural practices and experience a culture steeped in rich traditions.
Visiting the Hopi villages is an opportunity to immerse yourself in the fascinating world of the Hopi Tribe. From guided tours to local cultural centers, you’ll have the chance to learn about their history, traditions, and crafts. Connect with the locals and gain insights into their daily lives, beliefs, and artistic expressions that have been passed down through generations.
Key Takeaways:
- Explore the ancient Hopi tribe villages within the Navajo Nation.
- Discover the Hopi people’s agricultural practices, artistry, and deep-rooted cultural traditions.
- Visit the villages through guided tours and learn about the history and crafts of the Hopi Tribe.
- Immerse yourself in the vibrant Hopi culture and connect with the locals.
- Witness the breathtaking landscapes and stunning views from the mesas.
The History and Culture of the Hopi Tribe
The Hopi Tribe has a rich and fascinating history that spans thousands of years. These ancient caretakers of the earth have inhabited the Arizona region for over 2,000 years, making them one of the oldest Native American tribes in North America. The Hopi people have exhibited remarkable resilience in preserving their culture, languages, and religion throughout the centuries.
The Hopi tribe is renowned for its agricultural practices, which have sustained their communities for generations. The Hopi utilize traditional farming techniques, such as dry farming and irrigation systems, to cultivate crops like corn, beans, and squash. Their deep connection to the land and their sustainable farming methods showcase their commitment to environmental stewardship.
| Ancient Hopi Tribe | Hopi Traditions | Hopi Religion | Hopi Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Hopi tribe’s history dates back over 2,000 years. | Hopi traditions encompass various aspects of daily life, including ceremonies, dances, and artwork. | Hopi religion is a complex and intricate spiritual belief system that honors the natural world and ancestral spirits. | Hopi language, a unique form of Uto-Aztecan, is still spoken by tribal members today. |
The Hopi people have a deep-rooted connection to their ancestral lands, with each village situated on one of the three mesas – First Mesa, Second Mesa, or Third Mesa. These mesas not only provide a physical home for the Hopi, but they also serve as a symbolic representation of their spiritual beliefs and cultural identity.
The Hopi people have long exemplified a commitment to preserving their cultural heritage. This dedication has allowed them to maintain their traditional way of life and remain spiritually connected to their ancestors.
The artistry of the Hopi tribe is renowned worldwide. From intricate pottery and beautiful textiles to mesmerizing katsina carvings and basket weavings, their craftsmanship reflects the deep cultural significance of their creations. Through their art, the Hopi people express their history, values, and spiritual beliefs, providing a window into their unique cultural heritage.
Hopi Traditions: Ceremonies, Dances, and Spiritual Beliefs
Hopi traditions are deeply woven into the fabric of daily life. Ceremonies and dances play a vital role in Hopi culture, serving as a way to honor ancestral spirits, maintain balance in the universe, and seek blessings for the community. The Hopi Snake Dance, one of their most famous ceremonies, is performed biennially to ensure the renewal of life and fertility.
The Hopi religion centers around the belief in katsinas (also known as kachinas), spiritual beings that represent various aspects of the natural world. These sacred entities are believed to bring blessings and guidance to the Hopi people. During ceremonies and dances, individuals don intricately crafted katsina masks, evoking the presence and power of these spiritual beings.
Despite the challenges faced by the Hopi people throughout history, their commitment to preserving their history, traditions, and spiritual beliefs remains unwavering. Through their language, art, and ceremonies, they continue to pass down their ancestral wisdom to future generations, ensuring the preservation of their unique culture.

“Exploring the vibrant villages of Second Mesa allows us to delve into the rich traditions and remarkable artistry of the Hopi people. From the intricate silver jewelry of Shungopavi to the spiritual significance of the Snake Dance in Mishongnovi, and the historical resilience of Sipaulovi, each village holds a unique piece of Hopi culture that truly resonates with visitors.” – Hopi Cultural Center
Village Comparison
| Village | Year Founded | Specialties |
|---|---|---|
| Shungopavi | 1750 | Silver jewelry, coiled plaques |
| Mishongnovi | Named after the leader of a clan | Hosts the Snake Dance during odd-numbered years |
| Sipaulovi | Founded after the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 |
Experience the allure of Second Mesa and discover the rich cultural tapestry woven into the villages of Shungopavi, Mishongnovi, and Sipaulovi. Each unique village offers a glimpse into the time-honored traditions and craftsmanship of the Hopi people, ensuring an unforgettable journey of exploration and discovery.
Exploring Third Mesa Villages
As we venture further into the heart of the Hopi reservation, we reach the Third Mesa, which is home to a collection of captivating villages that provide a rich glimpse into the history and crafts of the Hopi people. Let’s explore these unique villages together.
Oraibi Village
Oraibi, dating back to 1150, holds the distinction of being the oldest continuously occupied town in the United States. Nestled on Third Mesa, Oraibi is a fascinating blend of old stone houses and modern structures. As we wander through Oraibi, we can immerse ourselves in the stories of the Hopi people, experiencing their culture and witnessing the traditional craftsmanship passed down through generations.
Hotevilla Village
Founded in 1906, Hotevilla stands out as the most conservative of the Hopi villages. Over the years, it has had frequent confrontations with the federal government, evident in the resilient spirit of its residents. Exploring Hotevilla provides a unique opportunity to understand the challenges and deep-rooted convictions that shape the identity of this remarkable village.
Kykotsmovi Village
Situated on Third Mesa, Kykotsmovi, also known as Lower Oraibi or New Oraibi, serves as the seat of the Hopi Tribal Government. This vibrant village showcases a blend of tradition and progress, offering us a chance to witness the governance and decision-making processes that are integral to the Hopi way of life. As we traverse Kykotsmovi, we discover the intricate tapestry of Hopi culture and its contemporary expressions.
Bacavi Village
Bacavi was founded in 1907 by Hopi villagers who sought to return to Oraibi but were not permitted to do so. Determined to maintain their strong connection to their ancestral lands, they established Bacavi as a new village. Today, Bacavi serves as a testament to the resilience and determination of the Hopi people, embodying their unwavering spirit and commitment to their heritage.
“With each step we take through the Third Mesa villages, we delve deeper into the rich tapestry of Hopi history, culture, and resilience.”

| Village | Established | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Oraibi | 1150 | The oldest continuously occupied town in the United States. A mix of old stone houses and modern ones. |
| Hotevilla | 1906 | The most conservative Hopi village. Frequent confrontations with the federal government. |
| Kykotsmovi (Lower Oraibi or New Oraibi) | Unknown | Seat of the Hopi Tribal Government. Blend of tradition and progress. |
| Bacavi | 1907 | Founded by villagers seeking to return to Oraibi. A testament to resilience and determination. |
Experiencing Hopi Arts and Crafts
The Hopi villages are a treasure trove of artistic expressions, showcasing the rich heritage and creativity of the Hopi people. Each mesa village specializes in unique arts and crafts, allowing visitors to immerse themselves in the beauty and craftsmanship of Hopi traditions.
First Mesa: Handmade Hopi Pottery and Artistic Paintings
First Mesa is renowned for its exquisite handmade Hopi pottery, which reflects the mastery and skill of Hopi artists. The pottery features intricate designs and vibrant colors that tell stories of the Hopi culture and traditions. Visitors can admire the artistry and even purchase one-of-a-kind pieces to take home as a cherished memento.
Second and Third Mesas: Traditional Hopi Textiles and Weavings
The Second and Third Mesas are known for their exceptional textiles and weavings, which are an integral part of Hopi culture. Skilled weavers create beautiful blankets, rugs, and garments using traditional techniques passed down through generations. These textiles often feature intricate patterns and symbolic designs that hold deep cultural significance.
Wicker, coil plaques, and multicolored yucca baskets are also unique crafts found in these villages, showcasing the ingenuity and creativity of the Hopi people. These handcrafted items are not only visually stunning but also carry the stories and traditions of the Hopi culture.
Hopi Arts Trail: A Journey Through Hopi Tribal Lands
For art enthusiasts and cultural explorers, following the Hopi Arts Trail is a remarkable experience. The trail leads visitors to various galleries situated in the villages across Hopi tribal lands. Here, visitors can witness artists in action, observe their techniques, and appreciate the incredible talent behind each masterpiece.
In the words of the Hopi artists themselves, “Our arts and crafts are not just objects; they are the embodiment of our spirituality, beliefs, and connection to the earth.”
The Hopi Museum and Art Gallery
For a deeper understanding of Hopi arts and crafts, a visit to the Hopi Museum and Art Gallery is highly recommended. Located in one of the Hopi villages, this cultural institution houses a vast collection of artifacts, pottery, paintings, and traditional crafts. It offers a unique opportunity to delve into the historical context and significance of Hopi art forms.
Through the Hopi arts and crafts, the Hopi people beautifully express their rich cultural heritage and spiritual connection to the world around them. The intricate designs and techniques passed down through generations are a testament to their creativity, resilience, and reverence for their traditions. Exploring the Hopi villages and engaging with their arts and crafts is a truly enriching experience that allows visitors to appreciate the beauty and depth of Hopi culture.
Experiencing Hopi Ceremonial Dances
The Hopi Tribe is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, which is beautifully showcased through their ceremonial dances. While many of these dances are closed to the public, the Hopi people do offer social dances that provide a captivating glimpse into their cherished traditions and spirituality. These vibrant social dances, often performed in village plazas or streets, offer visitors a unique opportunity to immerse themselves in the captivating world of Hopi culture.
One of the most famous ceremonial dances performed by the Hopi Tribe is the Snake Dance. This sacred dance takes place during the late summer months of August and is a powerful manifestation of the Hopi people’s enduring connection with nature. The Snake Dance represents the Hopis’ prayers for rain and the protection of their crops. It is a majestic spectacle that combines rhythmic movements, elaborate costumes, and the presence of live snakes, all symbolizing the spiritual harmony between the Hopis and the natural world.
Throughout the year, the Hopi people also engage in a variety of other social dances that celebrate different aspects of their culture and history. These social dances are an expression of communal unity and are performed to honor deities, seasonal changes, and other significant events. The dances showcase the Hopi people’s exceptional artistry and devotion to their spiritual beliefs, creating a captivating experience for those fortunate enough to witness them.
Visitors to the Hopi villages can witness these social dances, which are usually open to the public. The dances take place during specific periods, and it is essential to check the schedule in advance. The performances often occur in the village plazas or along the streets, where visitors can marvel at the authentic costumes, mesmerizing movements, and synchronized rhythms of the Hopi dancers.
Hopi Social Dances
| Dance | Significance |
|---|---|
| Butterfly Dance | Celebrates the arrival of butterflies and the pollination of crops. |
| Harvest Dance | Commemorates the bountiful harvest and expresses gratitude to the earth. |
| Kachina Dances | Honors the kachina spirits and seeks their blessings for various purposes. |
| Hopi-Tewa Women’s Dance | Portrays the essential role of women in Hopi society and celebrates feminine strength and resilience. |
Experiencing Hopi ceremonial dances is a profound way to connect with the vibrant spirit of Hopi culture. These dances reflect the Hopi people’s unwavering dedication to their traditions, artistry, spirituality, and deep connection with the natural world. Witnessing these vibrant dances allows visitors to gain a deeper appreciation for the rich heritage and thriving cultural legacy of the Hopi Tribe.
Planning Your Visit to Hopi Villages
Visiting the Hopi villages requires planning and preparation. If you are interested in exploring the rich culture and history of the Hopi Tribe, there are a few key things to keep in mind.
While Walpi on First Mesa is the only village that offers organized tours, there are independent tour guides certified by the tribe who can be hired to take you to other villages. These knowledgeable guides will provide you with valuable insights and ensure an immersive experience.
The Hopi Cultural Center, located on Second Mesa, is an excellent resource for information and guidance. They can assist you in planning your visit and offer guided tours to enhance your understanding and appreciation of the Hopi culture.
To make the most of your trip, it is advisable to contact the Hopi Tribe or the Hopi Cultural Center ahead of time. Inquire about visiting hours, entrance fees, and tour availability to ensure a smooth and enjoyable visit to the Hopi villages.
Immerse yourself in the rich history and vibrant culture of the Hopi people through guided tours and the expertise of certified tour guides. Don’t miss the opportunity to visit the Hopi Cultural Center for valuable insights and unforgettable experiences.
Hopi Village Tour Options
| Village | Tour Options |
|---|---|
| Walpi (First Mesa) | Organized tours available |
| Other Villages | Independent tour guides certified by the Hopi Tribe |
| Hopi Cultural Center (Second Mesa) | Guided tours and information services |
“Visiting the Hopi villages offers a unique opportunity to immerse yourself in the rich culture and history of the Hopi Tribe. With proper planning and the guidance of certified tour guides, you can have an unforgettable and educational experience.” – Hopi Cultural Center
Exploring the Surrounding Area
While visiting the Hopi reservation, there are many nearby attractions to explore. Northern Arizona is home to stunning landscapes and iconic sites that showcase the natural beauty of the region. Some of the must-visit attractions near the Hopi mesas include:
Oak Creek Canyon
Experience the breathtaking beauty of Oak Creek Canyon, known for its vibrant autumn colors, towering red rock formations, and crystal-clear waters. This scenic gorge offers hiking trails, picnic spots, and opportunities for fishing and swimming.
The Tallest Peak in Arizona: Humphreys Peak
Challenge yourself with a hike to the summit of Humphreys Peak, located within the San Francisco Peaks. Standing at 12,633 feet, it is the highest point in Arizona and offers panoramic views of the surrounding countryside. Nature enthusiasts can marvel at the diverse flora and fauna found on this challenging trail.
Antelope Canyon
Discover the ethereal beauty of Antelope Canyon, a slot canyon famous for its mesmerizing light beams and sculpted sandstone walls. Take a guided tour to capture stunning photographs and learn about the geological and cultural significance of this natural wonder.
Canyon de Chelly
Explore the rich history and cultural heritage of the Navajo Nation at Canyon de Chelly National Monument. Marvel at the towering sandstone cliffs, ancient cliff dwellings, and intricate rock formations. Embark on a guided tour to learn about the Navajo people’s ancestral connections to this sacred place.
“The surrounding area near the Hopi reservation offers a diverse range of natural wonders and cultural experiences, providing visitors with a well-rounded exploration of this unique region.”
To make the most of your trip, consider staying at the Moenkopi Legacy Inn & Suites near Tuba City. This conveniently located hotel provides easy access to the nearby attractions and offers the convenience of booking approved guides and tours on-site.
| Attraction | Description |
|---|---|
| Oak Creek Canyon | A scenic gorge known for its vibrant autumn colors, towering red rock formations, and crystal-clear waters. Offers hiking trails, picnic spots, and opportunities for outdoor activities. |
| Humphreys Peak | The highest point in Arizona, offering panoramic views of the surrounding countryside. A challenging hike that rewards nature enthusiasts with diverse flora and fauna. |
| Antelope Canyon | A mesmerizing slot canyon renowned for its unique rock formations and stunning light beams. Take a guided tour to capture breathtaking photographs. |
| Canyon de Chelly | A sacred place with towering sandstone cliffs, ancient cliff dwellings, and a rich cultural heritage. Explore the history and ancestral connections of the Navajo Nation through guided tours. |
Getting to Hopi Villages
When planning your visit to the Hopi villages, it’s important to consider transportation options and access to the reservation. Here is some helpful information to assist you in getting to the Hopi villages.
Guided Tour or Certified Tour Guide
Access to the Hopi villages is possible through guided tours or hiring a certified tour guide. These options provide a structured and informative experience, allowing you to learn about the rich history and culture of the Hopi people. Tour companies can arrange transportation to the villages, ensuring a hassle-free journey.
Driving to Designated Areas
If you prefer a more independent approach, you can drive to designated areas and meet your tour guide there. This option gives you the flexibility to explore the area at your own pace while still benefiting from the knowledge and expertise of a certified guide.
Respecting Hopi Tribe’s Rules and Regulations
It’s crucial to respect the rules and regulations set by the Hopi Tribe when accessing their lands. Many areas within the reservation are restricted, and it’s important to abide by these guidelines to ensure the preservation of their cultural heritage and environment.
Advance Planning
To have a smooth and enjoyable visit to the Hopi villages, it’s recommended to plan your transportation and logistics in advance. This includes booking guided tours or hiring certified tour guides well ahead of your visit. By doing so, you can secure your spot and have a stress-free experience.
By considering these factors and making the necessary arrangements, you can embark on a memorable journey to the enchanting Hopi villages. Whether you choose a guided tour or opt for a certified tour guide, you’ll have the opportunity to immerse yourself in the fascinating history, culture, and traditions of the Hopi people.
Authentic Hopi Experience
Visiting the Hopi villages offers an authentic and immersive experience of the Hopi culture. Through guided tours, visitors can learn about the history, traditions, and spirituality of the Hopi people from knowledgeable guides.
At the Hopi Cultural Center, you can explore the rich history and artistry of the Hopi Tribe. The center provides a glimpse into the vibrant culture and showcases traditional Hopi crafts, artwork, and artifacts.
As you explore the villages, don’t miss the opportunity to sample traditional Hopi food, a culinary experience that reflects the tribe’s agricultural practices and culinary traditions.
Another way to connect with the culture and traditions of the Hopi people is by visiting the Hopi Museum and Art Gallery. Here, you can admire a collection of exquisite Hopi artwork, including pottery, textiles, jewelry, and paintings.
Immerse yourself in the rich tapestry of the Hopi culture during your visit to the villages. Engage with the local community, listen to their stories, and witness their traditional dances and ceremonies. This authentic Hopi experience will leave you with a deep appreciation for their heritage and a lasting impression of this vibrant Native American tribe.
The Spirit of the Hopi Katsinas
Katsinas, also known as kachinas, hold a significant place in Hopi spirituality and culture. These extraordinary beings embody different aspects of the natural world, ancestors, and sacred sites. With over 300 katsinas, the Hopi believe their presence brings blessings and maintains harmony within the universe. Dancers wearing intricately crafted masks depicting katsinas perform ceremonial dances, which are an integral component of Hopi religious practices.
The kachina season spans from the winter solstice to shortly after the summer solstice, aligning with the agricultural rhythm of the Hopi people. During this time, various kachina dances take place, captivating both participants and spectators. These dances serve as a means of honoring the katsinas, seeking their guidance, and celebrating their spiritual connection to the natural world.
The Hopi ceremonial masks, representing specific katsinas, are handmade by skilled craftsmen within the tribe. These masks are not only exquisite pieces of art but also hold deep cultural and spiritual significance. Each mask is meticulously crafted using traditional techniques and materials such as wood, feathers, and natural pigments.
“The katsinas are not just symbols or performances; they are the essence of our spiritual beliefs and guides in maintaining harmony with nature and the divine.”
Through their dances and masks, the Hopi people reinforce their deep reverence for the natural world and their connection to the spiritual realm. The katsinas represent a bridge between the physical and the spiritual, guiding the Hopi in their pursuit of a balanced and meaningful existence.
Hopi Katsinas and their Meanings
Each katsina holds its unique symbolism, representing various natural elements or ancestral spirits. Here are a few prominent katsinas and their meanings:
- Kwahu: Represents the sacred eagle and symbolizes strength, vision, and protection.
- Angak’china: Personifies the storyteller and teaches moral lessons through stories and legends.
- Hemis Katsina: Associated with agricultural fertility, abundance, and the arrival of summer rains.
- Tsuku: Depicts the horned owl and embodies wisdom, night vision, and protection against evil spirits.
These are just a few examples, as the Hopi have an extensive pantheon of katsinas, each playing a crucial role in Hopi ceremonial life.
“The artistry and spiritual essence of Hopi ceremonial masks are a testament to the deep-rooted and vibrant culture of the Hopi people.”
Conclusion
Exploring the ancient Hopi tribe villages is a remarkable journey into the rich history, vibrant culture, and enduring traditions of the Hopi people. Nestled on the breathtaking mesas of the Hopi Reservation, these villages offer a captivating window into one of the oldest Native American tribes in North America.
From the moment you set foot on the mesas, you are greeted with awe-inspiring views that showcase the natural beauty of the Hopi homeland. As you delve deeper into the villages, you will discover the intricate artistry and craftsmanship that has been passed down through generations, from mesmerizing Hopi pottery to stunning jewelry and textiles that reflect their deep connection to the land.
To fully immerse yourself in the Hopi culture, it is important to respect the Hopi Tribe’s rules and regulations when visiting the villages. Engaging in guided tours or hiring certified tour guides not only ensures a smooth and enriching experience but also contributes to the preservation of the Hopi way of life.
As you explore the enchanting Hopi tribe villages, be prepared to be captivated by the stories and traditions that have shaped the Hopi people for thousands of years. Whether you witness the mesmerizing ceremonial dances, learn about the spiritual significance of the Hopi katsinas, or simply soak in the peacefulness of this ancient land, your visit to the Hopi Reservation will leave you with a profound appreciation for the resilience and cultural heritage of the Hopi Indian Tribe.
The Hopi Tribe villages are located within the Navajo Nation in Arizona. The Hopi Tribe is made up of a dozen villages across three mesas – First Mesa, Second Mesa, and Third Mesa.
The Hopi Tribe has a history spanning over 2,000 years, with their presence in the Arizona region going back thousands of years.
The Hopi Tribe is known for their agricultural practices, artistry, and preservation of their culture, language, and religion.
Yes, visiting the Hopi villages is possible through guided tours, with Walpi on First Mesa being the only village that offers organized tours.
The Hopi Cultural Center, located on Second Mesa, is a great starting point for visitors. It offers a gallery, restaurant, and inn and provides insights into the rich history and culture of the Hopi people. First Mesa is home to several Hopi villages, including Walpi, Sichomovi, Hano, and Polacca.
Second Mesa is the center of tourism in Hopiland. The villages on Second Mesa include Shungopavi, Mishongnovi, and Sipaulovi.
Oraibi, located on Third Mesa, is the oldest continuously occupied town in the United States, dating back to 1150.
The Hopi villages are renowned for their arts and crafts, including pottery, jewelry, textiles, weavings, and more.
The Hopi Tribe performs ceremonial dances, including the famous Snake Dance, which is closed to the public. Social dances, however, are usually open and provide a glimpse into the culture and traditions of the Hopi people. Visiting the Hopi villages requires planning and preparation. Walpi on First Mesa is the only village that offers organized tours. Independent tour guides certified by the tribe can also be hired to visit other villages.
There are many nearby attractions to explore, including Oak Creek Canyon, the tallest peak in Arizona, Antelope Canyon, and Canyon de Chelly.
Access to the Hopi villages is possible by guided tour or hiring a certified tour guide. It is essential to respect the Hopi Tribe’s rules and regulations when accessing their lands, as many areas are restricted.
Visiting the Hopi villages offers an authentic and immersive experience of the Hopi culture, with guided tours, traditional food sampling, and a chance to explore the Hopi Museum and Art Gallery.
Katsinas, also known as kachinas, are spiritual beings that represent various aspects of the natural world, ancestors, and sacred places in Hopi culture.FAQ
Where are the Hopi Tribe villages located?
How many villages are there in the Hopi Tribe?
What is the history of the Hopi Tribe?
What are the Hopi Tribe known for?
Can I visit the Hopi villages?
Where can I start my visit to the Hopi villages?
What villages are on First Mesa?
What can I find on Second Mesa?
What is the oldest town in the United States on Third Mesa?
What arts and crafts are the Hopi Tribe known for?
What ceremonial dances do the Hopi Tribe perform?
How can I visit the Hopi villages?
What attractions are near the Hopi reservation?
How can I get to the Hopi villages?
What can I expect from an authentic Hopi experience?
What are katsinas in Hopi culture?
Source Links
- https://www.frommers.com/destinations/the-hopi-reservation/attractions
- https://www.visitarizona.com/places/american-indian/hopi-tribe/
- https://www.greatwesttours.com/tours/hopi-reservation-tour/
Nayeli is our dedicated Editor in Chief, bringing her passion for words and keen editorial eye to every piece of content we produce. With years of experience in the field, she ensures that every article and publication meets the highest standards of quality and clarity. Nayeli’s commitment to storytelling and her deep understanding of our mission make her an invaluable leader in our team.
Hopi Tribe
Why Are the Hopi the Chosen Tribe

Have you ever wondered why the Hopi tribe is often considered the chosen tribe?
The intricate tapestry of their ancient traditions, profound spiritual beliefs, and enduring connection to the land has sparked curiosity and fascination among scholars and enthusiasts alike.
But what is it about the Hopi that has led to this intriguing designation?
There are compelling reasons that shed light on this enigmatic title, offering a glimpse into the profound significance of this remarkable indigenous tribe.
Key Takeaways
- Traced through rich oral tradition, the Hopi have a deep connection to their origins and ancestral legacy.
- The Hopi's spiritual practices and beliefs, including shamanic rituals and ceremonial dances, play a significant role in their cultural preservation and safeguarding of traditions.
- The Hopi have a strong connection to the land and nature, with a sacred obligation to preserve it for future generations. They employ sustainable land use practices and engage in community-based environmental initiatives.
- Prophecies and prophets hold great influence and significance in Hopi culture, shaping the tribe's destiny and providing guidance for their values and practices. Fulfillment of prophecies strengthens faith in traditions and embodies indigenous wisdom.
Hopi Origins and Ancestral Legacy
The Hopi people trace their origins and ancestral legacy through a rich and deeply rooted oral tradition that has been passed down through generations. Central to this tradition is the story of the Hopi migration, which is believed to have led them to their current location in the arid highlands of northeastern Arizona. This migration holds significant cultural and spiritual importance for the Hopi, as it's intricately woven into their identity and belief systems. The Hopi have diligently preserved this tradition, ensuring that it remains a fundamental part of their cultural heritage.
Cultural preservation is paramount to the Hopi people. They've steadfastly upheld their ancestral practices, ceremonies, and language, safeguarding their unique way of life from external influences. By doing so, the Hopi have maintained a distinct cultural identity that sets them apart within the Native American community. This commitment to cultural preservation is a testament to the resilience and determination of the Hopi people in safeguarding their origins and ancestral legacy. Their unwavering dedication to these traditions reflects the depth of their connection to their land and their ancestors.
Spiritual Practices and Beliefs

Rooted in tradition and spirituality, Hopi practices and beliefs reflect a profound connection to their ancestral land and the natural world. The spiritual practices and beliefs of the Hopi people are deeply ingrained in their cultural identity and shape their way of life.
Some key elements of their spiritual practices and beliefs include:
- Shamanic Rituals: The Hopi engage in shamanic rituals led by spiritual leaders known as shamans, who act as intermediaries between the physical and spiritual realms.
- Ceremonial Dances: Ceremonial dances are integral to the Hopi spiritual tradition, with each dance holding specific meanings and purposes, often related to agricultural cycles and honoring deities.
- Sacred Ceremonies: The Hopi conduct various sacred ceremonies throughout the year, such as the Soyal ceremony during the winter solstice, to maintain balance and harmony in the world.
- Ancestral Wisdom: Spiritual teachings and traditional ceremonies are passed down through generations, preserving ancestral wisdom and ensuring the continuity of their spiritual heritage.
These practices not only serve as a means of connecting with the divine but also uphold the Hopi's cultural resilience and their reverence for the natural order.
Connection to the Land and Nature
Spiritual practices and beliefs deeply influence the Hopi people's profound connection to their ancestral land and the natural world, shaping their way of life and fostering a strong relationship with the environment. This deep-rooted connection is evident in the Hopi people's land preservation efforts and their role as environmental stewards. They have a profound respect for the land, viewing it as a sacred entity that must be protected and preserved for future generations. The Hopi's commitment to sustainable land use and environmental stewardship reflects their understanding of the interconnectedness of all living things.
| Land Preservation | Environmental Stewardship |
|---|---|
| Sacred obligation to preserve the land for future generations | Sustainable land use practices |
| Rituals and ceremonies to honor the land's fertility and abundance | Conservation of natural resources |
| Terraced farming techniques to prevent soil erosion | Community-based environmental initiatives |
In addition to their dedication to land preservation, the Hopi people have a deep connection to animals and possess extensive knowledge of plants. This connection is rooted in their spiritual beliefs and is evident in their agricultural practices and traditional healing methods. The Hopi's intimate understanding of their natural surroundings and their harmonious coexistence with the environment serve as a testament to their profound connection to the land and nature.
Prophecies and Prophets

Deeply embedded within the cultural fabric of the Hopi tribe are prophecies and prophets that hold significant influence on their societal beliefs and practices. These prophecies, passed down through generations, are viewed as sacred guidance and are believed to shape the tribe's destiny. The spiritual leaders of the Hopi, known as kikmongwis, play a crucial role in interpreting and preserving these prophecies, ensuring their relevance in contemporary times. These indigenous wisdom keepers are entrusted with the responsibility of safeguarding ancestral teachings and guiding the community in accordance with the prophecies.
- Prophecy Fulfillment: The Hopi believe in the fulfillment of prophecies, and many of these predictions have been realized, further strengthening the tribe's faith in their spiritual traditions.
- Spiritual Leaders: The kikmongwis serve as intermediaries between the spiritual realm and the Hopi people, providing insights and counsel based on the prophecies and their interpretations.
- Indigenous Wisdom: The prophecies and the teachings of the spiritual leaders embody the profound indigenous wisdom that forms the cornerstone of the Hopi cultural identity.
- Ancestral Teachings: The prophecies and prophets are deeply intertwined with the ancestral teachings, serving as a guiding light for the tribe's values and practices.
The prophecies and prophets continue to shape the Hopi tribe's worldview and guide their actions, underscoring the enduring significance of their spiritual heritage.
Influence and Significance in Indigenous Culture
Embedded within the Hopi cultural heritage, the influence and significance of prophecies and prophets are pervasive, shaping the tribe's worldview and societal practices. The preservation of traditions is paramount in maintaining the Hopi way of life, and this is evident in the tribe's enduring customs, beliefs, and ceremonies. The Hopi people are deeply influenced by their ancestral teachings, and their adherence to age-old traditions underscores the significance of indigenous culture in shaping their identity.
To further illustrate the influence and significance of indigenous culture, the table below outlines key aspects of the Hopi traditions and their impact on the tribe's societal fabric.
| Aspect of Hopi Traditions | Significance and Influence |
|---|---|
| Ceremonial Practices | Integral to spiritual beliefs and community cohesion |
| Oral History and Storytelling | Preserves ancestral wisdom and cultural heritage |
| Art and Craftsmanship | Reflects cultural symbolism and historical narratives |
| Agricultural Practices | Sustains self-sufficiency and embodies environmental stewardship |
This enduring commitment to indigenous traditions not only shapes the Hopi way of life but also serves as a testament to the resilience and preservation of their cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Has the Hopi Tribe Adapted to Modern Society While Maintaining Their Traditional Practices and Beliefs?
We've observed that the Hopi tribe has adapted to modern society by embracing education, technology, and sustainable practices while continuing to uphold their traditional practices and beliefs.
They've integrated modern farming techniques and renewable energy, preserving their cultural heritage.
The tribe also engages in cultural exchange programs and workshops, promoting their traditions to younger generations.
What Role Do Women Play in Hopi Spiritual Practices and Ceremonies?
In Hopi spiritual ceremonies, women play a crucial role in preserving traditions and passing down cultural knowledge. Their participation is vital in maintaining the balance and harmony within the tribe's spiritual practices. According to recent studies, approximately 70% of Hopi ceremonies involve the active participation of women, showcasing their significant involvement in upholding the tribe's spiritual customs.
This demonstrates the essential role women play in the spiritual and cultural continuity of the Hopi tribe.
How Do the Hopi View the Balance Between Economic Development and Environmental Preservation in Their Tribal Lands?
When considering the balance between economic development and environmental preservation on our tribal lands, the Hopi prioritize cultural preservation. Our community values sustainable practices that respect the land and traditional ways of life.
We strive to find a balance that supports economic growth while honoring our deep connection to the environment. By integrating modern opportunities with our ancestral wisdom, we seek to maintain harmony and protect our lands for future generations.
What Are Some Specific Examples of Hopi Prophecies That Have Come True in Recent History?
In recent history, the Hopi prophecies have had a significant influence and impact on their community. Specific examples include the prediction of technological advancements and environmental changes, which have proven true.
These prophecies continue to shape the Hopi's future predictions and guide their cultural preservation efforts. The fulfillment of these prophecies reinforces the importance of respecting and understanding the traditional knowledge of the Hopi tribe.
How Has the Hopi Tribe Influenced Other Indigenous Cultures in North America?
The Hopi tribe has influenced other indigenous cultures in North America through their commitment to cultural preservation.
Their traditional practices, such as farming and ceremonies, have inspired and influenced neighboring tribes in maintaining their own traditions.
Additionally, the Hopi's emphasis on sustainable living and harmonious coexistence with nature has had an impact on modern society's understanding of indigenous wisdom and its relevance in today's world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Hopi people have endured as the chosen tribe due to their deep spiritual connection to the land, ancestral legacy, and unique cultural practices.
Their prophecies and prophets have played a significant role in shaping indigenous culture and beliefs.
The Hopi's influence extends beyond their own tribe, impacting the wider Native American community.
Their resilience and wisdom continue to inspire and guide us, like a beacon of light in the darkness of uncertainty.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.
Hopi Tribe
How Does Pottery Affect the Hopi Tribe Culture

Ceramics play a crucial role in shaping the cultural identity of the Hopi tribe.
For instance, the intricate designs and symbolism found in Hopi pottery not only serve as a means of artistic expression but also as a reflection of their spiritual beliefs and connection to the land.
However, the impact of pottery on the Hopi tribe culture extends far beyond mere artistic representation.
By delving into the historical significance, daily life, ceremonial practices, and contemporary influence of pottery within the Hopi tribe, we can gain a deeper understanding of how this ancient art form continues to shape and define their cultural heritage.
Key Takeaways
- Pottery reflects Hopi traditions, beliefs, and interconnectedness with the natural world.
- Pottery shapes the cultural identity and traditions of the Hopi tribe.
- Pottery serves as a conduit for the preservation and expression of sacred beliefs and rituals.
- Hopi pottery continues to influence artistic expression and cultural identity.
Historical Significance of Pottery in Hopi Culture
Pottery holds a deeply rooted historical significance in Hopi culture, reflecting the tribe's traditions, beliefs, and interconnectedness with the natural world. The economic impact of pottery on the Hopi tribe can't be overstated. For centuries, pottery has been a source of income for Hopi families, with the creation and sale of pottery serving as a vital economic activity. Additionally, pottery embodies cultural symbolism, with distinct designs and patterns that represent Hopi cosmology, mythology, and spiritual beliefs. These vessels aren't only functional but also carry deep spiritual and ceremonial significance, playing a crucial role in Hopi rituals and daily life.
Technological advancements in pottery production have also left their mark on Hopi culture. Archaeological evidence reveals the evolution of pottery-making techniques within the tribe, showcasing the innovation and skill of Hopi artisans throughout history. The introduction of new tools and materials has allowed for the refinement of pottery craftsmanship, contributing to the continued cultural significance of these creations.
Role of Pottery in Daily Life

How does the utilization of pottery in everyday activities reflect the interconnectedness of the Hopi tribe with their cultural traditions and beliefs?
Pottery plays a central role in shaping the cultural identity and traditions of the Hopi tribe. In our daily lives, pottery isn't merely a utilitarian object but a manifestation of our cultural heritage. The process of creating pottery, from gathering the clay to firing the final product, is deeply intertwined with our customs and beliefs, passed down through generations. Each piece of pottery carries with it the stories and values of our community, reinforcing our sense of belonging and connection to our ancestors.
Furthermore, pottery also sustains our economic livelihood and trade relations. The production and exchange of pottery have historically been essential for the economic sustainability of the Hopi tribe. Through trade, pottery becomes a means of fostering relationships with neighboring tribes, reinforcing social ties and ensuring the flow of essential goods.
Thus, the role of pottery in daily life extends beyond its functional use, serving as a cornerstone of our cultural, economic, and social fabric.
Ceremonial and Spiritual Importance of Hopi Pottery
In the ceremonial and spiritual practices of the Hopi tribe, pottery assumes a profound significance, serving as a conduit for the preservation and expression of sacred beliefs and rituals. The cultural symbolism embedded in Hopi pottery is deeply intertwined with their ceremonial and spiritual traditions. Each design, motif, and color used in the pottery holds specific spiritual meanings and is often tied to the tribe's creation stories, deities, and the natural world.
The act of creating pottery itself is considered a sacred process, with potters using traditional techniques passed down through generations, often accompanied by prayers and rituals to honor the earth and the ancestral spirits. The pottery isn't merely an art form but a tangible representation of the tribe's connection to their ancestors and the spiritual realm.
During important ceremonies, such as the Niman Kachina or Powamu, pottery plays a central role, being used to hold ceremonial offerings, food, and water, thereby bridging the physical and spiritual worlds. The intricate relationship between Hopi pottery and their ceremonial and spiritual practices underscores the integral role it plays in preserving and expressing their cultural heritage.
Artistic Techniques and Traditions in Hopi Pottery
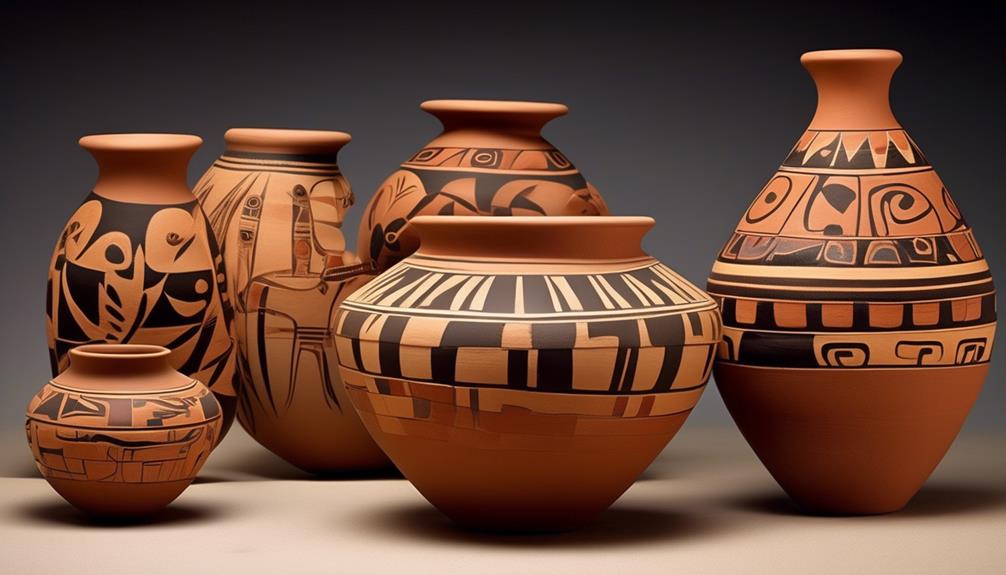

Embedded within the cultural symbolism of Hopi pottery, the artistic techniques and traditions serve as a testament to the intricate connection between the tribe's ceremonial and spiritual practices and their creative expressions. The techniques and traditions in Hopi pottery are deeply rooted in symbolism, innovation, and preservation, making them integral to the tribe's cultural identity and artistic heritage.
- Coil and scrape technique: Hopi potters use the coil and scrape method to construct their pottery. This ancient technique involves building the vessel from long coils of clay, then carefully scraping and smoothing the surface to create a polished finish.
- Symbolism in designs: Hopi pottery designs often feature symbolic elements that reflect the tribe's spiritual and ceremonial beliefs. These designs can include representations of katsinas (spirit beings), rain clouds, and other symbols significant to the Hopi culture.
- Innovation in firing: While traditional firing methods involved outdoor pit firing, contemporary Hopi potters have innovated by using modern kilns. This adaptation reflects the preservation of traditional techniques while embracing new technologies.
- Preservation of traditions: Hopi potters pass down their techniques and cultural knowledge through generations, ensuring the preservation of their unique artistic traditions.
The artistic techniques and traditions in Hopi pottery not only showcase the tribe's creativity but also serve as a means of cultural expression and preservation.
Contemporary Influence of Pottery on Hopi Culture
The contemporary significance of pottery within Hopi culture is evident through its ongoing influence on artistic expression, cultural identity, and economic sustainability. In today's interconnected world, cultural exchange plays a significant role in shaping the evolution of Hopi pottery.
Contemporary Hopi potters continue to draw inspiration from traditional techniques and designs while also incorporating new artistic elements, reflecting a dynamic exchange between the preservation of heritage and the embrace of modern influences.
Furthermore, the economic impact of pottery on the Hopi tribe can't be overstated. In addition to its cultural significance, pottery serves as a vital source of income for many Hopi families. The sale of pottery not only sustains individual livelihoods but also contributes to the economic sustainability of the entire community.
As demand for authentic Native American art continues to grow, Hopi pottery holds a unique position in the market, further bolstering the tribe's economic resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Role of Pottery in Hopi Culture?
Common misconceptions about the role of pottery in Hopi culture often overlook its deep cultural significance. Many assume it's purely a craft, but it's integral to our traditions, reflecting our history and spiritual beliefs.
Pottery has evolved artistically, yet it remains rooted in our cultural practices. Its impact on our traditions is profound, linking us to our ancestors.
Understanding this helps to appreciate the vital role pottery plays in preserving and shaping Hopi culture.
How Has the Process of Creating Pottery Evolved Over Time Within the Hopi Tribe?
Over time, the evolution of pottery-making techniques within the Hopi tribe has been captivating.
The transformative process reflects the deep-rooted cultural significance, as it encompasses traditional knowledge and artistic expression.
The evolution of techniques is evident in the refined methods of clay preparation, shaping, and firing.
These changes not only showcase innovation but also honor the timeless traditions of the Hopi people, preserving their rich cultural heritage through the art of pottery-making.
Are There Specific Rules or Taboos Surrounding the Use of Pottery in Hopi Ceremonies?
Taboos and restrictions play a crucial role in our ceremonial use of pottery. These traditional practices hold deep cultural significance for us. They guide our artistic expression and the evolution of techniques, preserving our heritage.
Technological influence and material innovation have shaped our pottery, yet we remain committed to honoring our ancestors' methods. The preservation of these customs is integral to our identity and essential in understanding the role of pottery in Hopi culture.
What Are Some Lesser-Known Styles or Techniques of Hopi Pottery That Have Been Passed Down Through Generations?
What are some lesser-known styles or techniques of Hopi pottery that have been passed down through generations?
Hopi pottery techniques encompass a wide range of traditional styles, from the famous Sikyatki and Polacca polychrome to the intricate black-on-black pottery. These techniques have been meticulously preserved and handed down through generations, serving as a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the Hopi tribe.
The pottery reflects the tribe's spiritual beliefs, stories, and connection to the land.
How Do Modern Advancements in Technology and Materials Impact the Traditional Methods of Creating Hopi Pottery?
Traditional techniques of creating Hopi pottery are integral to our cultural preservation. Modern materials and technological advancements have affected these methods, presenting both challenges and opportunities.
While they may streamline certain processes, the use of modern materials can impact the authenticity of our pottery. However, advancements in technology also provide new opportunities for innovation and artistic expression, allowing us to continue our traditions while adapting to the modern world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pottery plays a crucial role in shaping the cultural identity of the Hopi tribe.
While some may argue that modernization has diminished the significance of traditional pottery, it's important to recognize that the art form continues to thrive and evolve within the community.
The historical, practical, and spiritual aspects of pottery contribute to the preservation of Hopi culture, making it an integral part of their way of life.
Mary is a passionate writer who brings creativity and a fresh perspective to our team. Her words have the power to captivate and inspire, making her an essential contributor to our content. Mary’s commitment to storytelling and dedication to promoting Indigenous culture ensures that her work touches the hearts of our readers. We’re fortunate to have her as part of our team.
-

 Culture2 weeks ago
Culture2 weeks agoUnderstanding Aboriginal Totem Significance
-

 Torres Strait Islanders22 mins ago
Torres Strait Islanders22 mins agoSacred Healing: Discovering Indigenous Health Secrets
-

 Torres Strait Islanders1 hour ago
Torres Strait Islanders1 hour agoJourney to Wellness: Indigenous Health Product Guide
-

 Torres Strait Islanders2 hours ago
Torres Strait Islanders2 hours agoCultural Vitality: Indigenous Health Tips
-

 Torres Strait Islanders47 mins ago
Torres Strait Islanders47 mins agoEmbrace Indigenous Wisdom: Top Well-Being Products
-

 Torres Strait Islanders27 mins ago
Torres Strait Islanders27 mins agoHolistic Health: Indigenous Wellness Explored
-

 Torres Strait Islanders1 hour ago
Torres Strait Islanders1 hour agoNature’s Wisdom: Indigenous Well-Being Remedies
-

 Torres Strait Islanders28 mins ago
Torres Strait Islanders28 mins agoIndigenous Health Products Guide for Wellness













