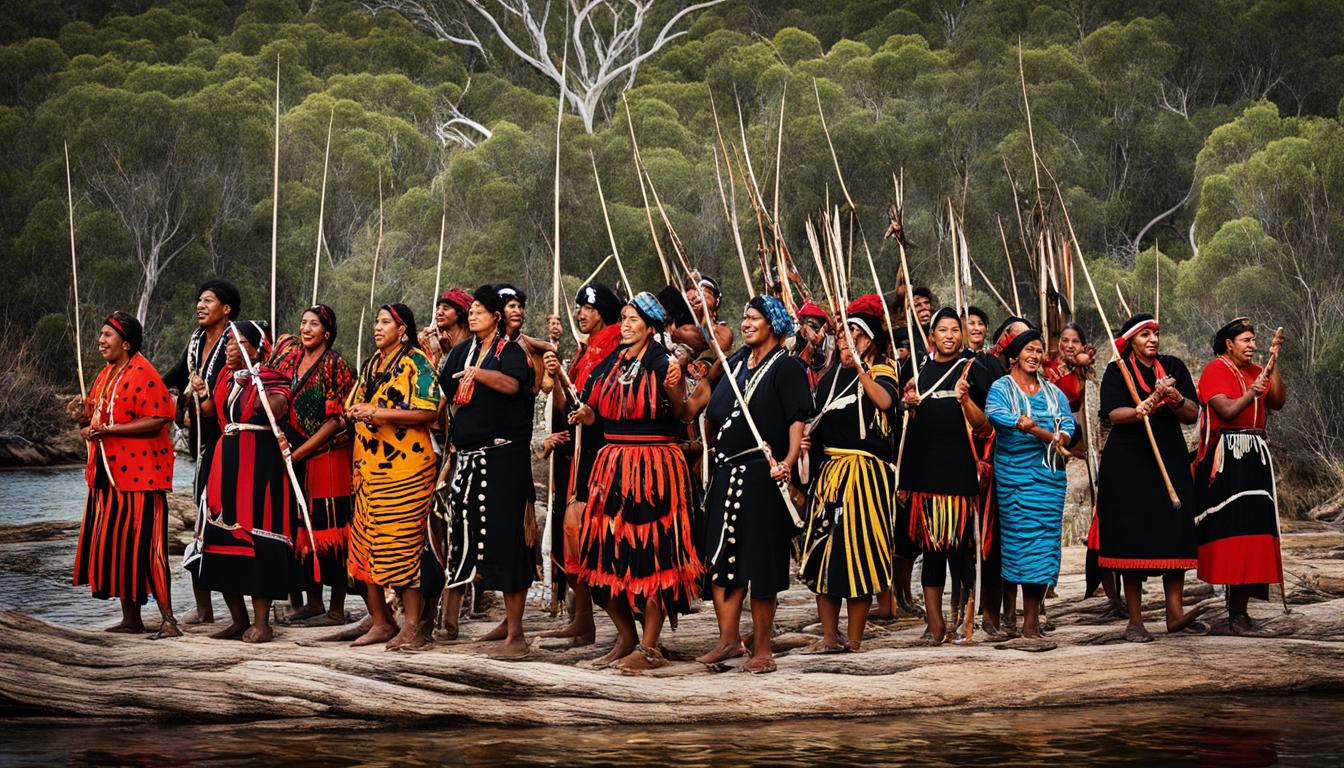
Welcome to our Language of the Month segment, where we explore the rich and diverse linguistic customs from cultures worldwide. In this edition, we are excited to focus on the Noongar language, a native tongue spoken by the Noongar community in Western Australia.
The Noongar language is a testament to the linguistic diversity found within the Australian Aboriginal community. With thirteen dialects spoken by different Noongar groups, this language offers a fascinating glimpse into the cultural heritage of the Noongar people.
Language is not just a means of communication; it is also a reflection of one’s identity and cultural heritage. By delving into the Noongar language, we gain a deeper understanding of the Noongar people’s rich history, traditions, and way of life.
Key Takeaways:
- The Noongar language is an indigenous language spoken by the Noongar people of Western Australia.
- There are thirteen dialects of the Noongar language spoken by different Noongar groups.
- Exploring the Noongar language provides insights into the cultural heritage and way of life of the Noongar people.
- Language is an integral part of identity, and studying the Noongar language helps us appreciate the linguistic diversity of the Australian Aboriginal community.
- The Noongar language is a valuable cultural resource that deserves preservation and revitalization for future generations.
Noongar Groups and Their Land
The Noongar cultural bloc is composed of 14 distinct groups, each with its own unique identity and connection to the land. These groups include:
- Amangu
- Ballardong
- Yued
- Kaneang
- Koreng
- Mineng
- Njakinjaki
- Njunga
- Pibelmen
- Pindjarup
- Wadandi
- Whadjuk
- Wiilman
- Wudjari
The Noongar people have a strong connection to their ancestral land, which they refer to as Noongar boodja. This land holds deep cultural significance for the Noongar people, as it is intertwined with their history, traditions, and spiritual beliefs.
The diversity of the Noongar groups reflects the rich cultural tapestry of the Noongar people and their deep-rooted connection to their land.
Map of Noongar Groups and Land
Explore the map below to see the different Noongar groups and their respective regions:
The map above illustrates the general regions associated with each Noongar group. The boundaries may not be exact as the Noongar cultural bloc encompasses a vast and diverse area.

Learning Sound Books, First English Words Sound Book, 21 Themes 470+ Words Interactive Electric Learning Books for Toddlers 2-6 Year Olds, Audio Books for Kids, Gifts for Boys and Girls
【Interactive Learning Experience】This engaging english words sound book introduces children to over 470 words across 21 themes, helping…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Noongar Language and Dialects
At the time of European settlement, the Noongar community spoke thirteen dialects of the Noongar language. However, today, only five dialects have speakers with living knowledge of the language. The Noongar language belongs to the Djiralay (northern dialect) group, one of the three main dialect groups within the wider Noongar region.

Despite the richness and diversity of the Noongar language, its contemporary use has significantly declined over the years. This decline can be attributed to various historical factors, including the impact of colonization and the suppression of indigenous languages.
However, efforts are being made to preserve and revitalize the Noongar language. Language revitalization programs are being implemented to teach Noongar language and culture to community members, especially the younger generation. These initiatives aim to ensure the survival and continued use of the Noongar language, which is an integral part of Noongar cultural identity.
The Importance of Language Preservation
Preserving the Noongar language is crucial for the Noongar community as it serves as a link to their cultural heritage and ancestral knowledge. Language is not merely a means of communication but also a repository of cultural practices, stories, and worldview.
“Language is at the heart of our culture. It holds the knowledge of our ancestors and connects us to the land and our traditions. By preserving and revitalizing the Noongar language, we are reclaiming our identity and strengthening our community.”
Language preservation efforts also contribute to the broader recognition and appreciation of indigenous languages and cultures. By promoting the use and value of indigenous languages, we foster inclusivity, diversity, and cultural understanding in society.

The Spell of the Sensuous: Perception and Language in a More-Than-Human World
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Noongar Ecological Context
The Noongar people have a deep connection to the land and its natural cycles. They perceive their environment through a unique lens, guided by the distinct Noongar seasons that shape their ecological context. These seasons are characterized by observable changes in the landscape, weather, and wildlife, and they serve as markers for traditional activities and resource management.
Kait (Summer)
During Kait, which roughly corresponds to the months of December and January, the Noongar people experience hot and dry conditions. The vegetation becomes sparse, and water sources may dwindle. Despite these challenges, the Noongar people have developed strategies to adapt to the harsh conditions.
Djeran (Autumn)
Djeran, falling in March and April, brings cooler weather and occasional rainfall. The landscape transforms, with new growth and blooming flowers emerging. The Noongar people engage in activities such as gathering edible wild plants and seeds, as well as hunting game that migrates or becomes more active during this season.
Makuru (Winter)
In May and June, Makuru marks the arrival of winter. The Noongar people experience colder temperatures, increased rainfall, and strong winds. This season is crucial for the replenishment of water sources and the growth of vegetation. The Noongar people focus on activities such as fishing in rivers, lakes, and wetlands, as well as gathering nuts and edible roots.
Djilba (Spring)
As spring arrives in August and September, Djilba brings milder temperatures and longer daylight hours. The Noongar people witness the blooming of wildflowers and the return of migratory birds. This season is abundant with food resources, including an array of edible plants and an increase in game availability.
Kambarang (Late Spring/Early Summer)
Kambarang, occurring in October and November, heralds the end of the Noongar year. The weather becomes warmer, and the Noongar people prepare for the upcoming hot summer. This season is characterized by the rising of water tables, providing sustenance for plants and animals. The Noongar people engage in activities such as collecting bush honey and continuing their foraging practices.
Birak (First Summer)
Birak, spanning November and December, signifies the start of the hot summer. This season is marked by high temperatures, low rainfall, and the prevalence of bushfires. The Noongar people exercise caution and respect for their environment during this time, ensuring the safety of themselves and their communities.
The Noongar people’s reliance on the land and its resources is reflected in their seasonal activities. They are skilled in navigating their unique ecological context, utilizing a diverse range of food and vegetation resources to sustain themselves and their communities. This deep connection to the land is a testament to their heritage and resilience.
| Noongar Season | Description | Activities and Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Kait (Summer) | Hot and dry conditions | Hunting game, resource conservation strategies |
| Djeran (Autumn) | Cooler weather, occasional rainfall | Gathering edible wild plants and seeds, hunting |
| Makuru (Winter) | Colder temperatures, increased rainfall | Fishing, gathering nuts and edible roots |
| Djilba (Spring) | Milder temperatures, blooming flowers | Gathering edible plants, hunting migratory birds |
| Kambarang (Late Spring/Early Summer) | Warmer weather, rising water tables | Collecting bush honey, foraging |
| Birak (First Summer) | High temperatures, low rainfall, bushfires | Cautionary practices, resource management |

550 Latin Nouns in Flash Cards
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
History of Contact and Colonization
Before the arrival of Europeans, the Noongar population in Western Australia was estimated to be between 6,000 and tens of thousands. However, with the arrival of British settlers and subsequent colonization, the Noongar people faced significant challenges and upheaval.
The impact of colonization on the Noongar population cannot be underestimated. The introduction of new diseases, along with violence and displacement, led to a dramatic reduction in the Noongar population. The disruption caused by European contact and colonization had a lasting impact on the Noongar people and their way of life.
“Our people had initial cordial relations with the settlers, but as the European settlement became more established, conflicts arose over land and resources. This led to the displacement of Noongar people from their traditional lands and the loss of their cultural practices.”
The Noongar people faced significant challenges as their land and resources were taken over by European settlers. The consequences of colonization continue to be felt today, as the Noongar people strive to reclaim their cultural heritage and regain control over their ancestral lands. Despite the adversity, the Noongar people have shown resilience and strength in preserving their identity and revitalizing their culture.
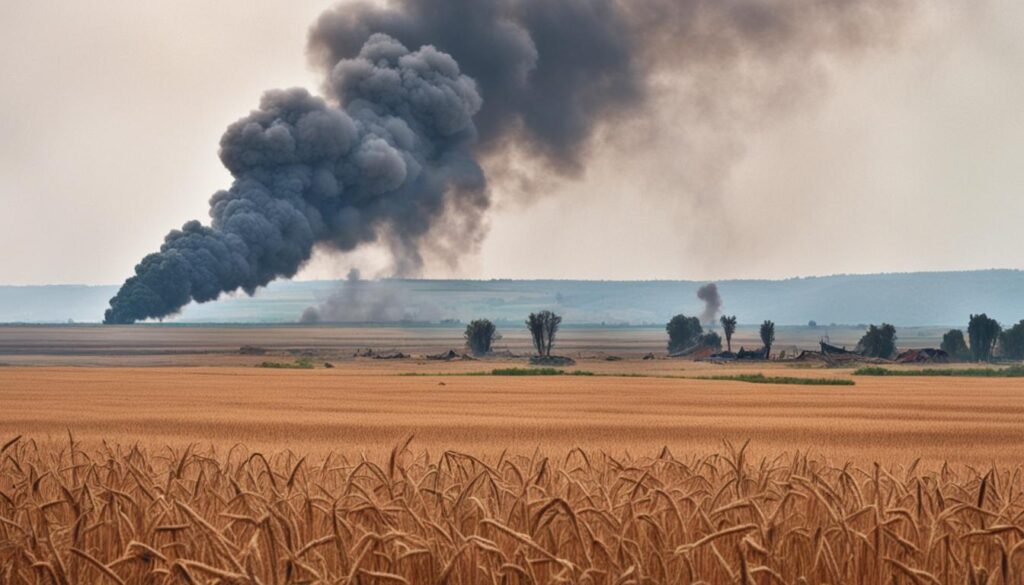

European Contact and Loss of Noongar Land
| Key Events | Impact on Noongar Land |
|---|---|
| Arrival of British settlers | Land taken over by European settlers |
| Violence and conflicts over land | Noongar people displaced from their ancestral lands |
| Loss of traditional resources | Noongar people faced challenges in sustaining their traditional way of life |
This table highlights the impact of European contact and colonization on Noongar land. It emphasizes the loss of land and resources that were vital to the Noongar people’s cultural practices and sustenance.

Australian Treasures Hand-Painted Didgeridoo with Aboriginal Motifs – Carry Bag Included – Suitable for All Skill Levels – FREE DIDGERIDOO KEYCHAIN AND DISCOUNT COUPON FOR DIDGERIDOO LESSONS INCLUDED
Resonant Teakwood Didgeridoo: Immerse yourself in the mesmerizing tones of this 51-inch Teakwood Didgeridoo, perfect for beginners and…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Cultural Significance and Language Revitalization
The Noongar language plays a pivotal role in preserving the cultural heritage of the Noongar people. We recognize the immense significance that language holds in shaping and preserving cultural identity. As such, efforts are being made to prioritize the preservation and revitalization of the Noongar language.
Language preservation is crucial not only for the Noongar community but also for the broader understanding and appreciation of indigenous cultures. By safeguarding the Noongar language, we are actively preserving a rich and ancient heritage that has shaped the identity and traditions of the Noongar people for generations.
To ensure the survival of the Noongar language for future generations, various programs and initiatives have been implemented. These include language learning classes, cultural immersion workshops, and the development of educational resources. Through these initiatives, individuals can engage with the Noongar language, deepening their connection to the cultural heritage it encompasses.
Language revitalization goes hand in hand with cultural revitalization. By revitalizing the Noongar language, we are actively working towards the preservation and promotion of Noongar cultural practices, traditions, and knowledge systems. This holistic approach ensures that the Noongar community’s cultural heritage remains intact, strengthening their sense of identity and fostering a greater appreciation for Noongar traditions.
“Language preservation is an essential part of protecting and maintaining the rich cultural heritage of indigenous communities.” – Noongar Elder
The importance of preserving and revitalizing the Noongar language extends beyond the community itself. It serves as a reminder of the diverse linguistic landscape of our world and the importance of cultural diversity. The Noongar language stands as a testament to the unique heritage and knowledge passed down through generations.
By supporting Noongar language preservation and revitalization efforts, we contribute to the broader goal of safeguarding and celebrating indigenous cultures. Together, we can ensure the legacy of the Noongar people and their cultural heritage lives on for generations to come.
Importance of Reviving Indigenous Languages
In our journey to explore Noongar culture and language, we have come to understand the significance of reviving indigenous languages. It is not merely a matter of linguistic preservation, but a fundamental act of cultural preservation and identity.
Language and culture are intimately linked, forming the pillars of a community’s heritage and traditions. When indigenous languages fade away, it is not just words that are lost; it is an entire worldview, a treasure trove of cultural knowledge and practices that vanish into the depths of history.

Reviving and preserving indigenous languages, such as the Noongar language, is a crucial endeavor that goes beyond language revival. It is about honoring and safeguarding the unique cultural diversity that indigenous communities have nurtured for centuries.
“Language revitalization is the key to sustaining the rich tapestry of indigenous cultures, allowing them to thrive and flourish in the modern world.”
Reviving indigenous languages serves as a powerful act of resistance against cultural assimilation and colonial erasure. It asserts the worth and value of indigenous cultures, reclaiming and affirming their rightful place in the tapestry of human diversity.
By reviving and preserving indigenous languages, we create opportunities for indigenous communities to reconnect with their cultural heritage and transmit it to future generations. A revived language becomes a bridge to the past, a celebration of indigenous identity, and a powerful tool for cultural revival and resilience.
The Impact of Language Revival
Reviving indigenous languages brings profound benefits to both individuals and communities:
- Preserving Cultural Knowledge: Indigenous languages serve as repositories of cultural knowledge, encompassing traditional wisdom, folklore, spirituality, and the deep connection between humans and the land.
- Fostering Cultural Pride: Language revival strengthens cultural identity, providing a sense of belonging and pride for indigenous individuals, reinforcing their resilience in the face of historical trauma and ongoing challenges.
- Celebrating Linguistic Diversity: Language diversity is a testament to humanity’s collective creativity and resilience. Reviving indigenous languages adds depth to the rich tapestry of global linguistic diversity, fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
- Enhancing Community Well-being: Language revival initiatives create a sense of solidarity and social cohesion within indigenous communities. They empower individuals, instill a sense of cultural continuity, and contribute to overall community well-being.
“Reviving indigenous languages is not mere nostalgia; it is an act of cultural and linguistic resilience that enriches us all.”
The Way Forward
To ensure the revival and preservation of indigenous languages, collaboration and support from all stakeholders are essential. Governments, educational institutions, community organizations, and individuals must come together to provide resources, funding, and opportunities for language revitalization.
Language revitalization programs, immersion experiences, and the integration of indigenous languages into formal education systems are vital steppingstones toward the long-term sustainability of indigenous languages and cultures.
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Loss of fluent speakers | Collaboration between indigenous and non-indigenous communities |
| Impact of colonization | Support from governments and educational institutions |
| Limited resources | Advocacy for indigenous language revitalization |
| Engaging the younger generation | Integration of indigenous languages into formal education |
“Together, we can ensure the survival of indigenous languages and contribute to the vibrant tapestry of human cultural heritage.”
Learning Noongar Language and Culture
Learning indigenous languages is not only a way to gain linguistic skills but also an opportunity to engage with and respect different cultures. If you are interested in delving into the Noongar language and culture, there are various resources available to assist you on your journey. These resources will not only enhance your language learning experience but also provide insights into the rich heritage of the Noongar people.
Language learning kits, guides, and online resources can serve as valuable tools for individuals interested in learning the Noongar language. These materials can provide structured lessons, vocabulary, grammar explanations, and exercises to help you develop your proficiency. By immersing yourself in these resources, you can build a solid foundation in the Noongar language.
Cultural immersion programs and activities offer another avenue to deepen your understanding of the Noongar language and culture. These programs allow you to engage with native speakers, learn from their firsthand experiences, and participate in traditional practices. Through cultural immersion, you can gain a holistic perspective and develop a more profound appreciation for the Noongar way of life.
“Language is the road map of a culture. It tells you where its people come from and where they are going.” – Rita Mae Brown
Noongar Language Learning Resources
Here are some recommended resources to get you started on your Noongar language learning journey:
- Noongar Dictionary by Yorgum Language Centre
- Noongar Language and Culture Centre
- Online language learning platforms such as Duolingo or Memrise (Note: availability may vary)
These resources can provide structured language lessons, vocabulary, and exercises to help you learn the basics of the Noongar language. Alongside language learning, it is essential to immerse yourself in the cultural context to gain a deeper understanding of the Noongar people and their traditions.
Remember, language learning is a continuous process, and it requires dedication and practice. Embrace the journey as you explore the Noongar language and culture, and let your newfound knowledge contribute to a more inclusive and diverse society.
Your Language Learning Journey
“Language is not just a communication tool; it is the lifeblood of a community’s identity and cultural heritage.”
Embarking on the journey of learning an indigenous language like Noongar is not only a personal endeavor but also a step towards cultural preservation and appreciation. By immersing ourselves in the richness of indigenous languages, we honor and uphold the diverse heritage of communities and help ensure their languages thrive.
Throughout this article, we have explored the Noongar language and its significance within the Noongar cultural bloc. From understanding the various Noongar groups and their land to delving into the ecological context and history of contact, we have gained insights into the intricate tapestry of the Noongar culture.
Learning the Noongar language and culture allows us to engage with and respect the Noongar people and their heritage. By delving into language learning resources and exploring cultural immersion programs, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Noongar language’s nuances and the cultural practices and traditions that shape the Noongar way of life.
So, let us take the leap and embark on this linguistic and cultural journey together. By embracing indigenous languages like Noongar, we not only enrich our own lives but also contribute to the preservation and celebration of vibrant cultural identities.
Reclaiming Noongar Place Names
Reclaiming Noongar place names is a crucial step in the ongoing preservation of Noongar culture and heritage. As Noongar people, we are actively involved in various projects aimed at reclaiming and explaining the original Noongar names of places in Western Australia. These efforts serve to reconnect us with our ancestral lands and maintain the significance of these places within the broader cultural context.
Reclaiming Noongar place names is not only about restoring historical accuracy but also about honoring our connection to the land and preserving our cultural identity. By restoring these names, we bring to light the deep historical and spiritual significance that these places hold for the Noongar people.
Our efforts to reclaim Noongar place names involve extensive research, consultation with elders, and collaboration with local communities and government entities. The knowledge and wisdom passed down from generation to generation guide us in the process of uncovering and documenting these names, ensuring their accuracy and cultural relevance.
Reconnecting with Ancestral Lands
Reclaiming and reinstating Noongar place names allows us to reestablish a meaningful connection to our ancestral lands. These names represent more than just geographical locations; they embody our cultural heritage, our spiritual beliefs, and our deep relationship with the land and its ecosystems.
By reclaiming Noongar place names, we reaffirm our identity as Noongar people and foster a sense of belonging within our communities. It serves as a reminder of our ancestors’ enduring presence and their intimate understanding of the land and its natural rhythms.
“Reclaiming Noongar place names is an ongoing process, one that requires collective effort and a commitment to preserving our cultural heritage. It is a way to honor our ancestors, ensure the survival of our language and traditions, and pass down our knowledge to future generations.”
The Significance of Noongar Place Names
Noongar place names carry a wealth of cultural and historical information. They reflect the Noongar people’s deep understanding of the land, its features, and its resources. These names often describe the physical characteristics, ecological importance, and spiritual significance of the places they denote.
When we reclaim Noongar place names, we rediscover the stories and knowledge that have been intricately tied to these locations for thousands of years. These names tell tales of creation, connection, and survival, offering valuable insights into our cultural heritage and the rich tapestry of Noongar traditions.
The Journey of Reclamation
The process of reclaiming Noongar place names is a collaborative endeavor that involves the wider Noongar community, cultural organizations, and government bodies. It requires a concerted effort to research historical records, consult with Noongar elders, and engage with local communities to ensure the accuracy and authenticity of the names.
Through educational programs, community workshops, and cultural events, we strive to raise awareness and appreciation for Noongar place names. By sharing the stories behind these names, we foster a deeper understanding and respect for Noongar culture among both Noongar and non-Noongar people.
Reclaiming Noongar place names is an ongoing journey, one that requires continuous dedication and support. It is a testament to our commitment to preserving our cultural heritage and passing it on to future generations.
| Noongar Place Name | English Equivalent |
|---|---|
| Bilya | River |
| Kakarup | Hill |
| Kwobidak | Lake |
| Booranie | Spring |
| Wilgara | Coast |
The Significance of Birds in Noongar Culture
Birds play a vital role in Noongar culture, symbolizing the deep connection between the Noongar people and their natural environment. The Noongar language reflects this relationship through the names given to birds, which often mimic the sounds of their calls. By learning the Noongar names of birds, we can gain insights into the rich cultural heritage and the intricate bond between the Noongar community and the avian world.
Here are some common Noongar bird names:
- Djiti Djiti (Willie Wagtail)
- Karrak (Red Tailed Black Cockatoo)
- Djer-Djer (Splendid Blue Wren)
These bird names hold deep meaning within Noongar culture, embodying the essence and characteristics of each bird species. They reflect the unique observations and interpretations of the Noongar people, passed down through generations.
In Noongar culture, birds are not merely creatures of the natural world. They are also intertwined with spirituality, serving as messengers between the physical and spiritual realms. Birds are seen as keepers of knowledge and play a significant role in the Dreamtime stories, which explain the creation of the land and its features.
The Symbolism of Noongar Birds
Noongar birds hold symbolic meanings that go beyond their natural traits. They are often associated with specific qualities or convey messages that hold significance within Noongar cultural beliefs. Here are a few examples:
| Noongar Bird | Symbolic Meaning |
|---|---|
| Djiti Djiti (Willie Wagtail) | Alertness, protection, and warning of danger |
| Karrak (Red Tailed Black Cockatoo) | Power, resilience, and connection to ancestral spirits |
| Djer-Djer (Splendid Blue Wren) | Beauty, grace, and the importance of harmony |
These symbolic meanings vary across Noongar groups and may have different interpretations based on personal experiences and cultural contexts.
“Birds hold a special place in Noongar culture, representing not only the beauty and diversity of the natural world but also carrying profound spiritual significance. The Noongar names for birds reflect the deep understanding and reverence the Noongar people have for their environment.”
Understanding the role of birds in Noongar culture fosters greater appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living beings and their environments. It is a reminder of the importance of conservation efforts to protect not only the avian species but also the cultural heritage and wisdom they embody.
Connection to the Land and Creation Stories
Noongar people have a profound and enduring connection to the land, which is deeply rooted in their cultural beliefs and values. Central to their cultural identity are the creation stories that explain the origins of the land and its features. These stories are passed down through generations, carrying the wisdom and spiritual understanding of the Noongar people.
The Dreamtime, also known as the Dreaming or Ngarrangkarni, is a significant concept in Noongar culture. It represents the time of creation when ancestral spirits shaped the land and all living things. According to Noongar beliefs, the Dreamtime is an eternal and interwoven realm where the spiritual and physical aspects of existence intersect.
“The land is a living entity, and the Dreamtime is our guide to understanding its creation and the spiritual essence that dwells within.” – Elder Noongar storykeeper
Noongar creation stories reveal the cultural beliefs and values that guide the Noongar people’s interactions with the land and each other. These stories provide insights into the interconnectedness of all living beings and the importance of reciprocity and respect for the land and its resources. They teach valuable lessons about the relationship between humans, nature, and the spiritual realm.
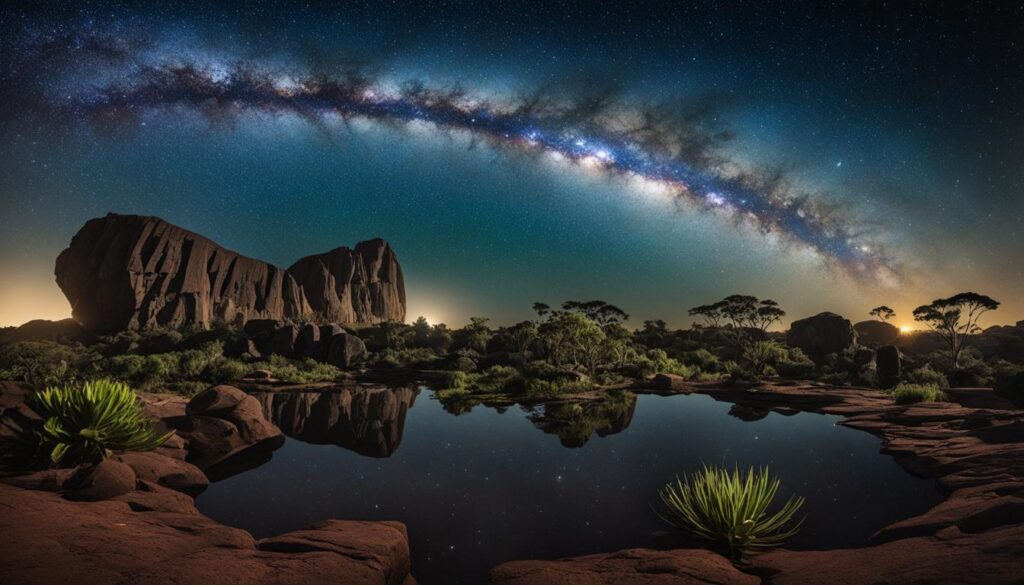

The Significance of Creation Stories
Creation stories act as a cultural compass, shaping Noongar identity and reinforcing the importance of cultural preservation. They provide a sense of belonging, grounding the Noongar people in their ancestral land and fostering a deep respect for the natural environment.
Through these timeless stories, the Noongar people pass on their cultural knowledge, traditions, and customs, ensuring that future generations understand the intimate connection between their cultural heritage and the land they call home.
Noongar Cultural Practices and Traditions
Noongar people have a rich cultural heritage consisting of various cultural practices and traditions. These include storytelling, dance, music, and art. Noongar cultural practices and traditions are deeply rooted in their connection to the land, their spirituality, and their social structures. Engaging with these cultural practices is a way to honor and preserve Noongar cultural identity.
The Art of Storytelling
Storytelling is an integral part of Noongar culture, passed down through generations. Through oral narratives, Noongar people share their history, knowledge, and values, connecting past and present. Traditional stories often reflect the relationship between the Noongar people and the land, animals, and celestial beings. Storytelling is not only a means of preserving cultural heritage but also a way to educate and entertain.
The Language of Dance
Dance plays a vital role in Noongar cultural practices, serving as a form of expression, communication, and storytelling. Each dance has its own significance, representing specific events, seasons, or animals. The rhythmic movements, gestures, and songs convey ancestral knowledge and celebrate the interconnectedness of Noongar people with the land. Dance is a powerful way to maintain cultural traditions and strengthen community bonds.
The Melody of Music
Music holds a special place in Noongar culture, with traditional songs and instruments serving as pathways to spiritual connections and cultural identity. Noongar music often combines rhythmic percussion, vocals, and natural sounds to evoke emotional responses and convey cultural meanings. Songs are passed down through generations, carrying the ancient wisdom and experiences of the Noongar people.
The Essence of Art
Artistic expression is intrinsic to Noongar culture, manifesting in various forms such as painting, carving, weaving, and ceremonial decorations. Noongar art is inspired by the intricate patterns found in nature and the Dreamtime stories of creation. It serves as a visual language, depicting cultural symbols, ancestral connections, and contemporary experiences. Noongar art not only preserves cultural traditions but also allows for artistic innovation and personal expression.
| Cultural Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Storytelling | Ancient narratives passed down through generations, sharing history, knowledge, and values. |
| Dance | Rhythmic movements and gestures representing specific events, seasons, or animals. |
| Music | Traditional songs and instruments carrying spiritual connections and cultural identity. |
| Art | Expression through painting, carving, weaving, and ceremonial decorations, depicting cultural symbols and ancestral connections. |
Challenges and Opportunities in Cultural Preservation
Preserving and revitalizing the Noongar language and culture face several challenges but also present opportunities for collaboration and support. The loss of fluent speakers and the impact of colonization pose significant hurdles. However, various organizations, institutions, and communities are actively involved in cultural revitalization efforts to ensure the preservation and revitalization of Noongar culture.
Language programs play a crucial role in preserving the Noongar language. These programs focus on teaching and promoting the language among younger generations. They aim to restore fluency and encourage its use in everyday life, thereby strengthening the connection to cultural heritage.
Cultural events provide platforms for showcasing Noongar traditions, arts, and crafts. Festivals and exhibitions celebrate Noongar culture and help raise awareness among the wider community. By inviting participation and engagement, these events foster a deeper appreciation for Noongar customs and traditions.
Collaborations between Noongar and non-Noongar groups are essential for the long-term sustainability of Noongar language and culture. These partnerships facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise. They also offer opportunities for mutual learning and understanding, promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity.
Intergenerational initiatives are designed to bridge the gap between generations and pass on cultural knowledge. Elderly Noongar community members serve as language and cultural mentors, ensuring that traditional practices and values continue to be transmitted to younger individuals.
By working together, we can create an environment that nurtures the Noongar language and culture. Collaborations facilitate the development of comprehensive strategies, resource allocation, and policy implementation necessary for their preservation. It is through these collective efforts that the challenges can be overcome and opportunities can be maximized for the enduring cultural preservation of the Noongar community.
Importance of Cultural Diversity and Recognition
Cultural diversity is a vital aspect of human society. It encompasses the richness of various cultures, traditions, and perspectives that contribute to a vibrant global community. In this context, recognizing and valuing indigenous cultures, such as the Noongar culture, is essential for promoting inclusivity, understanding, and respect.
Indigenous cultures possess unique knowledge, traditions, and perspectives that enrich the broader cultural landscape. Their ancestral wisdom, passed down through generations, holds valuable insights into sustainable practices, environmental stewardship, and holistic relationships with the natural world. Through recognizing and embracing indigenous cultures, we foster a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all people and the planet.
“The protection and respect of indigenous cultural heritage are vital for preserving the diversity and integrity of our collective human experience.”
Protecting and respecting indigenous cultural heritage is paramount in ensuring the continued existence and flourishing of diverse cultural practices and expressions. Indigenous communities often face significant challenges in preserving their traditions and safeguarding their cultural heritage. By actively supporting and engaging with indigenous cultures, we contribute to the revitalization and safeguarding of their rich language, art, music, storytelling, and ceremonial practices.
Promoting Cultural Exchange and Dialogue
Recognizing and valuing indigenous cultures go beyond surface-level appreciation. It involves fostering meaningful and reciprocal relationships based on mutual respect and understanding. By actively engaging with and learning from indigenous cultures, we create opportunities for cultural exchange, dialogue, and shared experiences.
Cultural diversity and recognition provide a foundation for building inclusive societies that embrace the uniqueness of every individual and community. By celebrating indigenous cultures, we cultivate an environment that nurtures cultural expression, supports cultural preservation efforts, and fosters intercultural dialogue that leads to a deeper understanding and appreciation of one another.
Embracing cultural diversity and recognizing the importance of indigenous cultures safeguards the richness of our collective human heritage and helps to shape a more inclusive and harmonious world.
The Benefits of Cultural Diversity and Recognition
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Preservation of Cultural Heritage | Recognition of indigenous cultures ensures the survival and transmission of traditional practices, languages, and knowledge. |
| Fostering Social Cohesion | Cultural diversity and recognition promote social cohesion, reduce prejudice and discrimination, and enhance intercultural understanding and empathy. |
| Enriching Cultural Expression | Embracing diverse cultural practices and expressions fosters creativity, innovation, and new perspectives on art, music, dance, literature, and more. |
| Enhancing Global Perspectives | Recognition of indigenous cultures broadens our understanding of global history, challenges dominant narratives, and encourages intercultural dialogue that leads to innovative solutions. |
| Promoting Sustainable Practices | Indigenous cultures provide valuable insights into sustainable practices, ecological wisdom, and the protection of natural resources. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, our exploration of Noongar culture and language has provided valuable insights into the rich cultural heritage of the Noongar people. The Noongar language, consisting of thirteen dialects, plays a significant role in their cultural identity. Preserving and revitalizing the Noongar language and culture is essential for the continued existence and cultural sustainability of the Noongar community.
Efforts are being made to ensure the survival of the Noongar language through various programs and initiatives. These initiatives aim to teach and promote the Noongar language, allowing future generations to connect with their cultural heritage. By embracing and respecting indigenous languages and cultures, we contribute to a more inclusive and diverse society.
By recognizing the importance of cultural diversity and heritage protection, we uphold the value of indigenous cultures like the Noongar culture. The unique knowledge, traditions, and perspectives of indigenous communities enrich our broader cultural landscape. It is our responsibility to protect and respect their cultural heritage, ensuring the continued existence and flourishing of diverse cultural practices and expressions.
FAQ
What are the different groups within the Noongar cultural bloc?
The Noongar cultural bloc consists of 14 different groups, including Amangu, Ballardong, Yued, Kaneang, Koreng, Mineng, Njakinjaki, Njunga, Pibelmen, Pindjarup, Wadandi, Whadjuk, Wiilman, and Wudjari.
How many dialects of the Noongar language are spoken?
There are thirteen dialects of the Noongar language spoken within the Noongar cultural bloc.
What is the ecological context for the Noongar people?
The Noongar people have six seasons that define their ecological context, and they rely on a variety of food and vegetation resources, including game, edible wild plants, and nuts.
What was the impact of colonization on the Noongar population?
The Noongar population was significantly reduced due to violence and new diseases introduced by European settlers. Initial cordial relations with settlers deteriorated as conflicts arose over land and resources.
Why is language revitalization important for the Noongar people?
The Noongar language and cultural heritage hold great significance to the Noongar people. Efforts to preserve and revitalize the Noongar language are crucial for the continued existence and cultural sustainability of the Noongar community.
Why is reviving indigenous languages important?
Reviving indigenous languages, such as the Noongar language, is crucial for cultural preservation and identity. Language is closely tied to culture, and the loss of indigenous languages can result in the erasure of cultural knowledge and practices.
Are there resources available for learning the Noongar language?
Yes, there are resources available for individuals interested in learning the Noongar language, including language learning kits, guides, and online resources. Cultural immersion programs and activities can also provide a deeper understanding of the Noongar language and culture.
Why is reclaiming Noongar place names important?
Reclaiming Noongar place names is an important aspect of preserving Noongar culture and heritage. These efforts help reconnect Noongar people with their ancestral lands and maintain the significance of these places within their cultural context.
What is the significance of birds in Noongar culture?
Birds hold significance in Noongar culture, and their names in the Noongar language often reflect the sounds of their calls. Learning the Noongar names of birds can provide insights into the relationship between Noongar people and their natural environment.
What are Noongar creation stories?
Noongar creation stories explain the origins of the land and its features. The Dreamtime, a significant concept in Noongar culture, represents the time of creation and the intertwining of spiritual and physical aspects of existence.
What are some Noongar cultural practices and traditions?
Noongar cultural practices and traditions include storytelling, dance, music, and art. These practices are deeply rooted in their connection to the land, spirituality, and social structures.
What challenges exist in preserving Noongar language and culture?
Challenges in preserving Noongar language and culture include the loss of fluent speakers and the impact of colonization. However, there are opportunities for collaboration and support from various organizations, institutions, and communities to ensure their preservation.
Why is recognition of indigenous cultures important?
Cultural diversity is a vital aspect of human society, and recognizing and valuing indigenous cultures, such as the Noongar culture, is essential for promoting inclusivity and understanding. Protecting and respecting indigenous cultural heritage helps to ensure the continued existence and flourishing of diverse cultural practices and expressions.






