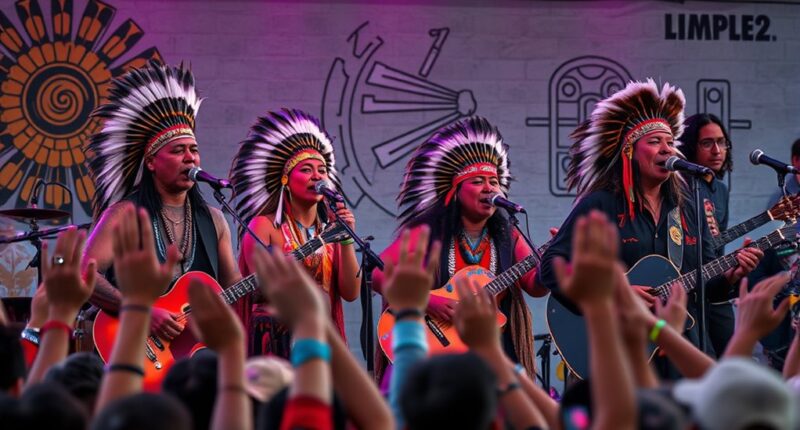
Music as protest empowers you to connect emotionally, unite communities, and challenge injustice, as seen with Yothu Yindi’s iconic “Treaty” which became a symbol for Indigenous rights in Australia. Their blend of traditional sounds and contemporary styles keeps cultural stories alive and inspires activism. Beyond Yothu Yindi, many artists harness music to resist oppression and preserve identities worldwide. To discover how these powerful melodies continue to shape social change, explore the ongoing legacy of Indigenous music and activism.
Key Takeaways
- Yothu Yindi’s “Treaty” became a symbol of Indigenous rights and political activism in Australia.
- Music serves as a powerful tool for cultural resistance, preserving Indigenous stories and challenging colonial narratives.
- Indigenous artists blend traditional sounds with contemporary styles to foster pride and engage youth.
- Music transforms activism into accessible, emotional expressions that unite communities and inspire social change.
- The legacy of Yothu Yindi exemplifies how music can sustain cultural resilience and advocate for justice beyond borders.
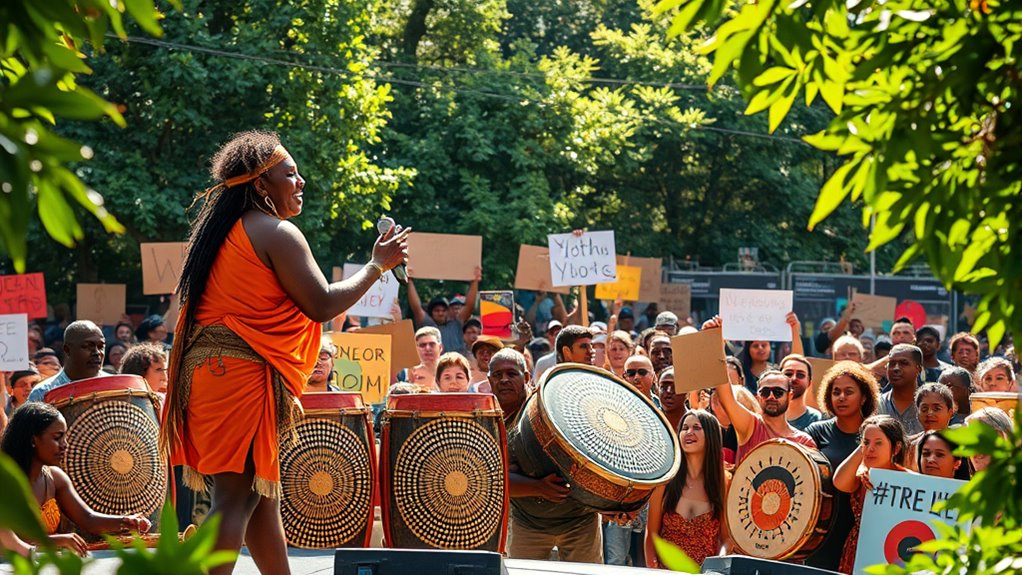

Have you ever wondered how music becomes a powerful tool for protest? It’s because music has a unique ability to evoke emotion, unite people, and communicate messages that words alone might fail to express. When it comes to Indigenous activism, music often plays a pivotal role in rallying communities and raising awareness about cultural resistance. Artists like Yothu Yindi exemplify how melodies and lyrics can serve as voices for marginalized groups, amplifying their struggles and aspirations. Through their songs, they not only celebrate Indigenous identity but also challenge injustices rooted in history and policy. It’s a form of cultural resistance that transcends spoken language, making it accessible and resonant across generations and borders.
In the context of Indigenous activism, music becomes more than entertainment; it’s a declaration of sovereignty and pride. When Indigenous artists incorporate traditional sounds with contemporary styles, they create a powerful fusion that underscores the importance of cultural preservation. This blending helps keep ancestral stories alive while also engaging younger audiences, ensuring that the message of resistance endures. By doing so, music transforms into a rallying cry that fosters community solidarity and asserts Indigenous rights in the face of ongoing marginalization. It’s a form of cultural resistance that not only challenges the cultural dominance of colonial narratives but also reclaims space for Indigenous voices to be heard and respected.
Yothu Yindi’s rise to prominence illustrates this phenomenon vividly. Their song “Treaty” became an anthem for Indigenous rights in Australia, symbolizing a demand for recognition and justice. The band’s success demonstrated how music could serve as a platform for activism, turning cultural expression into political action. Through their lyrics and performances, they communicated a message that resonated beyond the music industry, inspiring Indigenous communities and allies worldwide. Their work shows that music can be a form of resistance that preserves cultural identity while advocating for change. It’s a reminder that, when rooted in cultural authenticity, music can challenge oppressive systems and foster a sense of empowerment.
Beyond Yothu Yindi, countless other artists have used their craft to push for Indigenous causes and cultural resistance. Whether through protest songs, traditional melodies, or contemporary fusion, music becomes a vessel for storytelling and activism. You can see it as a way to honor heritage, resist assimilation, and demand recognition. In this way, music isn’t just entertainment; it’s a essential tool for Indigenous activism—a rallying force that keeps cultural resistance alive and thriving in the face of adversity.

Music in Brazil: Experiencing Music, Expressing CultureIncludes CD (Global Music Series)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Did Yothu Yindi Influence Indigenous Rights Movements Globally?
You see, Yothu Yindi influenced global indigenous rights movements by blending cultural exchange with political activism. Their music raised awareness and inspired communities worldwide to stand up for their rights. By incorporating traditional sounds and messages, they fostered understanding and solidarity across cultures. Their powerful activism through music showed how art can unite people, motivate change, and push for recognition and justice for indigenous peoples everywhere.
What Are the Most Significant Songs That Became Protest Anthems?
You’ll find that songs like “Beds Are Burning” by Midnight Oil and “We Shall Not Be Moved” serve as powerful protest anthems. These tracks embody Cultural Resistance and allow you to express your Identity through music. They rally people around important causes, inspiring action and unity. By singing these anthems, you actively participate in social change, making your voice heard and highlighting issues that matter to you.
How Has Indigenous Language Preservation Impacted Protest Music?
Like planting seeds in fertile ground, indigenous language preservation enriches protest music by strengthening cultural identity. When artists revitalize their languages, they create powerful anthems that resonate deeply, highlighting issues like land rights and social justice. This revitalization breathes new life into traditions, making protest songs more authentic and impactful. It’s a crucial tool for communities to voice their struggles and keep their heritage alive, ensuring their stories aren’t lost in the sands of time.
What Role Does Music Play in Reconciliation Processes?
Music plays a essential role in reconciliation by fostering cultural healing and community building. When you engage with music that celebrates indigenous traditions, you help bridge gaps and promote understanding. It creates shared experiences, heals wounds from past injustices, and strengthens community bonds. Through song, you participate in a collective journey toward reconciliation, honoring cultural diversity and fostering respect, ultimately helping to build a more inclusive and harmonious society.
Are There Contemporary Artists Continuing Yothu Yindi’s Legacy?
You see vibrant murals of Indigenous artists collaborating with diverse musicians, symbolizing ongoing cultural bridges. Contemporary artists continue Yothu Yindi’s legacy through powerful Indigenous collaborations, blending traditional sounds with modern music. These artists paint a fresh, dynamic picture of reconciliation, echoing the past while forging new paths. Their work embodies resilience and unity, inspiring change and awareness, ensuring the spirit of Yothu Yindi’s message remains alive in today’s musical landscape.

Modern Jazz & Fusion Guitar Book/Online Media
Book/Online Video
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
Music has the power to challenge injustice and inspire change. Yothu Yindi’s legacy proves that melodies can become a form of resistance, uniting communities and amplifying voices often unheard. As you reflect on their impact, ask yourself: isn’t it music’s ability to evoke emotion and ignite action that makes it such a potent tool for protest? When we harness music’s strength, we carry forward the fight for a more just and equitable world.

Native American Tribes Map Indigenous Peoples Day Decorations Heritage History Classroom Decor Cool Wall Art Print Poster 16×24
Poster measures 16×24 inches (41×61 cm) and ideal size for any standard 16×24 frame. Lightweight and low-glare satin…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

El Sistema: Music to Change Life
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.