Have you ever thought about the types of foods that make up the traditional diet of Aboriginal Australians? The dietary practices of Indigenous Australians have long been a source of fascination for good reason.
The rich and diverse landscape of Australia has provided a variety of unique food sources for Aboriginal communities to utilize, each with its own nutritional and cultural significance. From traditional protein sources to edible plants and bush tucker, the Aboriginal diet offers a fascinating glimpse into the connection between food, culture, and the land.
Key Takeaways
- Aboriginal Australians have a diverse diet that includes traditional protein sources such as kangaroo, emu, fish, and shellfish.
- Indigenous fruits and vegetables like bush tomato, Kakadu plum, quandong, and muntries are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C and are used in various culinary preparations.
- Foraging for edible plants and bush tucker is an important practice for Aboriginal Australians, with a focus on sustainable techniques and preservation.
- Traditional foods hold cultural significance, reflecting a connection to the land, honoring seasonal cycles, fostering social cohesion, and preserving unique cultural heritage.
Traditional Protein Sources
Aboriginal Australians traditionally hunted and gathered a diverse range of protein sources from the land and sea, including kangaroo, emu, fish, and shellfish. Traditional hunting and sustainable foraging were integral to the Aboriginal Australian way of life, providing not only sustenance but also a deep cultural connection to the land.
The hunting of kangaroos, known for its lean and nutritious meat, required great skill and knowledge of the animal's behavior and habitat. Similarly, the pursuit of emus, with their large, flightless bodies, demanded careful planning and communal cooperation.
Moreover, the rich waters surrounding the continent offered an abundance of fish and shellfish, which were harvested using traditional methods passed down through generations. The sustainability of foraging practices ensured that these vital resources would continue to be available for future generations.
The gathering of such protein sources wasn't merely a means of survival but a deeply ingrained cultural practice, with rituals and traditions associated with the hunting and preparation of these foods. Understanding the significance of these traditional protein sources provides insight into the deep-rooted connection between Aboriginal Australians and the natural world.
Indigenous Fruits and Vegetables

In the lush landscapes of Australia, a vibrant array of indigenous fruits and vegetables thrives, each offering a unique blend of flavors and nutritional benefits deeply intertwined with the cultural heritage of the land's traditional custodians. These native foods have sustained Aboriginal Australians for generations, providing essential nutrients and forming a crucial part of their culinary traditions. Here are some examples of indigenous fruits and vegetables, showcasing their nutritional value and culinary uses:
| Indigenous Fruits | Nutritional Value & Culinary Uses |
|---|---|
| Bush Tomato | Rich in antioxidants and used in chutneys and sauces. |
| Kakadu Plum | High in vitamin C and utilized in jams, sauces, and marinades. |
| Quandong | Packed with vitamin C and used in jams, pies, and desserts. |
| Muntries | Abundant in antioxidants and employed in jams, jellies, and chutneys. |
These indigenous fruits not only contribute to a diverse and flavorful diet but also hold significant cultural importance, reflecting the deep connection between Aboriginal Australians and the land. As we continue to explore the traditional foods of Aboriginal Australians, it becomes evident that these fruits and vegetables are not only nourishing but also an integral part of their rich cultural tapestry.
Edible Plants and Bush Tucker
Exploring the vast Australian landscape reveals an abundance of edible plants and bush tucker, each offering a unique blend of flavors deeply rooted in the cultural heritage of the land's traditional custodians.
- Foraging Techniques
- The art of foraging for edible plants and bush tucker involves a deep understanding of the land, passed down through generations. Indigenous Australians possess intricate knowledge of the seasonal cycles and specific habitats where these plants thrive.
- Sustainable practices are paramount in foraging, ensuring that the land continues to yield an abundance of these edible treasures for generations to come.
- Culinary Uses
- These indigenous plants and bush tucker aren't only rich in cultural significance but also boast a diverse range of culinary uses. From the tangy, citrusy flavors of finger limes to the earthy, nutty taste of wattleseed, each ingredient adds depth and complexity to traditional dishes.
- The nutritional value of these native plants is remarkable, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that have sustained Aboriginal communities for centuries.
As we immerse ourselves in the rich tapestry of Aboriginal Australian culture, it becomes evident that the foraging techniques and culinary uses of these edible plants and bush tucker are deeply intertwined with sustainable practices, preserving both the land and the heritage of its custodians.
Hunting and Gathering Techniques
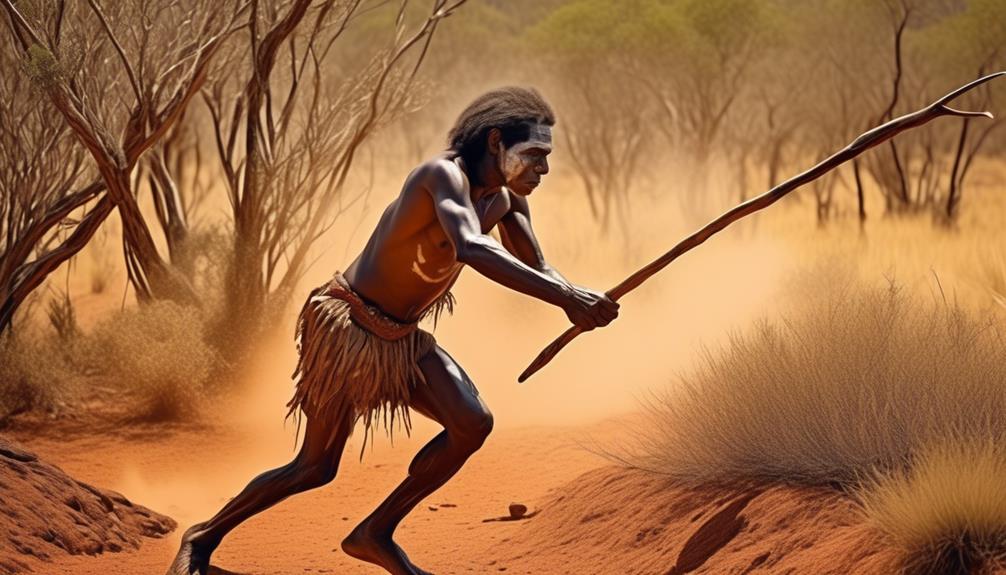

As we traverse the expansive Australian landscape, we encounter a diverse array of hunting and gathering techniques employed by the traditional custodians to sustain their communities and preserve their cultural heritage.
Animal tracking is a skill that has been passed down through generations, allowing Aboriginal Australians to locate and hunt animals for food. Through keen observation and intimate knowledge of the land, they're able to track the movements of kangaroos, emus, and other game animals, ensuring a sustainable supply of meat for their communities.
Food preservation techniques are also crucial for ensuring a reliable food source throughout the year. Aboriginal Australians have developed various methods to preserve meat, such as smoking and drying, allowing them to store food for times of scarcity.
Additionally, the abundant plant life in the Australian landscape provides an array of edible plants, which are carefully gathered and stored for consumption. These food preservation techniques not only sustain the communities during lean times but also serve as a way to honor and respect the land by ensuring that resources are used wisely and efficiently.
Cultural Significance of Foods
The traditional foods of Aboriginal Australians hold deep cultural significance, reflecting a profound connection to the land and a rich tapestry of ancestral knowledge. In our cultural practices, dietary traditions are intertwined with storytelling, rituals, and the passing down of knowledge from one generation to the next.
Here are some key aspects of the cultural significance of our foods:
- Connection to the Land: Our dietary traditions are deeply rooted in the land, with each food item holding a unique connection to specific geographic locations. For example, the gathering of certain bush foods may be tied to particular sacred sites, reinforcing the spiritual bond between our people and the land.
- Seasonal Cycles: Our cultural practices emphasize the importance of seasonal cycles in gathering and consuming traditional foods. This awareness of seasonal changes and the availability of different food sources has been passed down through generations, ensuring sustainable practices and a profound respect for nature.
- Social Cohesion: The preparation and consumption of traditional foods often serve as a focal point for social gatherings and community events, fostering a sense of unity and shared identity among our people.
Through these cultural practices and dietary traditions, our foods not only nourish our bodies but also serve as a means of preserving our unique cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Modern Dietary Trends and Western Influences Impact the Traditional Aboriginal Australian Diet?
Modern dietary trends and western influences have significantly impacted the traditional Aboriginal Australian diet. Globalization has led to a dietary transition, with processed foods replacing traditional ingredients. This shift has posed challenges to cultural preservation and the transmission of traditional knowledge.
As a result, there's a need to find a balance between embracing modern influences and safeguarding the heritage of Aboriginal Australian food practices.
Are There Any Specific Rituals or Ceremonies Associated With the Preparation and Consumption of Traditional Aboriginal Foods?
Cultural significance and traditional rituals are integral to the preparation and consumption of indigenous ingredients in Aboriginal Australian cuisine. Ethical hunting and cooking techniques are deeply rooted in these practices, reflecting a profound respect for the land and its resources.
The communal nature of food gathering and preparation strengthens the community bond and honors the ancestral traditions. These rituals provide a visual representation of cultural heritage and serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness between people and the land.
How Do Aboriginal Australians Pass Down Knowledge About Food and Traditional Cooking Methods to Younger Generations?
Passing down knowledge about food and traditional cooking methods is vital in Aboriginal Australian culture. Elders teach younger generations through oral storytelling, hands-on demonstrations, and shared experiences.
Cultural traditions are preserved as generational knowledge is transferred, ensuring the continuation of traditional cooking methods. This process fosters a deep connection to the land and a profound respect for the ingredients.
It's a beautiful and integral part of preserving our cultural heritage.
What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Aboriginal Australian Diet and Traditional Food Practices?
Common misconceptions about the Aboriginal Australian diet and traditional food practices often stem from a lack of understanding. Western influences and modern dietary trends have overshadowed the rich tapestry of traditional cooking methods, sustainability efforts, and the promotion of preservation.
It's important to recognize the significance of rituals and ceremonies in passing down knowledge. By acknowledging these cultural practices, we can better appreciate the deep connection between food and community in Aboriginal Australian culture.
Are There Any Efforts to Promote the Preservation and Sustainability of Traditional Food Sources Within the Aboriginal Australian Community?
Efforts to promote the preservation and sustainability of traditional food sources within the Aboriginal community are inspiring. Many elders and community leaders are actively working to pass down knowledge of hunting, gathering, and traditional food preparation to the younger generations.
This not only ensures the continuation of cultural practices but also fosters a deeper connection to the land and traditional food sources.
The community's commitment to sustainability is truly commendable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rich and diverse diet of Aboriginal Australians encompasses traditional protein sources, indigenous fruits and vegetables, edible plants and bush tucker, and hunting and gathering techniques.
These foods hold deep cultural significance and are a vital part of the Aboriginal way of life.
The connection to the land and the rituals of gathering and preparing these foods create a beautiful tapestry of tradition and sustenance that has sustained the Aboriginal people for generations.