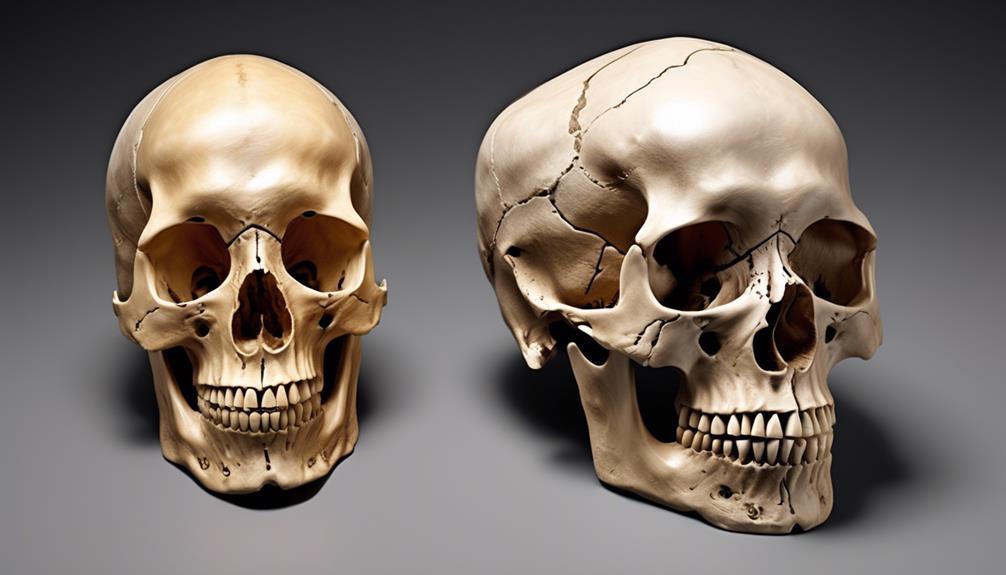
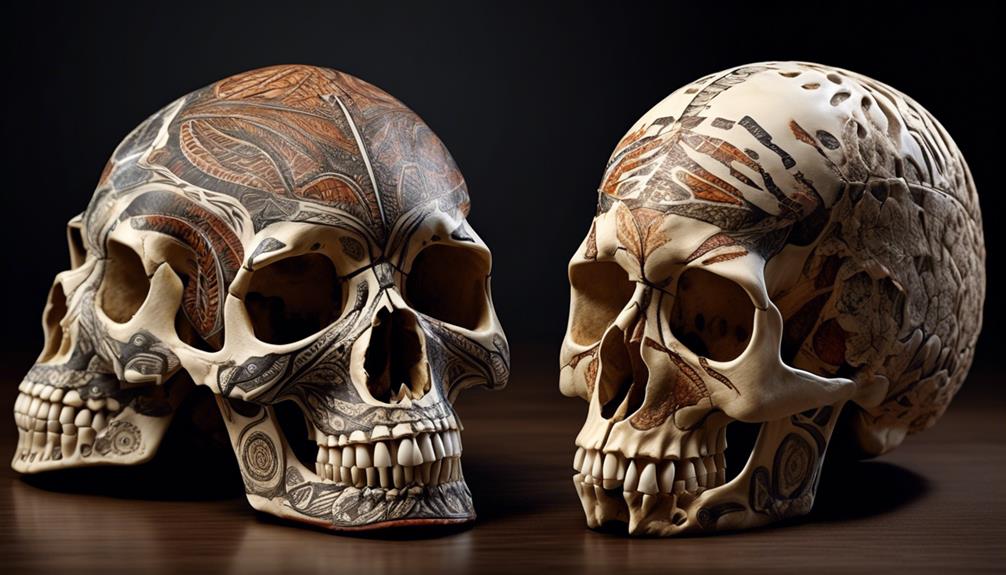
Delving into the subject of skull variances between Aboriginal and Caucasian individuals may be daunting. No one wants to unintentionally perpetuate outdated misconceptions or conflate fact with fiction. However, understanding these distinctions is crucial for professionals in fields such as anthropology and forensic investigation.
The study of skull morphology not only sheds light on the cultural and historical significance of different populations, but also has important implications for evolutionary biology and forensic investigations.
As you delve into this complex and multifaceted topic, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the ethical considerations and practical applications of examining these differences.
Key Takeaways
- Aboriginal skulls tend to be smaller in size compared to Caucasian skulls.
- Variations in skull shape are evident, including differences in width, length, and height.
- The robustness of the skull, the shape of the orbits, and the angle of the mandible provide clear distinctions between Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls.
- Analyzing skull variations provides insights into diverse anatomical traits in human populations.
EVOTECH SCIENTIFIC Classic Numbered Human Skull Model, Life Size 9" Medical Quality-3 Part-W/Sutures Painted, 54pcs Labeled Numbered for Medical Student Shows Most Major Foramen Fossa and Canals
💖 Medical Quality : Our Numbered skull model is made of durable PVC material and anatomically correct. And…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Anatomical Differences Between Aboriginal and Caucasian Skulls
When comparing the anatomical features of Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls, discernible differences in size, shape, and cranial morphology become apparent. One of the most striking anatomical differences lies in the overall size of the skull. Studies have shown that, on average, Aboriginal skulls tend to be smaller in size compared to Caucasian skulls.
Additionally, variations in skull shape are evident, with differences in the width, length, and height of the skull. These differences in shape can be attributed to genetic and environmental factors that have influenced the development of distinct cranial features within these populations.
Furthermore, when examining the cranial morphology, variations in the structure of the skull are observable. For instance, differences in the robustness of the skull, the shape of the orbits, and the angle of the mandible provide clear distinctions between Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls.
These anatomical differences are crucial in understanding the unique evolutionary pathways and genetic adaptations that have shaped the cranial characteristics of these populations. By analyzing these skull variations, researchers can gain valuable insights into the diverse anatomical traits present in human populations.
EUDDOO Human Skull Anatomical Model, Life Size Replica Adult Human Anatomy Head Model with Removable Skull Cap and Articulated Mandible, Labeled Diagram Poster Included
【Human Skull Model, Medical Quality】 Anatomical Skull Model is 1:1 Life-Size. Not only simulate skull model, but also…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Skull Morphology

The observed anatomical differences between Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls underscore the cultural and historical significance of skull morphology. This sheds light on the intricate interplay between genetic heritage, environmental influences, and the unique evolutionary pathways that have shaped these distinct cranial features.
Cultural interpretations of skull morphology offer valuable insights into the traditions, beliefs, and practices of different human societies. Historically, skull morphology has been linked to societal hierarchies, identity, and even spiritual or religious customs. For instance, some cultures have practiced cranial modification, shaping the skull during infancy for cultural or ritualistic purposes. These practices reflect the deep-rooted historical significance of skull morphology in various societies.
Additionally, the study of skull morphology provides a window into population movements and interactions throughout history. By analyzing the morphological variations between Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls, researchers gain a deeper understanding of the historical migrations and evolutionary processes that have contributed to the diversity of human populations.
The historical significance of skull morphology is thus multifaceted, encompassing cultural interpretations, societal practices, and the intricate tapestry of human history.

Skillssist Upgraded Life Size Human Colored Head Skull Anatomical Model with Newest Laser-Etched Fonts for Medical Student Human Anatomy Study Course Demonstration
COLORFUL ANATOMICAL SKULL MODEL: Utilizing advanced laser-etched technology, our human anatomical skull model boasts permanent engraving of fonts…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Evolutionary Implications of Skull Variations
Comparative analysis of skull morphology in Aboriginal and Caucasian populations reveals significant evolutionary implications that provide insights into the adaptive processes and genetic influences shaping cranial variations. The morphological variations observed in these populations suggest a complex interplay between genetic, environmental, and selective factors over time. Evolutionary implications of these variations indicate that environmental pressures, such as climate, diet, and lifestyle, have contributed to the shaping of skull morphology in both populations. Additionally, genetic influences have played a substantial role in the development of these variations, reflecting patterns of genetic drift, gene flow, and adaptation to diverse ecological niches.
Understanding the evolutionary implications of skull variations is essential for elucidating the mechanisms driving human cranial diversity. It offers valuable information regarding the adaptive strategies employed by different populations in response to varying environmental challenges. Moreover, this comparative analysis sheds light on the intricate relationship between genetic heritage and environmental adaptation, providing crucial insights into the evolutionary history of human populations.

Educational Life Size Human Skull Model, Anatomical Study Model with 3 Removable Parts, Numbered Sutures, Professional Teaching Tool for Medical Students Shows and Science Education
LIFE-SIZE DESIGN: Anatomically accurate human skull model at true 1:1 scale with detailed bone structures and natural coloring…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Forensic Applications in Differentiating Skull Characteristics
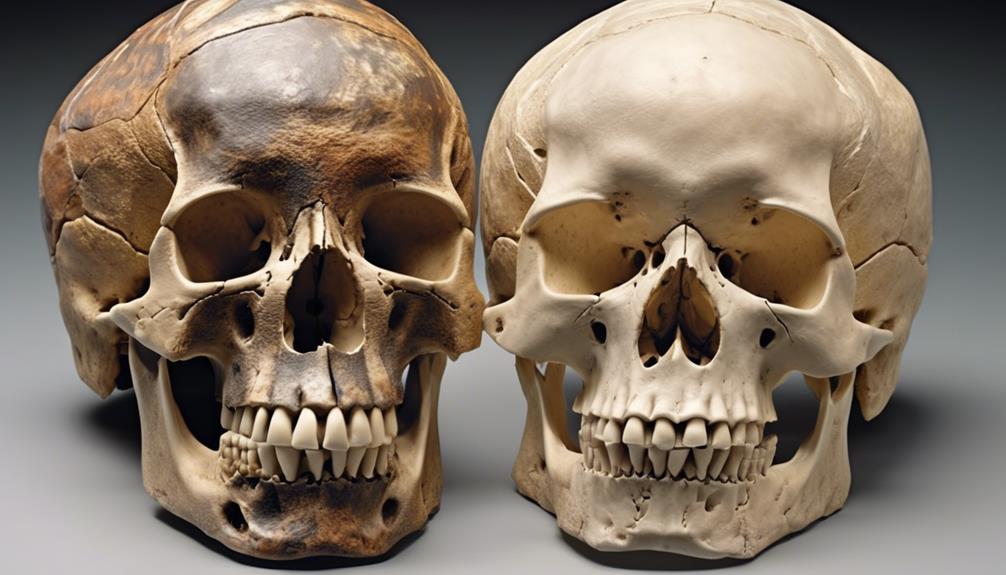
Utilize cranial features to effectively differentiate between Aboriginal and Caucasian populations for forensic purposes, enabling precise identification and analysis in medico-legal investigations.
Forensic identification relies on the distinct cranial morphology of Aboriginal and Caucasian populations. Aboriginal skulls commonly exhibit a more robust and prognathic facial structure, with broader nasal openings and a larger interorbital distance, while Caucasian skulls tend to have a narrower nasal cavity, smaller interorbital distance, and a more orthognathic facial profile.
These differences are crucial in forensic applications, as they allow for the accurate determination of ancestry, aiding in the identification of human remains and providing valuable information in criminal investigations and mass disaster scenarios. By understanding the unique cranial characteristics of different populations, forensic experts can effectively differentiate between Aboriginal and Caucasian individuals, contributing to the accurate analysis and resolution of medico-legal cases.
Therefore, the application of cranial features in forensic investigations plays a pivotal role in distinguishing skull characteristics and establishing the ancestry of human remains, ultimately serving the pursuit of justice and truth.
Ethical Considerations in the Study of Skull Morphology
Considering the ethical implications of studying skull morphology, it's essential to acknowledge the significance of understanding cranial features in the context of forensic analysis and the implications for diverse populations. As a researcher, you must carefully navigate the complexities of research ethics and scientific responsibility when studying skull morphology.
Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
- Informed Consent: Respect for individuals and communities necessitates obtaining informed consent when studying human remains, particularly when working with indigenous populations.
- Cultural Sensitivity: It's imperative to approach the study of skull morphology with cultural sensitivity, recognizing the historical and cultural significance of human remains to different communities.
- Beneficence and Non-maleficence: Researchers have a responsibility to ensure that their work contributes to the greater good while minimizing harm to individuals and communities.
- Transparency: Communicating findings in a transparent and accessible manner fosters trust and understanding among diverse populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Skull Morphology Be Used to Determine an Individual's Race With Absolute Certainty?
Skull morphology can provide valuable insights into racial identification, but absolute certainty is elusive.
Genetic implications and environmental factors influence skull characteristics, complicating forensic identification and ancestral determination.
Ethical considerations arise in population studies using skull morphology for racial classification. While useful, caution is necessary in interpreting such data, as it may perpetuate harmful stereotypes.
Understanding the limitations of skull morphology in racial identification is crucial for responsible and accurate scientific investigation.
Are There Any Genetic Implications for the Differences in Skull Morphology Between Aboriginal and Caucasian Populations?
Genetic implications play a crucial role in population differences, particularly in skull morphology and racial identification. Understanding the genetic basis for these differences can provide valuable insights into the evolutionary and biological factors shaping human diversity.
How Do Other Factors Such as Diet and Environment Contribute to the Variations in Skull Morphology Between Different Populations?
Consider the impact of diet on skull morphology. Different populations have evolved to adapt to their specific dietary needs, leading to variations in skull structure.
Environmental factors also play a crucial role, influencing how the skull develops in response to climate, altitude, and other geographical elements.
Understanding these influences provides valuable insight into the complexities of human evolution and the diverse adaptations that have emerged across different populations.
What Are the Limitations and Potential Biases in Using Skull Morphology for Forensic Identification and Ancestral Determination?
When considering forensic identification, it's crucial to acknowledge the ethical considerations and limitations associated with using skull morphology. Factors such as cranial variation within populations and potential biases in ancestral determination should be carefully assessed. Understanding these limitations is essential for accurate and respectful forensic identification.
It's important to recognize the potential for error and the need for a comprehensive approach that considers a range of factors beyond just skull morphology.
What Ethical Considerations Should Be Taken Into Account When Studying and Comparing the Skulls of Different Populations?
When studying and comparing the skulls of different populations, ethical considerations are crucial. Research methods must prioritize cultural sensitivity and respect the anthropological implications of such comparisons.
It's essential to acknowledge the potential for bias and be mindful of the historical context surrounding the collection and study of human remains. Understanding and addressing these ethical concerns is vital for ensuring the responsible and respectful pursuit of knowledge in the field of anthropology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while there are anatomical differences between Aboriginal and Caucasian skulls, it's important to approach the study of skull morphology with cultural sensitivity and ethical considerations.
Anticipating objections regarding the potential for misuse in forensic applications, it's crucial to emphasize the importance of respectful and responsible research practices in understanding the evolutionary and cultural significance of these variations.
Ultimately, the study of skull morphology contributes to our understanding of human diversity and history.