The evolution of Aboriginal education has shifted from systems focused on cultural erasure to those that embrace Indigenous identities and traditions. You’ll see policies now aim to include Indigenous languages, knowledge, and community involvement, fostering pride and cultural preservation. Modern approaches prioritize inclusivity, culturally relevant teaching, and community-led initiatives. This ongoing transformation moves toward reconciliation and respect, blending traditional values with contemporary education. Continuing to explore this journey will reveal how these changes deepen understanding and empower Indigenous communities.
Key Takeaways
- Historically, Aboriginal education aimed to assimilate and erase Indigenous cultures, creating a disconnect with communities.
- Policy reforms now focus on integrating Indigenous languages and traditional knowledge to foster cultural pride.
- Emphasis on inclusivity involves Indigenous participation in decision-making, bridging Western standards and Indigenous worldviews.
- Culturally relevant teaching and community-led initiatives empower Indigenous communities to control their educational futures.
- The evolution reflects a broader move toward reconciliation, respecting Indigenous sovereignty, and balancing cultural preservation with modern education.
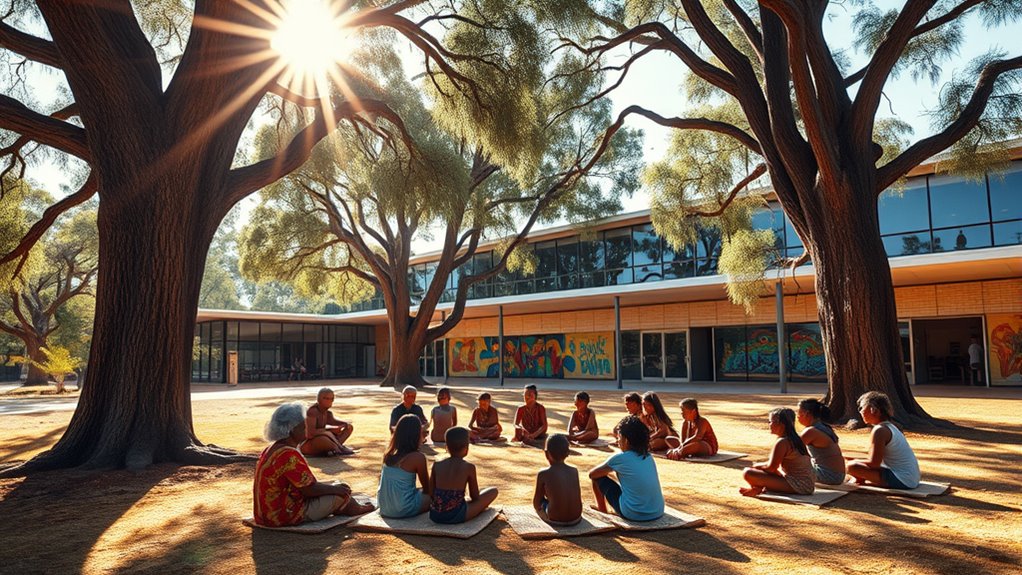

How has Aboriginal education transformed over the years? It’s a journey marked by significant changes, especially in how it balances cultural preservation with modern policy reforms. In the early days, education for Aboriginal communities was often designed to assimilate rather than celebrate their unique identities. Schools operated under policies that aimed to erase Indigenous cultures, languages, and traditions, forcing many Aboriginal children to abandon their heritage. These policies, rooted in colonial mindsets, created a painful disconnect between communities and the education system. Over time, however, there’s been a shift. Governments and educators began recognizing that for Aboriginal students to thrive, their cultural identities needed to be integrated into their learning experiences. This realization sparked policy reforms aimed at respecting and revitalizing Indigenous cultures within formal education. These reforms include incorporating Indigenous languages into curricula, acknowledging traditional knowledge systems, and fostering a sense of pride in cultural heritage. Such efforts are vital for cultural preservation, ensuring that Indigenous traditions are passed on to future generations rather than lost to history.
Modern policies also focus on creating more inclusive and equitable educational environments. They emphasize the importance of involving Indigenous communities in decision-making processes, allowing them to shape the education that reflects their values and history. This participatory approach helps bridge the gap between Western educational standards and Indigenous worldviews. As a result, students are not only gaining academic skills but also reconnecting with their roots, which nurtures a stronger sense of identity and belonging. The evolution of Aboriginal education has also seen an increase in culturally relevant teaching methods, where educators are trained to deliver content that respects Indigenous perspectives. Such approaches foster engagement and improve educational outcomes for Indigenous students.
Furthermore, there’s a growing recognition of the importance of community-led initiatives, which prioritize local knowledge and traditions. These programs empower Indigenous communities to take control of their educational futures, fostering resilience and pride. Policy reforms now aim to support this independence, providing funding and resources for community-driven projects. This shift from the historic mission-style approach to a more collaborative and culturally respectful system marks a significant milestone. It demonstrates a commitment to honoring Indigenous identities while providing quality education that prepares students for the modern world. Essentially, the transformation of Aboriginal education reflects a broader societal move toward reconciliation, respect, and recognition of Indigenous sovereignty. It’s an ongoing process that continues to evolve, driven by a desire to preserve cultural heritage while embracing the opportunities of contemporary education.

Indigenous Language Baby Board Book (English, Navajo, Cherokee & Lakota): Learn Native American First Words for Babies Ages 0–2
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Have Indigenous Languages Been Integrated Into Current Curricula?
You’ll find indigenous languages integrated into current curricula through dedicated language preservation programs and curriculum inclusion initiatives. Schools actively promote learning these languages by offering classes, cultural activities, and resources that highlight their importance. This approach helps preserve indigenous languages, fosters cultural pride, and guarantees that students connect with their heritage. By embedding these languages into everyday learning, education systems support ongoing language revitalization and respect for indigenous cultures.
What Role Do Elders Play in Modern Aboriginal Education?
Elders play a essential role in modern Aboriginal education by serving as mentors and cultural storytellers. You benefit from their wisdom, learning traditional practices and histories firsthand. Their mentorship helps preserve cultural identity and instills respect for traditions. Through cultural storytelling, elders connect you to your roots, ensuring that valuable knowledge and language are passed down to future generations, strengthening community bonds and cultural continuity.
How Is Technology Used to Preserve Aboriginal Cultures Today?
You use technology like virtual storytelling and digital archives to preserve Aboriginal cultures today. Virtual storytelling lets you share traditional stories with a wider audience, keeping language and customs alive. Digital archives store cultural artifacts, photos, and recordings securely online, making them accessible to community members and researchers. This approach helps you maintain cultural heritage, pass it on to future generations, and foster understanding and appreciation of Aboriginal traditions worldwide.
What Challenges Do Remote Communities Face in Accessing Education?
You face significant challenges in accessing education due to transport barriers and funding shortages. Remote communities often struggle with limited transportation options, making it hard to reach schools regularly. Additionally, funding shortages mean fewer resources and support services, which hampers your educational opportunities. These obstacles can lead to gaps in learning and hinder your community’s overall development, making it essential to find solutions that improve access and resource allocation.
How Do Aboriginal Students Perceive Their Educational Experiences?
Imagine your educational journey as a tapestry woven with cultural threads—you feel proud when your cultural identity is honored, boosting your student engagement. Aboriginal students often see their experiences as empowering when schools respect their traditions, making learning meaningful. However, when their identities are overlooked, it can feel like a disjointed patchwork, diminishing engagement and connection. Recognizing and integrating cultural identity transforms education into a vibrant, inclusive experience.

Culturally Relevant Teaching
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
As you reflect on this journey, remember that Aboriginal education is like a river, flowing from its traditional roots to embrace modernity. Just as a river finds new paths around obstacles, education adapts and grows, honoring history while paving the way for future generations. Your support can be the current that keeps this essential stream alive, nurturing resilience and hope. Together, you help guarantee that this sacred journey continues to thrive and inspire.

Daydream Education Australian Aboriginal Art Classroom Poster – EXTRA LARGE 33” x 23.5” – Gloss Paper – Art Middle & High School Class Decoration – Wall Charts
EDUCATIONAL CHART DESIGNED BY TEACHERS: Our Australian Aboriginal Art poster helps students to learn, engage and remember more…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

Fun Express Native American History Educational Activity Pack – Engaging Learning Tools for Kids Featuring Maps Diagrams Photos Historical Insights – Perfect for Social Studies Curriculum – 20 Pieces
Comprehensive Educational Pack: Explore the rich history of Native Americans with 20 historical documents featuring illustrations, photos, speeches,…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.