Many people may not realize that the history of Aboriginal Australians dates back over 65,000 years, making them the oldest continuous culture on Earth. Their strong connection to the land, rich traditions, and unique spiritual beliefs have shaped their way of life for millennia.
However, their story is often overshadowed by the impact of colonization and ongoing struggles for recognition and equality. As we explore the complexities of their history and the challenges they face today, we gain a deeper understanding of the resilience and cultural significance of Aboriginal Australians.
Key Takeaways
- Aboriginal Australians have a rich and ancient history, dating back over 65,000 years, making them the world's oldest living culture.
- The traditional way of life of Aboriginal Australians is deeply connected to the land, with hunting techniques and spiritual beliefs that showcase their resourcefulness and respect for nature.
- Colonization had a devastating impact on Aboriginal communities, leading to the loss of land, cultural practices, and identity. However, efforts for cultural preservation and revival are ongoing.
- Aboriginal Australians face challenges in health and well-being, education, employment, and political representation, but there are promising opportunities for reconciliation, activism, and community-led development.
Origins and Migration
The origins and migration of Aboriginal Australians are deeply intertwined with the rich tapestry of our cultural heritage and historical narrative. Genetic evidence suggests that Aboriginal Australians are one of the oldest continuous cultures on Earth, with ancestors who migrated from Africa over 50,000 years ago. This remarkable journey is reflected in the diversity of Indigenous traditions and the preservation of cultural practices that have been passed down through countless generations.
Through the study of genetic markers and migration patterns, scientists have been able to trace the movement of Aboriginal peoples across the Australian continent and beyond. These findings not only provide insight into the ancient connections between different Aboriginal groups but also challenge previous misconceptions about the static nature of Indigenous societies. It's a testament to the resilience and adaptability of our ancestors, who navigated diverse landscapes and climates to establish vibrant communities with distinct languages, customs, and spiritual beliefs.
Despite the challenges posed by colonization and forced assimilation, the resilience of Aboriginal Australians has ensured the continuation of our cultural heritage. The deep connection to the land, the intricate kinship systems, and the rich oral traditions have all contributed to the cultural preservation that remains a cornerstone of our identity today. Our ongoing commitment to honoring the wisdom of our ancestors and safeguarding our traditions reflects a profound dedication to cultural autonomy and liberation.
Traditional Way of Life

As we delve into the traditional way of life of Aboriginal Australians, it becomes evident that our connection to the land shapes every aspect of our existence. Our hunting techniques are deeply intertwined with our spiritual beliefs and cultural practices. Hunting isn't just a means of sustenance but a sacred ritual that requires a profound understanding of the land and its inhabitants. We utilize various methods such as spears, boomerangs, and traps, passed down through generations, showcasing our resourcefulness and respect for the natural world.
Our social structure is founded on kinship and communal living. The family unit extends beyond biological ties, encompassing a network of interconnected relationships that form the basis of our society. Elders hold a revered position, serving as custodians of knowledge and wisdom, guiding the younger generations through storytelling and oral traditions. This intergenerational transfer of knowledge reinforces our cultural identity and fosters a deep sense of belonging.
Spiritual beliefs permeate every aspect of our lives, shaping our interactions with the land, animals, and each other. Our connection to the Dreaming, the time of creation when ancestral spirits shaped the land, underpins our spiritual worldview. This belief system guides our ethical framework, instilling a profound respect for nature and a responsibility to safeguard the land for future generations.
In essence, our traditional way of life is a harmonious interplay of hunting techniques, cultural practices, social structure, and spiritual beliefs, all intricately woven together to sustain a rich and enduring heritage.
Dreamtime Stories
In our oral tradition, Dreamtime stories weave together the history of creation and the spiritual essence of our existence. These stories aren't just tales but hold deep cultural significance, passing on spiritual beliefs and creation stories from one generation to the next. As Aboriginal Australians, Dreamtime stories are at the core of our cultural identity, shaping our understanding of the world and our place in it.
- Oral Storytelling: Dreamtime stories are passed down orally, from elders to the younger members of the community. This oral tradition ensures that the stories remain authentic and preserves the cultural knowledge embedded within them.
- Cultural Significance: Dreamtime stories are more than mere entertainment; they form the foundation of our cultural beliefs and practices. They teach us about our ancestors, the natural world, and the spiritual forces that govern our lives.
- Spiritual Beliefs and Creation Stories: These stories are deeply intertwined with our spiritual beliefs, as they explain the creation of the universe, the land, and all living things. They provide insights into the sacred relationship between the land and our people, emphasizing the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Through Dreamtime stories, we find a profound connection to our past, present, and future. These stories aren't confined to the past; they continue to shape our identities and guide us in our contemporary lives, providing a sense of belonging and spiritual grounding.
Impact of Colonization

As we reflect on the impact of colonization on Aboriginal Australians, it's crucial to acknowledge the profound loss of land that occurred as a result of European settlement. This displacement not only disrupted traditional ways of life but also led to the erosion of cultural practices and knowledge.
Additionally, the introduction of new diseases had devastating consequences, resulting in the tragic loss of many lives within Aboriginal communities.
Loss of Land
Throughout history, the forced displacement of Aboriginal Australians from their ancestral lands has had profound and enduring impacts on their communities and cultures. The loss of land has been a deeply painful experience for us, impacting our identity and well-being in significant ways.
Land ownership, displacement: The dispossession of our traditional lands has led to a loss of economic independence and self-sufficiency, disrupting the social and cultural fabric of our communities.
Cultural significance, connection to land: Our connection to the land is integral to our spirituality, cultural practices, and identity. The disruption of this connection has caused immense suffering and a sense of dislocation among our people.
Environmental stewardship: Our ancestral lands hold invaluable knowledge of sustainable land management practices, which have been lost due to displacement, impacting not only our communities but also the wider environment.
Cultural Disruption
The displacement from our ancestral lands has not only resulted in the loss of economic independence and cultural disruption but has also deeply affected the fabric of our communities, particularly in terms of the impact of colonization on our cultural practices and identity. The imposition of colonial rule brought about a systematic attempt to erase our traditional ways of life, leading to cultural assimilation and the erosion of our unique identity. However, despite these challenges, we have persistently strived for cultural preservation, seeking to revive and protect our customs, languages, and spiritual beliefs. Our resilience in the face of cultural disruption is evident in our ongoing efforts to reclaim and celebrate our heritage, ensuring that the rich tapestry of our traditions endures for future generations.
| Cultural Preservation | Cultural Assimilation | Impact on Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Reviving languages | Forced adoption of European customs | Erosion of traditional practices |
| Protecting customs | Loss of spiritual beliefs | Struggle to maintain cultural identity |
| Celebrating heritage | Suppression of traditional knowledge | Resilience amidst adversity |
Disease and Death
In confronting the impact of colonization, our communities have grappled with the devastating consequences of diseases and death, which have profoundly reshaped our way of life and left enduring scars on our collective history.
1) Healthcare Disparities: The disparities in access to healthcare have been a significant challenge for our communities, leading to inadequate support in disease prevention and treatment.
2) Impact on Traditional Healing: The introduction of Western medicine disrupted our traditional healing practices, leading to a loss of valuable knowledge and wisdom in managing health and wellness.
3) Resilience and Advocacy: Despite these challenges, our communities have shown resilience and have been advocating for better healthcare resources and culturally sensitive approaches to disease prevention and treatment.
Navigating the impact of diseases and death in the wake of colonization has been a complex and ongoing struggle, but our communities continue to strive for better health outcomes and equitable access to healthcare.
Stolen Generations

During the 20th century, Australian government policies forcibly removed thousands of Aboriginal children from their families, an act that has come to be known as the Stolen Generations. This systematic removal, which continued until the 1970s, resulted in intergenerational trauma that continues to impact Aboriginal communities today. The trauma of being forcibly separated from family, culture, and community has had deep and lasting effects on the stolen individuals, their descendants, and the broader Aboriginal community.
Healing and reconciliation are ongoing processes that are crucial for addressing the deep wounds caused by the Stolen Generations. These processes involve acknowledging the historical injustices, supporting the healing of individuals and communities, and working towards creating a more inclusive and equitable society for Aboriginal Australians. It's essential to provide culturally sensitive support services and programs that facilitate healing and reconnect individuals with their culture and community.
As a society, we must actively listen to the experiences of the Stolen Generations and their descendants, and work towards creating spaces of understanding, empathy, and support. This involves amplifying Aboriginal voices, respecting their agency in the healing process, and advocating for policies that address the ongoing impacts of the Stolen Generations.
Land Rights and Sacred Sites

Land rights and sacred sites hold significant cultural and spiritual importance for Aboriginal Australians, embodying a deep connection to the land and the ancestral heritage of their communities.
- Land Management: Aboriginal Australians have a profound understanding of sustainable land management, passed down through generations. They have a holistic approach to land, viewing it as a living entity that must be cared for and respected. This includes traditional practices such as controlled burning to maintain the health of the land.
- Heritage Preservation: Sacred sites are a testament to the rich cultural heritage of Aboriginal Australians. These sites hold immense spiritual significance and are often the physical remains of ancient ceremonies, stories, and rituals. Preserving these sites is crucial not only for the Aboriginal communities but also for the broader understanding of Australia's history and heritage.
- Legal Recognition: The struggle for land rights has been a long and arduous one for Aboriginal Australians. The landmark Mabo decision in 1992 recognized the concept of native title, affirming the rights of Indigenous Australians to their traditional lands. This legal recognition was a significant milestone in the ongoing battle for land rights and the protection of sacred sites.
It is imperative to recognize the importance of land rights and sacred sites in the broader context of Aboriginal Australians' cultural identity and spiritual connection to the land. The preservation of these rights and sites is essential for the well-being and liberation of Aboriginal communities.
Art and Cultural Expression
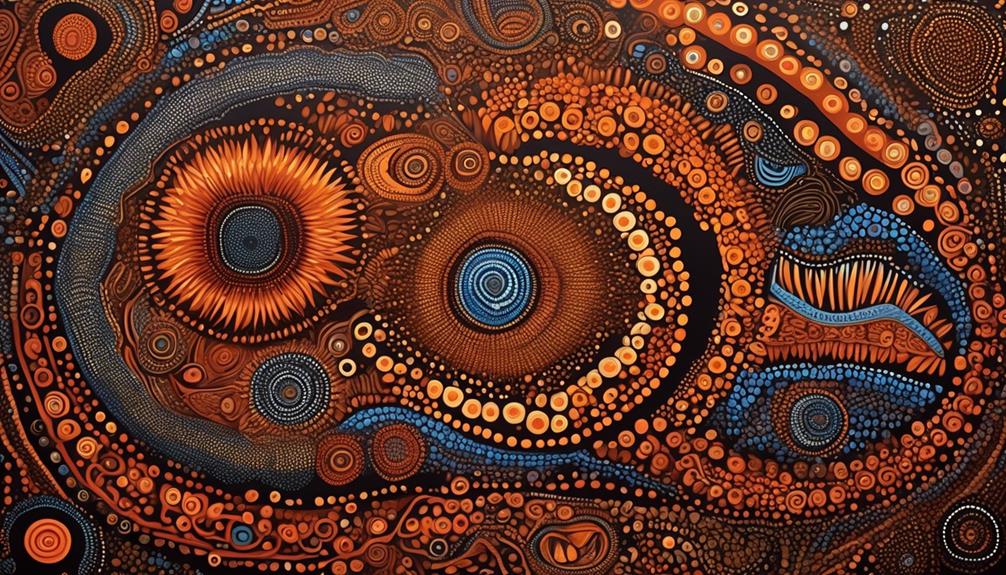

We've been fascinated by the rich tradition of art and cultural expression among Aboriginal Australians.
Their traditional art forms and the deep symbolism in their art have captured our interest and admiration.
It's a testament to the depth and complexity of their cultural heritage.
Traditional Art Forms
Aboriginal Australians express their rich cultural heritage through a diverse array of traditional art forms. These include bark painting, rock art, and ceremonial body painting. These art forms are deeply rooted in Indigenous crafts and hold immense cultural significance. They serve as a means of preserving and passing down traditional knowledge and stories through visual representation.
Artistic techniques, such as cross-hatching and dot painting, are employed to convey intricate storytelling traditions. These techniques reflect the interconnectedness of Aboriginal people with the land and their ancestral spirits. Each stroke and symbol carries layers of meaning, encompassing the spiritual, social, and historical dimensions of their culture.
These traditional art forms not only showcase exceptional artistic skill but also serve as a powerful medium for cultural expression and identity affirmation.
Symbolism in Art
Deeply embedded within the traditional art forms of Aboriginal Australians is a rich symbolism that serves as a profound expression of their cultural heritage and identity. Symbolism in art plays a crucial role in cultural preservation, conveying stories of the land, spiritual beliefs, and creation myths. Each symbol carries layers of meaning, connecting the artwork to the ancestral knowledge passed down through generations.
The use of dots, lines, and patterns in Aboriginal art represents the interconnectedness of all living things and the ongoing relationship between the people, the land, and the Dreamtime. The vibrant colors and intricate designs reflect the diversity and richness of Aboriginal culture.
Languages and Communication

Historically, Aboriginal Australians have utilized a rich and diverse array of languages and communication methods to convey their cultural knowledge and traditions. Indigenous languages play a vital role in preserving the unique cultural heritage of Aboriginal Australians, reflecting their deep connection to the land and spiritual beliefs.
Cultural communication among Aboriginal Australians encompasses a wide range of traditional practices, including storytelling, songlines, and ceremonial rituals. These forms of communication are deeply rooted in the cultural identity of Aboriginal communities and are essential for passing down knowledge from one generation to another.
- Diversity of Indigenous Languages: The linguistic landscape of Aboriginal Australia is incredibly diverse, with hundreds of distinct languages spoken across different regions. Each language is a repository of cultural knowledge, encompassing unique vocabularies, grammatical structures, and ways of expressing complex cultural concepts.
- Oral Tradition and Storytelling: Storytelling is a fundamental aspect of Aboriginal culture, serving as a means of transmitting knowledge, history, and spiritual beliefs. Through intricate narratives and oral traditions, Aboriginal Australians preserve their cultural heritage and maintain a profound connection to the land.
- Significance of Songlines: Songlines are intricate musical compositions that map the landscape and contain valuable information about the land, sacred sites, and ancestral stories. These songs serve as a form of cultural communication, encoding geographical and spiritual knowledge that's passed down through generations.
The preservation and revitalization of Indigenous languages and cultural communication are essential for upholding the rich traditions and identity of Aboriginal Australians. It's crucial to support efforts aimed at preserving these languages and communication methods, as they're integral to the cultural liberation and empowerment of Aboriginal communities.
Health and Well-being

Utilizing a holistic approach that encompasses traditional cultural practices, the health and well-being of Aboriginal Australians is deeply interconnected with their cultural identity and spiritual beliefs. Mental health is a crucial aspect of our overall well-being, and it's essential to consider the unique challenges faced by Aboriginal communities.
Historical trauma, dispossession, and the ongoing impact of colonization have significantly affected the mental health of our people. However, there's a growing recognition of the importance of community support in addressing these issues. Many Aboriginal communities have established culturally sensitive mental health services that incorporate traditional healing methods, fostering a sense of belonging and connection.
Access to healthcare remains a significant concern for many Aboriginal Australians. Cultural barriers, including language differences and a lack of culturally appropriate care, often prevent our people from seeking medical assistance. Efforts to increase the cultural competence of healthcare providers and improve accessibility to healthcare services are ongoing, but there's still much work to be done.
It's crucial to ensure that healthcare services are respectful of our cultural practices and beliefs, and that they're easily accessible to all members of our communities.
Education and Employment

Improving access to quality education and creating sustainable employment opportunities are vital for the advancement and empowerment of Aboriginal Australians. Education reform is essential to address the historical injustices and systemic barriers that have hindered the educational attainment of Aboriginal Australians. As a community, we recognize the need for culturally responsive education that honors Indigenous knowledge and traditions, while also providing access to modern academic and vocational skills.
- Culturally Inclusive Curriculum: It's imperative that the education system incorporates Indigenous perspectives, histories, and knowledges into the curriculum. This not only validates the cultural identity of Aboriginal students but also fosters a more inclusive and diverse learning environment for all students.
- Mentorship and Support Programs: Implementing mentorship and support programs within educational institutions can help Aboriginal students navigate the challenges they may face, providing guidance, encouragement, and a sense of belonging.
- Breaking Employment Barriers: Sustainable employment opportunities can break the cycle of economic disadvantage. Addressing employment barriers such as discrimination, lack of access to training, and limited job opportunities is crucial for creating a more equitable workforce.
Furthermore, addressing employment barriers is essential in creating a more inclusive workforce. Employers and policymakers need to actively work towards eliminating discrimination and creating pathways for Aboriginal Australians to access and thrive in various employment opportunities. By advocating for these changes, we can pave the way for a brighter future where education and employment are truly accessible and empowering for all Aboriginal Australians.
Political Representation

Addressing the systemic barriers that have hindered educational attainment can also be seen in the realm of political representation for Aboriginal Australians. The representation challenges faced by Aboriginal communities in political spheres are significant. Despite the increased government engagement and acknowledgment of the need for inclusive representation, there's still a substantial underrepresentation of Indigenous voices in decision-making bodies. This underrepresentation perpetuates the cycle of marginalization and hinders the progress of policies that directly affect Aboriginal communities.
Policy advocacy plays a crucial role in addressing the representation challenges. It involves actively engaging with governmental bodies to ensure that the unique needs and perspectives of Aboriginal Australians are considered in the formulation and implementation of policies. By advocating for policies that address the historical and ongoing injustices faced by Aboriginal peoples, we can strive towards a more inclusive and equitable political landscape.
Furthermore, leadership roles within political structures are essential for fostering genuine representation. Encouraging and supporting Aboriginal individuals to take up leadership positions can lead to more nuanced and authentic decision-making. It's imperative to create pathways for Indigenous leadership to ensure that the voices of Aboriginal Australians aren't only heard but also heeded in the political arena.
Reconciliation and Apology

Reconciliation between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians has been a pivotal aspect of acknowledging historical injustices and fostering a shared path towards healing and understanding. The journey towards reconciliation has been marked by significant milestones, including the government's formal apology for past wrongs and ongoing efforts to bridge the divide between the two communities.
- Government Apology:
The formal apology delivered by then-Prime Minister Kevin Rudd in 2008 was a watershed moment in Australian history. The apology acknowledged the mistreatment of Indigenous Australians, particularly the forced removal of children from their families, and expressed deep regret for the pain and suffering caused.
- Reconciliation Efforts:
In the aftermath of the government apology, reconciliation efforts have gained momentum across the country. Initiatives aimed at promoting understanding, respect, and equality between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians have been prioritized, with a focus on addressing social, economic, and health disparities.
- Community Engagement:
Reconciliation isn't solely a task for the government; it requires active engagement from individuals, communities, and organizations. Grassroots reconciliation initiatives, cultural awareness programs, and collaborative projects have emerged, fostering meaningful interactions and relationships between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians.
The government's apology and continued reconciliation efforts serve as important steps towards healing the wounds of the past and building a more inclusive and equitable future for all Australians. It's a journey that demands ongoing commitment, understanding, and empathy from both Indigenous and non-Indigenous communities.
Contemporary Activism

Contemporary activism among Aboriginal Australians continues to shape and challenge societal norms and policies, promoting awareness and advocating for meaningful change. In the current landscape, advocacy efforts for cultural preservation and social justice are at the forefront of Aboriginal activism. These initiatives strive to address the historical and ongoing injustices faced by Aboriginal communities, while also celebrating and preserving their rich cultural heritage.
| Advocacy Efforts | Examples |
|---|---|
| Land Rights | Campaigns for the return of traditional lands and recognition of native title rights. |
| Political Representation | Push for increased Aboriginal representation in government and decision-making processes. |
| Education Reform | Calls for culturally sensitive and inclusive education, highlighting the importance of Aboriginal histories and perspectives. |
Contemporary activism is diverse and multifaceted, encompassing grassroots movements, social media campaigns, and organized protests. It is a powerful force driving change and challenging systemic inequalities. This activism is rooted in a deep desire for social justice and equality, aiming to dismantle the barriers that continue to marginalize Aboriginal Australians. While progress has been made, there is still much work to be done in order to create a more equitable and inclusive society. The resilience and determination of Aboriginal activists serve as a testament to their unwavering commitment to effecting positive change for themselves and future generations.
Celebrations and Festivals

As we turn our attention to celebrations and festivals, it's fascinating to explore the rich traditions of Aboriginal Australians. Traditional dance is a vibrant and integral part of these festivities, with each movement telling a story of cultural significance.
Furthermore, the Dreamtime stories, which are passed down through generations, play a central role in these joyous occasions, connecting the community to their ancestral roots.
Traditional Dance
During traditional Aboriginal Australian celebrations and festivals, the vibrant and rhythmic traditional dances serve as a cultural expression and a form of storytelling. These dances are deeply rooted in our cultural preservation, passed down through generations, and are also open to modern interpretations, evolving with the times.
The traditional dances reflect the cross-cultural influences that have shaped our community, showcasing the impact of globalization while maintaining our unique identity. Each movement and gesture in these dances conveys a rich history, spiritual connection, and a profound respect for the land.
The mesmerizing rhythm and movements of these traditional dances not only captivate the audience but also serve as a powerful reminder of our heritage, resilience, and the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Dreamtime Stories
The rhythmic traditional dances, deeply rooted in our cultural preservation and open to modern interpretations, seamlessly lead into the captivating Dreamtime Stories that are celebrated during Aboriginal Australian festivals. Dreamtime Stories hold spiritual significance and are integral to our ancestral connection, serving as a powerful medium for cultural preservation and storytelling. These stories, passed down through generations, convey our beliefs, history, and values. They are not merely tales, but a living, breathing essence of our identity. Through Dreamtime Stories, we honor our past, celebrate our present, and envision our future. The festivals provide a communal space for sharing these narratives, fostering a sense of unity and belonging among our people. They are a testament to the enduring power of our cultural heritage.
| Dreamtime Stories | Celebrations and Festivals |
|---|---|
| Spiritual significance | Communal space for sharing |
| Ancestral connection | Fostering unity and belonging |
Future Challenges and Opportunities

Amidst the changing landscape of modern Australia, Aboriginal Australians are facing both formidable challenges and promising opportunities for their future. As we navigate this complex terrain, it's essential to acknowledge the hurdles that hinder our progress and the pathways that lead towards empowerment and growth.
- Challenges in Education: Access to quality education remains a significant challenge for many Aboriginal Australians. Historical injustices, socio-economic disparities, and cultural insensitivity in educational institutions continue to impede the academic success of Aboriginal students. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates culturally relevant curriculum, support for Indigenous languages, and initiatives to recruit and retain Indigenous educators.
- Employment Barriers: The lack of employment opportunities and systemic barriers in the workforce present formidable challenges for Aboriginal communities. Discrimination, limited access to vocational training, and geographical isolation contribute to disproportionately high unemployment rates among Indigenous Australians. To address this, targeted employment programs, mentorship initiatives, and partnerships with businesses are crucial for creating pathways to sustainable employment and economic stability.
- Promising Opportunities: Despite these challenges, there are promising opportunities on the horizon. The growing recognition of Indigenous knowledge systems, the resurgence of cultural practices, and the increasing representation of Aboriginal voices in various sectors are paving the way for a more inclusive and equitable future. Additionally, initiatives that prioritize community-led development, entrepreneurship, and land rights are creating opportunities for self-determination and sustainable growth within Aboriginal communities. Embracing these opportunities will be instrumental in shaping a future where Aboriginal Australians can thrive and contribute to the diverse tapestry of modern Australia.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Aboriginal Australians View the Concept of Time and the Future?
We all perceive the concept of time differently, shaping our future outlook. It's a complex blend of cultural, historical, and personal experiences.
For some, time is linear, while for others, it's cyclical. Our perception of time influences our decisions and plans for the future.
It's fascinating how diverse perspectives on time can enrich our understanding of the world and our place in it.
What Are Some Traditional Foods and Cooking Methods of Aboriginal Australians?
We enjoy exploring traditional recipes and indigenous culinary techniques from various cultures. Preserving cultural cuisine is important to us. Understanding the way different cultures approach food and cooking provides insights into their traditions and values.
It's fascinating to see how these culinary practices integrate into festivities and impact contemporary issues. We're also interested in learning about future challenges related to cultural preservation and how activism participation plays a role in shaping the future outlook.
How Do Aboriginal Australians Incorporate Their Cultural Practices and Beliefs Into Modern Celebrations and Festivals?
In modern celebrations, cultural integration is important for many communities. Incorporating traditions into contemporary events helps maintain a sense of identity and connection to the past.
This can be seen in various ways, such as through traditional dances, music, and storytelling at festivals. It's a beautiful way to honor our heritage and share it with others, fostering understanding and appreciation for diverse cultural practices.
What Are Some Contemporary Activism Movements and Issues That Aboriginal Australians Are Involved In?
Contemporary activism involves fighting for issues like land rights, social justice, and political representation. It's a powerful way to bring about positive change in society.
As for the specific context of Aboriginal Australians, they're deeply involved in contemporary activism movements, advocating for their land rights, seeking social justice, and striving for better political representation. These efforts are crucial for addressing historical injustices and creating a more equitable future.
What Are Some Future Opportunities and Challenges That Aboriginal Australians Face in Terms of Preserving Their Culture and Traditions?
Preserving culture and traditions presents opportunities and challenges for many communities.
In the future, cultural preservation will require resilience and innovation. Opportunities for revitalization and sharing traditions with the next generation abound, but challenges such as modernization and cultural appropriation will need to be addressed.
Future perspectives will shape the approach to preserving culture, emphasizing the importance of adaptability and community engagement.
Conclusion
As we reflect on the rich and resilient history of Aboriginal Australians, we see a tapestry woven with strength, wisdom, and cultural richness.
Their journey has been like a river, flowing through time, carving its path amidst challenges and triumphs. It's a story of survival, adaptation, and hope that continues to inspire and shape the future.
Let's embrace the beauty of their traditions and work towards a future where their voices are heard and respected.