You may be surprised to learn that indigenous cultures have been using the fragrant oils of plants for various purposes, including in spiritual ceremonies and healing rituals, for a long time.
But have you ever wondered which native scent is considered the best? Imagine being able to bring the invigorating essence of the wilderness into your home or workplace.
Well, the answer may surprise you.
Key Takeaways
- Cedarwood is a grounding and calming scent that promotes restful sleep and acts as a natural insect repellent.
- Sage has a fresh and revitalizing aroma and can be used to enhance the flavor of dishes, soothe sore throats, and aid digestion. It is also used in spiritual and cleansing rituals.
- Lavender is a soothing and floral scent that promotes relaxation and improves sleep quality.
- Juniper has an aromatic and refreshing bouquet and is traditionally used to alleviate stress and anxiety. It also cleanses and purifies the air and adds natural elegance to botanical decorations.

Handcraft Blends Cedarwood Essential Oil – Huge 4 Fl Oz – 100% Pure and Natural – Premium Grade Essential Oil for Diffuser and Aromatherapy, Skin, Massage, Candle and Soap Making Fragrance
100% PURE & NATURAL CEDARWOOD OIL – Handcraft Blends oils are exactly that! Many oils being sold make…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Cedarwood: A Rich and Earthy Fragrance
Embrace the rich and earthy fragrance of cedarwood, evoking a sense of grounding and warmth in your surroundings. The benefits of cedarwood in aromatherapy are truly remarkable.
This ancient and revered essential oil not only has a calming and soothing effect on the mind and body but also acts as a natural insect repellent. When used in aromatherapy, cedarwood oil can help alleviate stress and anxiety, promoting a sense of tranquility and emotional well-being.
Its warm, woody aroma creates a comforting atmosphere, making it an ideal choice for relaxation and meditation practices. Using cedarwood in aromatherapy can also aid in promoting a restful night's sleep. Its sedative properties can help combat insomnia and improve the overall quality of sleep.
Additionally, cedarwood oil has been found to have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, making it a valuable tool in skincare and wound healing. Its astringent nature also makes it effective in treating acne and oily skin conditions.
Incorporating cedarwood into your aromatherapy routine can truly elevate your overall well-being, offering a myriad of physical and emotional benefits.

Handcrafted 4 Inch White Sage Sticks – Fresh, Natural California Sage Smudge Sticks with Instructions & Blessings – Wand Sage for Cleansing House Negative Energy & Other Smudging Rituals
🌙 Let the Good Vibes Roll With Our Sage: This is the sage to burn for cleansing negative…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Sage: Fresh and Invigorating Aroma

Invigorate your senses with the fresh and revitalizing aroma of sage, a herb renowned for its cleansing and uplifting properties. Sage, with its soft, silvery-green leaves, offers a myriad of benefits that extend beyond its culinary uses.
In the kitchen, it adds a distinct earthy flavor to dishes, while in traditional medicine, it has been treasured for its medicinal properties. The aroma of sage not only tantalizes the taste buds but also holds a rich history of spiritual and cleansing rituals.
In the culinary world, sage is a staple herb known for enhancing the flavor of various dishes, particularly those featuring poultry and stuffings. Medicinally, it has been used to soothe sore throats, aid digestion, and even improve memory and cognitive function.
In spiritual and cleansing rituals, sage is burned as a smudge to purify the air, dispel negative energy, and bring about a sense of clarity and renewal.
Whether you're savoring its culinary delights or partaking in its cleansing rituals, sage offers a fresh and invigorating aroma that encompasses a wealth of benefits for both the body and the soul.

Majestic Pure Essential Oil with Glass Dropper – 100% Pure and Natural – Essential Oils for Diffuser, Aromatherapy, Soap and Candle Making, Lavender Essential Oil, Lavender Oil, 4 Fl Oz
100% PURE & NATURAL LAVENDER OIL – Majestic Pure Blends oils are exactly that! Many oils being sold…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Lavender: Soothing and Floral Scent
Sage's invigorating essence gives way to the soothing and floral scent of lavender, a fragrant herb celebrated for its calming properties and delicate aroma. Lavender has long been revered for its ability to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality. Its benefits extend to stress relief, making it a popular choice for those seeking a moment of tranquility in their daily lives.
Lavender's versatility is reflected in the wide array of products it's used in. Essential oils are a popular choice for harnessing the herb's calming effects. A few drops in a diffuser can create a serene atmosphere, perfect for unwinding after a long day.
Additionally, lavender-infused bath bombs offer a luxurious way to incorporate this soothing scent into your self-care routine. The gentle fizz of the bath bomb combined with the floral aroma creates a spa-like experience in the comfort of your own home.
Whether you're seeking a natural sleep aid or a stress-relieving solution, lavender's gentle, floral scent offers a delightful way to introduce moments of calm into your day.

Stress Relief Roll On Essential Oil Sage Juniper Berry Spiritual Energy Clearing Protection Destress Smokeless Smudging Calm Aromatherapy Gifts Women
Clear Mind Roll-On Essential Oil Blend- infused with juniper berry, sage, and nerolina. This protective aromatherapy oil offers…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Pine: Crisp and Woodsy Essence
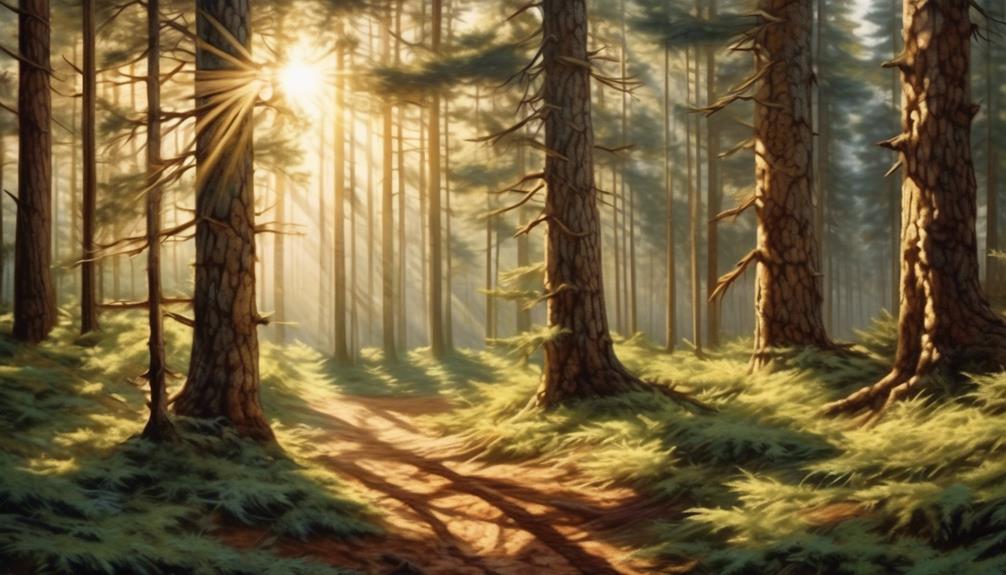

With its crisp and woodsy essence, pine brings a refreshing and invigorating scent to any space. Imagine standing in the midst of a majestic pine forest, the air filled with the clean, resinous aroma of the towering trees. The scent of pine is like a breath of fresh air, awakening your senses and transporting you to the heart of nature's splendor.
Pine forests exude a sense of serenity and grandeur, and the fragrance of pine captures this essence perfectly. It evokes images of towering evergreens reaching for the sky, their fragrant boughs swaying gently in the breeze. The aroma of pine is reminiscent of the great outdoors, where the air is pure and the surroundings are untouched and untamed.
In addition to its natural allure, pine is also associated with charming rustic crafts made from pinecones. The scent of pine brings to mind the cozy warmth of a cabin in the woods, adorned with pinecone crafts that add a touch of woodland charm to the decor. The earthy, resinous aroma of pine is a reminder of the beauty and simplicity of nature, making it a timeless and beloved scent for any space.
Juniper: Aromatic and Refreshing Bouquet
Aromatic and refreshing, juniper brings a delightful burst of nature's essence to any environment. This remarkable botanical offers a wide array of benefits and uses, making it a versatile addition to your aromatic repertoire. Here's why juniper is an indispensable scent:
- Cleansing and Purifying: Juniper's crisp, piney aroma is renowned for its cleansing properties. It clears the air of stagnant energy, making it perfect for meditation spaces or to freshen up a room.
- Therapeutic Effects: The invigorating scent of juniper has been traditionally used to alleviate stress and anxiety. Its aroma can uplift your spirits and create a sense of tranquility.
- Culinary and Decorative Uses: Beyond its aromatic benefits, juniper berries are utilized in various cuisines to impart a distinct flavor. They're also used in crafting botanical decorations, adding a touch of natural elegance to any setting.
Juniper's benefits extend beyond its captivating scent, offering a myriad of practical and holistic advantages. Whether you seek a natural air freshener, therapeutic remedy, or culinary ingredient, juniper remains an invaluable botanical ally.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are There Any Traditional Uses of These Native Scents in Different Cultures or Regions?
In different cultures and regions, traditional practices have used native scents for centuries. These scents hold cultural significance and are often used in rituals, ceremonies, and daily life.
Ethical sourcing and conservation efforts are important to preserve these native scents for future generations. From smudging ceremonies in Indigenous cultures to the use of aromatic herbs in traditional medicine, these scents play a vital role in many communities.
Can These Native Scents Be Used in Natural Remedies or for Aromatherapy Purposes?
You can absolutely harness the power of native scents for natural remedies and aromatherapy. These fragrant treasures have been used for centuries in traditional medicine, offering a wealth of benefits for mental health.
The soothing aroma of these native scents can calm the mind and uplift the spirit, providing a natural remedy for stress and anxiety. Incorporating these scents into your wellness routine can truly be a game-changer for your overall well-being.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using Native Scents Compared to Synthetic Fragrances?
Using native scents has environmental benefits compared to synthetic fragrances. They're sustainable, often harvested in ways that support biodiversity.
Culturally, native scents have been used for centuries in traditional practices and ceremonies. They provide a deeper connection to the land and its history.
When used in aromatherapy, they offer a natural and holistic approach to well-being. Embracing native scents supports both the environment and cultural heritage.
Are There Any Potential Allergic Reactions or Sensitivities to These Native Scents?
Potential reactions to native scents are a valid concern, especially for individuals with sensitivities. It's essential to recognize that even natural fragrances can trigger allergic responses in some people. Common native scents like lavender or eucalyptus may still cause sensitivity concerns.
Always perform a patch test before using a new scent and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any existing allergies or sensitivities.
How Can These Native Scents Be Sustainably Sourced and Harvested to Support Conservation Efforts?
To support conservation efforts, sustainable sourcing of native scents is crucial.
Imagine a delicate dance between nature and industry, where careful harvesting practices preserve the ecosystem.
By partnering with local communities, you can ensure fair and ethical sourcing, benefiting both people and the environment.
Through sustainable practices, you can protect the native plants and support conservation efforts, ensuring that future generations can continue to enjoy these precious scents.
Conclusion
Now that you know the best native scents, you can bring the rich and earthy essence of cedarwood into your life. Embrace the natural beauty and power of this scent, and let it transport you to a place of serenity and rejuvenation.
You can also enjoy the fresh and invigorating aroma of sage. Allow this scent to invigorate your senses and create a refreshing atmosphere in your surroundings.
For a soothing and floral experience, embrace the scent of lavender. Let the calming properties of lavender envelop you, bringing a sense of tranquility and relaxation to your space.
To add a touch of crispness and woodsiness to your environment, opt for the essence of pine. Allow the refreshing scent of pine to create a revitalizing ambiance in your surroundings.
Lastly, experience the aromatic and refreshing bouquet of juniper. Let the invigorating qualities of juniper uplift your spirits and bring a sense of renewal to your space.
Embrace the natural beauty and power of these scents, and let them transport you to a place of serenity and rejuvenation.