Did you know that recent archaeological discoveries suggest that humans may have inhabited Australia up to 65,000 years before the arrival of the Aboriginal people?
The question of who inhabited the land before the Aboriginal has sparked intense curiosity and debate among researchers.
As we explore this topic, we will uncover intriguing findings about early human migration, genetic studies, and evidence of pre-Aboriginal settlements, shedding light on a part of Australia's history that is often overlooked.
Key Takeaways
- Migration to Australia occurred over 65,000 years ago, challenging the traditional narrative of Aboriginal people being the first and only inhabitants.
- Genetic studies reveal diverse ancestral origins and population dynamics, highlighting multiple waves of migration and genetic contributions.
- Pre-Aboriginal technology and cultural achievements, such as advanced tool-making techniques and mastery of fire, contribute to human history.
- The land bridge hypothesis and migration routes provide evidence of ancient migration routes connecting Australia to neighboring landmasses, supporting the idea of human dispersal across the region.

JOINPAYA Archaeological Excavation Tools for Kids: 3 Sets Dinosaur Fossil Digging Kits with Mini Hammer Chisel Brush Scraper and Magnifier Science Kits for Dino Eggs and Gem Dig
Portable and Easy to Store: The compact size of each tool makes this dig tool set portable.Each lightweight…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Early Human Migration to Australia
Early human migration to Australia occurred over 65,000 years ago, marking one of the earliest known movements of anatomically modern humans out of Africa. This significant event is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of our ancestors. The prehistoric migrations to Australia were no small feat, as they required immense courage, ingenuity, and determination to navigate the vast and often treacherous landscapes that separated Africa from Australia.
In understanding early human migration to Australia, it's crucial to acknowledge the profound cultural exchange that took place. As our ancestors ventured across continents, they carried with them not only their physical belongings but also their rich cultural heritage. This resulted in a beautiful tapestry of traditions, beliefs, and practices interwoven with those of the indigenous peoples they encountered in Australia. The intricate web of cultural exchange that ensued continues to shape the identity of Australia and its people today.
Studying prehistoric migrations allows us to appreciate the interconnectedness of humanity. It highlights our shared history and the remarkable tenacity that has driven us to explore and settle in new lands. This knowledge empowers us to cherish and celebrate diversity, recognizing that cultural exchange has been an integral part of human existence since time immemorial.

The Shortest History of Migration (The Shortest History Series)
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Paleo-Aboriginal Settlements
Paleo-Aboriginal settlements reveal a nuanced and intricate tapestry of early human habitation in Australia, reflecting the complexities of cultural adaptation and environmental interaction. Understanding paleo-Aboriginal settlement patterns provides significant insights into the ancient land use practices of the first peoples of Australia.
The archaeological evidence suggests that these early inhabitants displayed a remarkable ability to adapt to diverse ecological niches and climatic variations, demonstrating a deep understanding of their environment and its resources.
The study of paleo-Aboriginal settlement patterns unveils a sophisticated understanding of resource management and a complex social organization that facilitated the sustainable use of the land. These ancient peoples exhibited a deep connection to the land and its resources, shaping their settlement patterns and societal structures to suit the diverse environments they encountered. The evidence indicates a dynamic interaction between human populations and the Australian landscape, with adaptation and innovation being central to their survival and success.
Furthermore, the examination of paleo-Aboriginal settlements highlights the rich cultural heritage of Australia's first peoples. Their deep understanding of the land and its resources is reflected in the intricate ways in which they utilized and managed the environment. This not only underscores the resilience and adaptability of these early inhabitants but also emphasizes the importance of recognizing and respecting their ancient land use practices.
Understanding these settlement patterns is crucial in appreciating the enduring connection of Aboriginal peoples to the Australian landscape.

Human Body Activities & Experiments Science Kit for Kids,Human Anatomy Body Parts with Broken Bones X Ray,Lung Breathing Model, Vessels, Digestive System,Muscles Model,Skeleton,Human Organ STEM 5+
HANDS-ON LEARNING: Explore the human body parts, create and learn how to identify multiple organs, and discover x-rays…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Evidence of Pre-Aboriginal Artifacts
Examining the archaeological record of Australia reveals compelling evidence of pre-Aboriginal artifacts, shedding light on the complex history of human habitation in the region. This evidence challenges the traditional narrative of Aboriginal people being the first and only inhabitants of Australia.
The discovery of paleo-Aboriginal artifacts suggests a more intricate picture of ancient migration routes and cultural interactions.
- The presence of paleo-Aboriginal artifacts, such as stone tools and rock art, indicates a much earlier human presence in Australia than previously thought. These artifacts have been found in various locations across the continent, suggesting a widespread and enduring human occupation.
- The analysis of these artifacts provides valuable insights into the technological advancements and cultural practices of these early inhabitants. It highlights their ability to adapt to and thrive in diverse environments, challenging misconceptions about the capabilities of ancient societies.
- Furthermore, the distribution of these artifacts suggests complex patterns of migration and interaction between different groups of early settlers. This challenges the notion of a singular, homogeneous pre-Aboriginal population and emphasizes the diversity and richness of Australia's ancient human history.
Understanding the presence of pre-Aboriginal artifacts prompts a reevaluation of Australia's history and cultural heritage. It encourages us to acknowledge and celebrate the contributions of diverse ancient populations to the shaping of the continent. This knowledge is crucial for promoting a more inclusive and comprehensive understanding of Australia's past, fostering a sense of liberation from limited historical perspectives.

PSKOOK Metal Fire Piston Educational Campers/Survival/Preppers Scientific Lesson
✔️ An amazing survival fire starting kit that causes instantaneous combustions using air energy change of physics experiments…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Genetic Studies on Pre-Aboriginal Populations
Analyzing genetic studies on pre-Aboriginal populations provides valuable insights into the diverse ancestral origins and population dynamics of ancient human groups in Australia. Genetic diversity and population genetics studies have shed light on the complex tapestry of human migration and settlement in the continent. These studies have revealed that Australia wasn't a static or homogenous population, but rather a dynamic landscape of human movement and interaction.
Genetic diversity studies have highlighted the presence of multiple waves of migration into Australia, with different ancestral groups contributing to the genetic makeup of pre-Aboriginal populations. These findings challenge the notion of a singular, uniform pre-Aboriginal population and underscore the rich and varied tapestry of human history in Australia.
Population genetics research has also provided insights into the interactions between different pre-Aboriginal groups, revealing patterns of intermarriage, exchange, and cultural diffusion. This has deepened our understanding of the social and cultural dynamics of ancient Australian societies, emphasizing the interconnectedness of diverse ancestral groups.
Moreover, by uncovering the genetic legacies of pre-Aboriginal populations, these studies contribute to a more inclusive and nuanced narrative of Australia's ancient history. They highlight the importance of recognizing the diverse ancestral origins and population dynamics that have shaped the continent, offering a more comprehensive understanding of Australia's rich tapestry of human heritage.
Climate Change and Pre-Aboriginal Inhabitants
As we examine the impact of climate change on pre-Aboriginal inhabitants in Australia, it's crucial to understand how environmental shifts influenced their adaptation and survival.
The availability of resources and the ability to harness them in the face of changing climates likely played a significant role in shaping the early inhabitants' strategies for sustenance and livelihood.
Environmental Impact on Inhabitants
The environmental impact on pre-Aboriginal inhabitants in Australia, particularly concerning climate change, is a topic of significant scholarly interest and cultural sensitivity. Understanding the impact on ecosystems and human adaptation provides insight into the resilience and resourcefulness of ancient inhabitants. This knowledge offers a deeper understanding of historical human-environment interactions, shedding light on the complex ways in which these early societies navigated and adapted to environmental changes.
The interplay between climate fluctuations and human responses highlights the intricate relationship between inhabitants and their surroundings, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices and adaptability. Recognizing the historical precedence of environmental challenges and human ingenuity fosters a sense of empowerment and liberation, encouraging contemporary societies to draw inspiration from the past to address current environmental issues.
Adaptation and Survival
Before the arrival of the Aboriginal people, the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants of Australia demonstrated remarkable resilience and resourcefulness in adapting to the challenges posed by climate change. They developed sophisticated adaptation strategies and survival techniques to thrive in diverse environments.
| Adaptation Strategies | Survival Techniques | Environmental Management |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled burning to renew landscapes | Water conservation methods | Sustainable hunting practices |
| Nomadic lifestyle to follow food sources | Shelter construction using local materials | Crop rotation and cultivation |
The pre-Aboriginal inhabitants' adaptation strategies included controlled burning to regenerate landscapes and a nomadic lifestyle to track food sources. They also employed survival techniques such as water conservation, constructing shelters from local materials, and sustainable hunting practices. These approaches reflect their deep understanding of and harmonious relationship with the environment, offering valuable insights for contemporary sustainability efforts.
Resource Availability
In considering resource availability amidst climate change and the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants of Australia, it's imperative to examine their adaptive strategies and utilization of natural resources. The management of resources played a crucial role in the environmental impact and sustainability of their communities. Our research indicates the following key points:
- Resource Management
The pre-Aboriginal inhabitants exhibited resource management techniques that were deeply integrated with their cultural practices. Their resource management strategies were designed to mitigate resource scarcity and ensure the sustainability of their communities.
- Adaptation Strategies
The adaptation strategies of the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants were closely linked to their understanding and utilization of the natural environment. These strategies allowed them to thrive in the face of environmental changes, showcasing their resilience and ingenuity in adapting to resource availability fluctuations.
Theories of Multiple Migration Waves

Multiple migration waves to Australia are theorized by researchers to explain the diverse origins and genetic history of the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants. Paleoanthropological evidence suggests that multiple waves of migration occurred, leading to the complex mosaic of populations that inhabited the continent before the arrival of the Aboriginal peoples. These migration patterns are crucial to understanding the rich tapestry of human history in Australia.
The exploration of multiple migration waves is essential for comprehending the intricate web of human movement and settlement across ancient Australia. By examining the genetic, archaeological, and anthropological data, researchers have been able to discern distinct migration events that contributed to the peopling of the continent. This approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the diverse ancestral lineages and cultural influences that shaped the pre-Aboriginal societies.
Furthermore, acknowledging the theories of multiple migration waves contributes to a more inclusive narrative of Australia's early human history. It recognizes the presence and contributions of various ancestral groups, each with its own unique heritage and traditions. Embracing the complexity of multiple migration waves fosters a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of diverse cultural identities within the broader tapestry of human history.
Pre-Aboriginal Tools and Technology
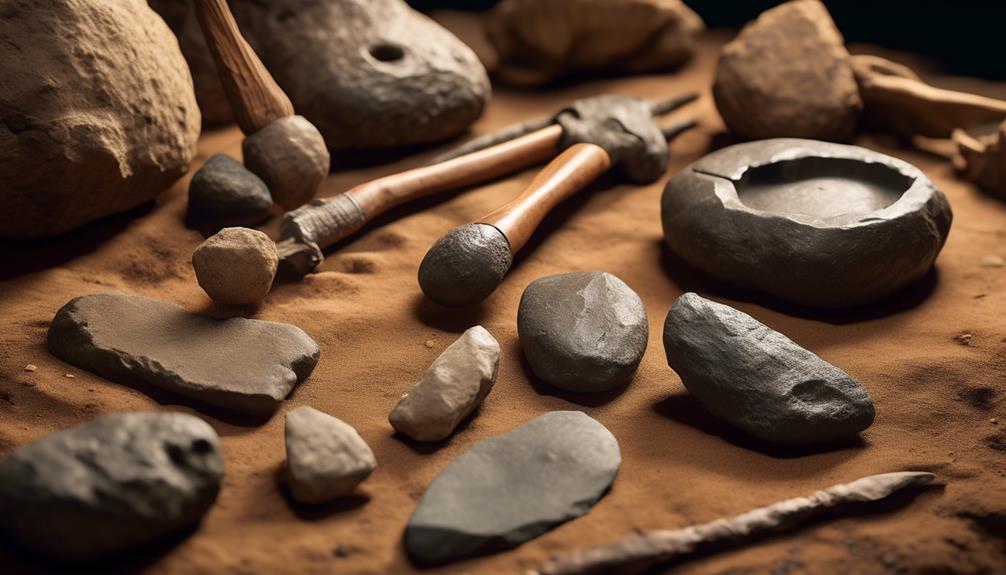

The evidence of tools and technology used by the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants of Australia provides valuable insights into their cultural practices and adaptation to the environment. The technological advancements of these early inhabitants were remarkable, indicating a deep understanding of their surroundings and the ability to innovate to meet their needs. This sheds light on their resourcefulness and resilience in the face of environmental challenges.
- Technological Advancements
- Stone Tools: The use of stone tools, such as axes, knives, and scrapers, reflects an advanced understanding of tool-making techniques. The precision and variety of these tools indicate a sophisticated level of craftsmanship and knowledge of materials.
- Fire Control: The mastery of fire for cooking, warmth, and land management was a significant technological advancement. It not only provided practical benefits but also played a crucial role in shaping the landscape and ecosystems.
- Cultural Practices
- Hunting and Gathering: The tools used for hunting and gathering reveal insights into the dietary habits and subsistence strategies of these early inhabitants. Their ability to fashion effective hunting tools and gather a diverse range of food demonstrates a deep understanding of the natural world.
- Art and Rituals: The presence of artistic and ceremonial objects indicates a rich cultural and spiritual life. These artifacts offer glimpses into the belief systems, social structures, and symbolic expressions of the pre-Aboriginal communities.
Studying the tools and technology of the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants not only enriches our understanding of their material culture but also highlights their ingenuity and adaptability. It's essential to recognize and celebrate the technological and cultural achievements of these early Australians, acknowledging their profound contributions to human history.
Land Bridge Hypothesis
We will explore the Land Bridge Hypothesis, which suggests that ancient migration routes may have connected Australia to neighboring landmasses.
Geological evidence supporting the existence of such land bridges will be examined, shedding light on the potential pathways that pre-Aboriginal populations might've taken.
Additionally, we'll consider the cultural implications of this hypothesis, recognizing the significance of understanding the diverse historical narratives of Australia's earliest inhabitants.
Ancient Migration Routes
Traversing the ancient migration routes, early inhabitants of Australia likely journeyed via land bridges, connecting the continent with neighboring landmasses during periods of lower sea levels. This hypothesis is supported by evidence of ancient trade and migration patterns found in the archaeological record and genetic studies.
- Archaeological Evidence
- Artifacts and tools discovered along the proposed migration routes provide insights into the movement of ancient populations and their interactions with the environment.
- Examination of ancient settlements and cultural remains offers clues about the lifestyles and adaptive strategies of early inhabitants as they navigated these migration routes.
The examination of ancient migration routes offers a deeper understanding of the intricate pathways and connections that shaped the movement of early populations, shedding light on the diverse cultural and historical narratives of ancient Australia.
Geological Evidence Support
Journeying along the ancient migration routes, we encounter compelling geological evidence that supports the Land Bridge Hypothesis, shedding light on the pathways used by early inhabitants to reach Australia during periods of lower sea levels.
Geological formations such as the Sahul Shelf, a vast expanse of ancient landscapes now submerged beneath the Arafura Sea, provide crucial evidence of a land bridge that once connected Australia to New Guinea. These formations indicate a feasible migration route for early populations, allowing for the dispersal of human communities across the region.
The geological evidence aligns with oral histories and archaeological findings, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the peopling of Australia.
It's through the examination of these geological formations that we can piece together the complex history of human migration and settlement in this part of the world.
Cultural Implications Discussed
During periods of lower sea levels, the Land Bridge Hypothesis suggests that cultural exchange and migration between Australia and neighboring regions could have significantly influenced the development of early human societies in the area. This hypothesis opens up a realm of possibilities regarding the societal impact of such cultural exchange.
As we delve deeper into the implications of this hypothesis, it becomes apparent that:
- Cultural Exchange: The exchange of ideas, technologies, and social practices between different human groups could have led to the enrichment and diversification of cultural norms and traditions.
- Societal Impact: The resulting amalgamation of diverse cultural elements may have contributed to the formation of unique societal structures and belief systems, shaping the early human communities in Australia.
These implications highlight the intricate tapestry of human interaction and its profound influence on the development of societies.
Cultural and Linguistic Diversity
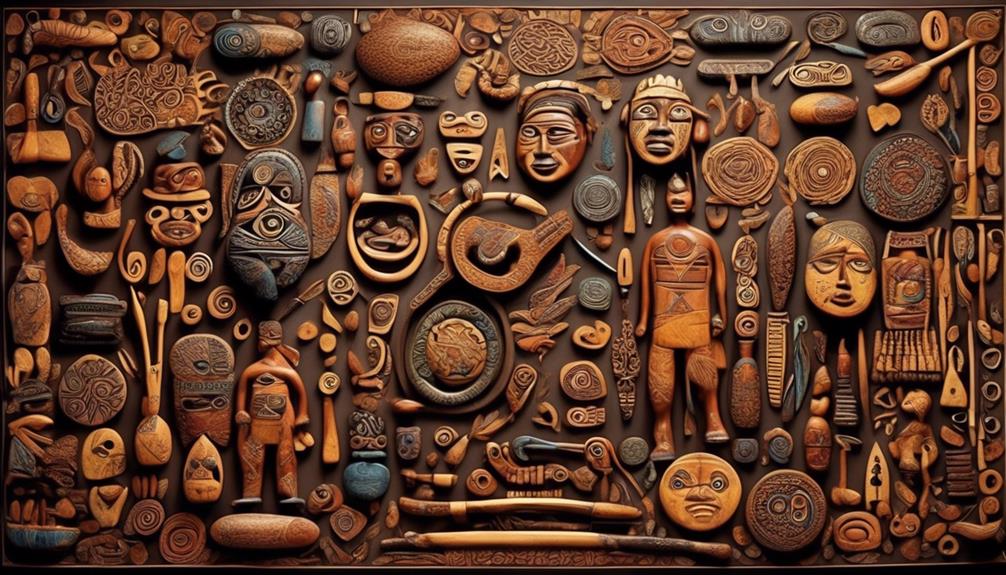

Examining the cultural and linguistic diversity of pre-European Australia reveals a rich tapestry of traditions, languages, and customs that were practiced by various indigenous groups across the continent. The linguistic evolution in Australia before European contact was incredibly diverse, with over 250 distinct language groups and an even greater number of dialects. This linguistic diversity reflects the complexity and depth of indigenous cultures, as each language group was intricately connected to specific territories, kinship systems, and belief structures.
The cultural exchange among different indigenous groups was facilitated through trade, intermarriage, and ceremonial gatherings, resulting in a dynamic and interconnected network of traditions and practices.
Furthermore, the cultural and linguistic diversity of pre-European Australia challenges the misconception of a homogenous indigenous population. Instead, it underscores the reality of a multifaceted and intricate tapestry of cultures, each with its own unique customs, spiritual beliefs, and social structures. This diversity highlights the resilience and adaptability of indigenous societies, as they navigated and thrived in diverse ecological and social landscapes across the continent.
The linguistic and cultural diversity of pre-European Australia provides a window into the rich and varied heritage of indigenous peoples. Understanding and respecting this diversity is crucial for recognizing the depth of indigenous knowledge systems and for fostering cultural sensitivity and inclusivity in contemporary Australia. It's imperative to celebrate and preserve this diversity as a testament to the enduring legacy of Australia's first peoples.
Rock Art Depicting Pre-Aboriginal Life
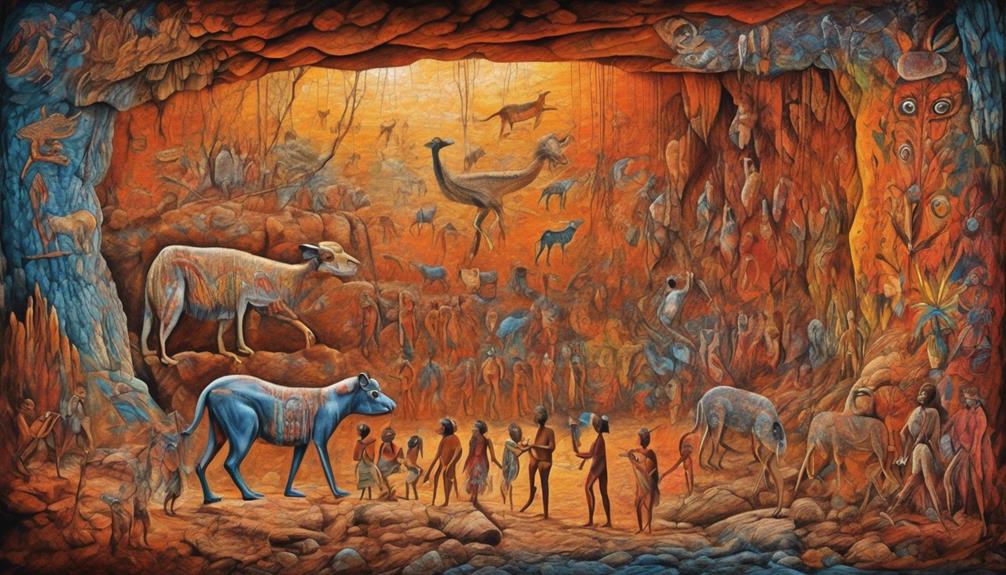

The rich cultural and linguistic diversity of pre-European Australia provides a foundation for understanding the significance of rock art depicting pre-Aboriginal life, revealing insights into the intricate tapestry of traditions and customs practiced by indigenous groups across the continent. Rock art interpretation offers a window into the pre-Aboriginal lifestyle, including hunting practices, and holds immense cultural significance.
- Rock Art Interpretation
Rock art depictions provide valuable insights into the daily lives and activities of the pre-Aboriginal inhabitants of Australia. These artworks often showcase scenes of hunting, gathering, and communal rituals, offering a glimpse into the cultural practices and beliefs of these ancient societies.
- Cultural Significance
The rock art not only serves as a historical record but also holds deep cultural significance for contemporary indigenous communities. It fosters a connection to their ancestral heritage and aids in the preservation and transmission of traditional knowledge, strengthening their cultural identity and sense of belonging.
The interpretation of rock art depicting pre-Aboriginal life goes beyond mere visual representation; it serves as a testament to the enduring heritage of Australia's first peoples. Understanding the intricate details of pre-Aboriginal life, such as hunting practices, through these ancient artworks enriches our appreciation of the diverse and complex tapestry of indigenous traditions that have shaped the continent for millennia.
Pre-Aboriginal Burial Sites

Studying pre-Aboriginal burial sites yields valuable insights into the cultural practices and beliefs of Australia's ancient inhabitants, shedding light on their funerary customs and the reverence they held for their departed.
Burial practices of the pre-Aboriginal people were diverse and often carried ritual significance, reflecting their spiritual beliefs and the importance they placed on honoring the deceased.
The discovery of burial sites in various locations across Australia has revealed a range of burial practices. Some sites indicate that bodies were buried in flexed or extended positions, with grave goods such as tools, ochre, and ornaments, suggesting a belief in an afterlife or the continuation of the individual's journey beyond death. The presence of ochre, a significant material in Aboriginal rituals, indicates the ritual significance attached to the burial process.
Moreover, the careful placement of the deceased, the orientation of the body, and the inclusion of specific artifacts in the burial sites provide evidence of the cultural and spiritual significance of these practices. Such findings offer a glimpse into the belief systems and social structures of the pre-Aboriginal communities, enriching our understanding of their ways of life.
Interaction With Megafauna

Our investigation into the pre-Aboriginal communities' existence in Australia leads us to explore their interaction with the megafauna that once roamed the continent. This interaction is of great significance as it sheds light on the ecological impact of human presence on the megafauna and the subsequent extinction of these large animals.
- Megafauna extinction, human impact
- The arrival of pre-Aboriginal communities in Australia coincided with the decline and eventual extinction of many megafauna species. The overhunting and habitat alteration by these early human populations are believed to have played a significant role in the demise of the megafauna. Understanding the extent of human impact on megafauna extinction is crucial in comprehending the ecological consequences of early human presence in Australia.
- Megafauna hunting techniques, ecological implications
- Research suggests that pre-Aboriginal communities employed sophisticated hunting techniques to capture megafauna, including the use of fire and cooperative hunting strategies. These hunting practices not only affected the megafauna populations but also had broader ecological implications, altering vegetation patterns and disrupting the natural balance of the ecosystem. Exploring the ecological implications of these hunting techniques provides valuable insights into the complex relationship between early human populations and the megafauna, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the prehistoric Australian landscape.
Understanding the dynamics of interaction between pre-Aboriginal communities and the megafauna is essential in unraveling the complexities of Australia's ancient history and the ecological impact of human presence on the continent.
Archaeological Discoveries of Pre-Aboriginal Sites

We will now explore the fascinating archaeological discoveries of pre-Aboriginal sites in Australia.
Ancient tool artifacts, rock art evidence, and DNA analysis findings provide crucial insights into the early human presence on the continent.
These discoveries offer a window into the diverse and complex history of Australia before the arrival of the Aboriginal people.
Ancient Tool Artifacts
Rarely do archaeological discoveries of pre-Aboriginal sites yield such a wealth of ancient tool artifacts, shedding light on the early inhabitants of Australia. The ancient tool artifacts found provide crucial insights into ancient technology advancements and the migration patterns and routes of the early people in Australia.
This evidence suggests a sophisticated understanding of stone tool production and the ability to adapt to diverse environments. The presence of these artifacts indicates a deep connection to the land and a rich cultural heritage that predates the Aboriginal culture. Understanding the intricate designs and functions of these tools opens a window into the complexities of early human societies and their innovative approaches to survival.
The study of these ancient tool artifacts not only deepens our understanding of the ancient history of Australia but also honors the enduring legacy of its first inhabitants.
Rock Art Evidence
The archaeological discoveries of pre-Aboriginal sites, particularly the rock art evidence, offer a profound glimpse into the cultural and artistic expressions of the early inhabitants of Australia, building upon the insights gained from the study of ancient tool artifacts. The preservation of rock art has allowed researchers to interpret ancient symbolism, shedding light on the spiritual and cultural practices of the early peoples. Through intricate depictions of animals, humans, and geometric patterns, these rock art sites provide invaluable clues about the beliefs, traditions, and daily life of Australia's earliest inhabitants. The interpretation of these ancient symbols is crucial in understanding the rich tapestry of Australia's prehistoric cultural heritage, and it underscores the significance of rock art preservation for future generations.
| Rock Art Preservation | Ancient Symbolism Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Ensuring long-term conservation of rock art sites | Deciphering the meanings and cultural significance of ancient symbols |
| Collaborative efforts between archaeologists and Indigenous communities | Unraveling the spiritual and societal aspects of pre-Aboriginal life |
DNA Analysis Findings
Utilizing advanced DNA analysis techniques, the archaeological discoveries of pre-Aboriginal sites have yielded significant insights into the genetic ancestry and migration patterns of the early inhabitants of Australia. This groundbreaking research has provided a deeper understanding of ancient migration and population movements in the region.
- Genetic Ancestry Insights
DNA analysis has revealed a complex web of genetic lineages, indicating diverse ancestral origins among the early populations. This challenges previous assumptions and underscores the rich tapestry of human history in Australia.
- Migration Patterns
By analyzing ancient DNA samples, researchers have traced the migratory paths of early human groups, shedding light on the interconnectedness of ancient populations and their movements across the continent. These findings offer valuable perspectives on the dynamic nature of human settlement in Australia.
These findings not only expand our knowledge of ancient migration but also contribute to a more inclusive and comprehensive understanding of Australia's early inhabitants.
Coastal Migration Theories

Recent archaeological evidence supports the theory of early coastal migration to Australia by ancient populations. Coastal migration theories propose that early human populations utilized ancient trade routes and coastal watercraft to navigate and settle in Australia. This theory challenges the traditional belief that the first inhabitants of Australia arrived solely through land bridges during the last ice age. The discovery of ancient artifacts and remains along Australia's coastlines suggests that these early populations had the seafaring capabilities to undertake long and deliberate voyages.
The exploration of ancient trade routes provides insight into the maritime capabilities of early human populations. It challenges the notion that ancient peoples were confined to land-based migrations and suggests a more sophisticated understanding of navigation and maritime technology. The presence of early human settlements along coastal regions signifies the importance of coastal migration in shaping the demographic history of Australia.
Understanding coastal migration theories is vital for comprehending the diverse cultural and historical tapestry of Australia. It challenges preconceived notions about the capabilities of ancient populations and their ability to traverse vast bodies of water. This knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for the resilience and adaptability of early human societies, laying the foundation for a more inclusive and comprehensive understanding of Australia's pre-Aboriginal history.
Unraveling the complexities of coastal migration theories contributes to a more nuanced and enriched narrative of the ancient human experience in Australia.
Controversies and Debates in Pre-Aboriginal Research

Controversies and debates in pre-Aboriginal research emerge from the need to critically assess the implications of coastal migration theories on our understanding of Australia's ancient human history. In recent years, controversial findings have sparked intense discussions within the academic community and among indigenous perspectives, challenging established narratives and prompting a reevaluation of Australia's pre-Aboriginal past.
Two main points arise from these debates:
- Challenging Traditional Narratives
The emergence of controversial findings has led to a reexamination of long-held beliefs about the peopling of Australia. As new evidence continues to surface, researchers are prompted to critically evaluate existing theories and narratives, recognizing the need to incorporate diverse perspectives, including those of indigenous communities, in shaping a more comprehensive understanding of Australia's ancient history.
- Ethical and Cultural Implications
The controversies in pre-Aboriginal research also raise important ethical and cultural considerations. As researchers navigate through these debates, it's crucial to approach the study of Australia's ancient human history with cultural sensitivity and respect for indigenous knowledge. Engaging in meaningful dialogue with indigenous communities and integrating their perspectives is essential in ensuring that the research is conducted in a manner that aligns with the values and beliefs of the communities whose history is being explored.
These debates underscore the evolving nature of pre-Aboriginal research and the importance of engaging with controversial findings and indigenous perspectives in a manner that respects and acknowledges the diversity of voices shaping our understanding of Australia's ancient past.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Was the Diet and Lifestyle of the Pre-Aboriginal Populations in Australia?
We'll delve into the diet and lifestyle of pre-Aboriginal populations in Australia. Their existence revolved around foraging, hunting, and gathering. This lifestyle provided a diverse diet rich in plants, animals, and seafood, reflecting a deep understanding of their environment.
Their foraging practices were integral to their survival, fostering a deep connection to the land. Our analysis underscores the significance of their sustainable practices, offering valuable insights into ancestral ways of life.
How Did Pre-Aboriginal Populations Interact With the Megafauna in Australia?
We interacted with the megafauna in Australia through our hunting techniques and cultural practices.
Our linguistic diversity reflected the rich tapestry of our interactions with these magnificent creatures.
Despite the challenges of coexisting with such large animals, our resourcefulness and adaptability allowed us to thrive in this unique environment.
Our deep connection with the land and its inhabitants shaped our identity and laid the foundation for the Aboriginal culture that followed.
What Are Some of the Controversies and Debates Surrounding Pre-Aboriginal Research?
Controversial findings and research methodologies in pre-Aboriginal studies have sparked heated debates. Scholars grapple with interpretations of archaeological evidence and genetic analyses, which sometimes challenge established narratives.
The controversies often arise from differing perspectives on colonization, decolonization, and historical accuracy. Research methodologies vary widely, influencing the interpretation of pre-Aboriginal cultures and populations.
These debates are crucial for understanding and respecting the diverse narratives of Australia's ancient history.
What Evidence Exists for the Cultural and Linguistic Diversity of Pre-Aboriginal Populations?
In examining the cultural evidence and linguistic diversity of pre-aboriginal populations, we find a rich tapestry of traditions and languages that challenge traditional narratives.
Through archaeological finds and linguistic analysis, we uncover a complex mosaic of ancient societies.
This evidence reshapes our understanding of Australia's pre-colonial past, illuminating the diverse and vibrant cultures that existed prior to the arrival of the Aboriginal peoples.
How Did Climate Change Impact the Settlement and Migration Patterns of Pre-Aboriginal Inhabitants in Australia?
Climate change significantly impacted the settlement and migration patterns of pre-aboriginal inhabitants in Australia. The shifting environmental conditions forced these populations to adapt and relocate, influencing their movement across the continent.
As researchers, we recognize the importance of understanding these historical dynamics and the impact of environment on human migration patterns. Our analysis aims to shed light on the complexities of pre-aboriginal settlement and how environmental factors shaped their movements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the research surrounding pre-Aboriginal inhabitants in Australia is complex and ongoing. While some may question the evidence of their existence, it's important to acknowledge the diverse history of the land.
By exploring and understanding the presence of early human populations before the Aboriginal people, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich and varied cultural tapestry of Australia.
This research invites us to consider the depth of human history on this continent and the importance of preserving and honoring all aspects of its heritage.









